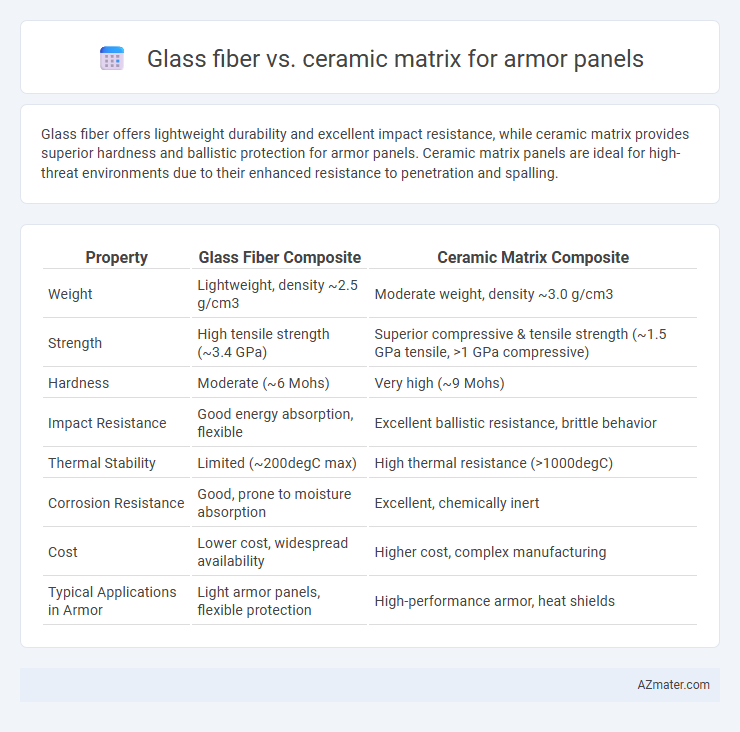
Glass fiber offers lightweight durability and excellent impact resistance, while ceramic matrix provides superior hardness and ballistic protection for armor panels. Ceramic matrix panels are ideal for high-threat environments due to their enhanced resistance to penetration and spalling.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber Composite | Ceramic Matrix Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, density ~2.5 g/cm3 | Moderate weight, density ~3.0 g/cm3 |
| Strength | High tensile strength (~3.4 GPa) | Superior compressive & tensile strength (~1.5 GPa tensile, >1 GPa compressive) |
| Hardness | Moderate (~6 Mohs) | Very high (~9 Mohs) |
| Impact Resistance | Good energy absorption, flexible | Excellent ballistic resistance, brittle behavior |
| Thermal Stability | Limited (~200degC max) | High thermal resistance (>1000degC) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, prone to moisture absorption | Excellent, chemically inert |
| Cost | Lower cost, widespread availability | Higher cost, complex manufacturing |
| Typical Applications in Armor | Light armor panels, flexible protection | High-performance armor, heat shields |
Introduction to Armor Panel Materials
Glass fiber offers lightweight, high tensile strength properties ideal for flexible armor panels, while ceramic matrix composites provide superior hardness and ballistic resistance essential for penetration deflection. Ceramic matrix armor panels excel in mitigating high-velocity projectiles due to their fracture toughness and thermal stability, contrasting with glass fiber's emphasis on structural flexibility and energy absorption. Material selection balances weight, durability, and protective performance tailored to specific armor applications such as military vehicle plating or personal body armor.
Overview of Glass Fiber Reinforced Armor
Glass fiber reinforced armor panels offer exceptional impact resistance and lightweight durability, making them ideal for ballistic protection applications. The high tensile strength and flexibility of glass fibers allow these panels to absorb and disperse energy efficiently, reducing blunt force trauma. Unlike ceramic matrix composites, glass fiber armor provides superior resistance to cracking under multiple impacts while maintaining cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication.
Characteristics of Ceramic Matrix Armor
Ceramic matrix armor panels exhibit exceptional hardness and high compressive strength, making them highly effective at dissipating kinetic energy from ballistic impacts. Their low density offers superior weight-to-protection ratios compared to traditional metal armor, enhancing mobility without sacrificing defense. Ceramic matrices also demonstrate excellent thermal stability and resistance to corrosion, ensuring long-term durability in extreme environments.
Weight Comparison: Glass Fiber vs Ceramic Matrix
Glass fiber armor panels typically offer a lighter weight alternative compared to ceramic matrix composites, making them suitable for applications demanding high mobility. Ceramic matrix panels, despite their increased weight, provide superior hardness and ballistic resistance, justifying the additional mass in high-threat environments. Weight differences impact wearer endurance and armor system design, with glass fiber enabling more extended wear periods while ceramic matrices prioritize protection over weight reduction.
Protective Performance and Ballistic Resistance
Ceramic matrix armor panels exhibit superior ballistic resistance compared to glass fiber composites, effectively dissipating high-velocity projectile energy through hard brittle fracture mechanisms. Glass fiber armor offers enhanced flexibility and lightweight protection but falls short in stopping high-caliber rounds and multiple impacts. The advanced hardness and thermal stability of ceramic matrices enable better protective performance against armor-piercing rounds in military and tactical applications.
Durability and Longevity of Each Material
Glass fiber armor panels offer good impact resistance and flexibility but may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and moisture, affecting long-term durability. Ceramic matrix armor panels provide superior hardness and resistance to wear, maintaining structural integrity under high-stress conditions for extended periods. Overall, ceramic matrix materials typically exhibit greater longevity and consistent performance in harsh environments compared to glass fiber alternatives.
Cost Analysis: Glass Fiber vs Ceramic Matrix
Glass fiber armor panels generally offer a lower initial cost compared to ceramic matrix alternatives due to cheaper raw materials and less complex manufacturing processes. Ceramic matrix panels, while more expensive upfront, provide enhanced durability and higher resistance against ballistic impacts, potentially reducing long-term replacement and maintenance expenses. Evaluating total lifecycle costs including performance benefits is critical for informed decision-making in armor panel selection.
Applications in Military and Civilian Sectors
Glass fiber armor panels offer high tensile strength and lightweight properties, making them suitable for military vehicle protection, personal body armor, and civilian security barriers. Ceramic matrix composites provide superior hardness and ballistic resistance, ideal for advanced military combat helmets, armored vehicle plating, and critical infrastructure protection in civil environments. The choice between glass fiber and ceramic matrix depends on required impact resistance, weight constraints, and environmental durability for specific military and civilian defense applications.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Glass fiber armor panels are manufactured