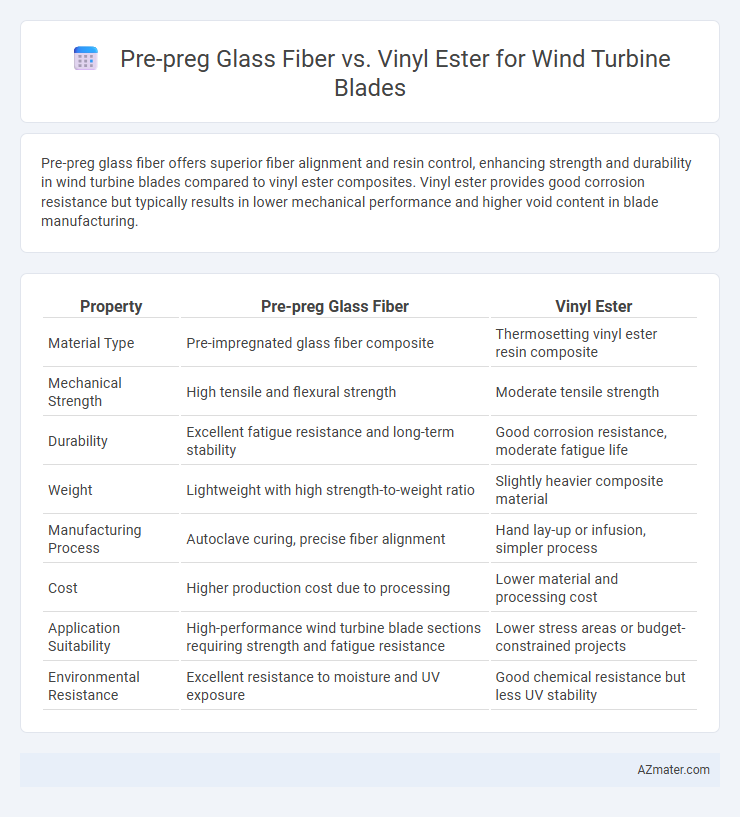
Pre-preg glass fiber offers superior fiber alignment and resin control, enhancing strength and durability in wind turbine blades compared to vinyl ester composites. Vinyl ester provides good corrosion resistance but typically results in lower mechanical performance and higher void content in blade manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Pre-preg Glass Fiber | Vinyl Ester |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Pre-impregnated glass fiber composite | Thermosetting vinyl ester resin composite |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile and flexural strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Durability | Excellent fatigue resistance and long-term stability | Good corrosion resistance, moderate fatigue life |
| Weight | Lightweight with high strength-to-weight ratio | Slightly heavier composite material |
| Manufacturing Process | Autoclave curing, precise fiber alignment | Hand lay-up or infusion, simpler process |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to processing | Lower material and processing cost |
| Application Suitability | High-performance wind turbine blade sections requiring strength and fatigue resistance | Lower stress areas or budget-constrained projects |
| Environmental Resistance | Excellent resistance to moisture and UV exposure | Good chemical resistance but less UV stability |
Introduction to Wind Turbine Blade Materials
Wind turbine blades commonly utilize advanced composite materials such as pre-preg glass fiber and vinyl ester resins to achieve optimal strength-to-weight ratios and durability. Pre-preg glass fiber offers enhanced fiber alignment and resin control, resulting in improved mechanical properties and fatigue resistance essential for blade performance. Vinyl ester provides excellent corrosion resistance and toughness, making it a popular choice for harsh environmental conditions encountered by wind turbine blades.
Overview of Pre-preg Glass Fiber
Pre-preg glass fiber is widely used in wind turbine blades due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent mechanical properties. This material offers superior fiber alignment and resin distribution, resulting in enhanced structural performance and durability under cyclic loading conditions typical in wind energy applications. Its compatibility with advanced resin systems, such as vinyl ester, ensures improved fatigue resistance and corrosion protection essential for the longevity of wind turbine blades.
Understanding Vinyl Ester Resin Systems
Vinyl ester resin systems offer superior chemical resistance and toughness compared to pre-preg glass fiber materials, making them ideal for wind turbine blades exposed to harsh environmental conditions. The high adhesion properties of vinyl ester resins enhance the structural integrity and fatigue resistance of composite blades, improving their lifespan and performance. Advanced vinyl ester formulations allow for better processing flexibility and reduced void content, critical factors in manufacturing large, durable wind turbine blades.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Pre-preg glass fiber composites exhibit superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to vinyl ester resin systems, making them ideal for wind turbine blade applications where high mechanical performance is critical. The pre-preg process ensures optimal fiber-resin bonding and fiber alignment, resulting in enhanced fatigue resistance and impact toughness relative to traditional vinyl ester composites. Vinyl ester materials, while offering good corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, generally demonstrate lower interlaminar shear strength and flexural modulus, limiting their suitability for high-load sections of wind turbine blades.
Durability and Fatigue Resistance
Pre-preg glass fiber composites exhibit superior fiber-matrix adhesion and reduced void content, resulting in enhanced durability and fatigue resistance for wind turbine blades compared to vinyl ester composites. Vinyl ester resins offer good corrosion resistance and moderate toughness but tend to have lower fatigue life under cyclic loading conditions typical of wind turbine operation. Optimizing blade longevity involves prioritizing pre-preg glass fiber materials due to their improved mechanical stability and resistance to microcrack formation under repetitive stress.
Manufacturing and Processing Techniques
Pre-preg glass fiber offers superior fiber alignment and resin control in manufacturing wind turbine blades, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties and consistency compared to vinyl ester composites. The pre-impregnation process ensures reduced void content and improved fiber-resin bonding, facilitating automated layup and curing cycles that optimize production efficiency. Vinyl ester's liquid molding techniques, such as resin transfer molding (RTM), provide faster cycle times but often face challenges in achieving uniform fiber distribution and minimizing defects, impacting blade performance and longevity.
Cost Analysis: Pre-preg Glass Fiber vs. Vinyl Ester
Pre-preg glass fiber incurs higher upfront material costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and resin pre-impregnation, whereas vinyl ester offers a more cost-effective raw material alternative with simpler processing requirements. The labor and curing energy expenses for pre-preg composites typically increase overall production costs, offset partially by superior mechanical properties that may reduce maintenance and lifecycle costs. Vinyl ester composites, while cheaper initially, may demand more frequent repairs and replacements, affecting total cost of ownership in wind turbine blade applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Pre-preg glass fiber exhibits lower environmental impact due to its recyclability and lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions compared to vinyl ester resin, which often relies on petroleum-based components with higher carbon footprints. Vinyl ester offers superior chemical resistance and mechanical properties but poses challenges in end-of-life disposal, contributing to landfill accumulation and limited recycling options. Sustainable wind turbine blade manufacturing increasingly favors pre-preg glass fiber for its balance of performance and reduced ecological footprint, supporting circular economy initiatives in renewable energy sectors.
Performance in Real-World Applications
Pre-preg glass fiber offers superior fiber alignment and resin control, resulting in higher mechanical strength and fatigue resistance crucial for wind turbine blades operating under fluctuating loads. Vinyl ester resins provide excellent corrosion resistance and toughness, enhancing blade durability against environmental stressors such as moisture and UV exposure. In real-world applications, pre-preg glass fiber composites demonstrate enhanced structural integrity and longer service life, making them ideal for high-performance wind turbine blade manufacturing.
Conclusion: Optimal Choice for Wind Turbine Blades
Pre-preg glass fiber offers superior fiber alignment, enhanced mechanical properties, and consistent resin distribution, resulting in higher fatigue resistance and durability for wind turbine blades. Vinyl ester resins provide excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, but often lack the mechanical performance necessary for large-scale blade applications. For optimal wind turbine blade performance, pre-preg glass fiber composites are preferred due to their balanced strength-to-weight ratio and long-term structural integrity.
Infographic: Pre-preg Glass Fiber vs Vinyl Ester for Wind Turbine Blade
 azmater.com
azmater.com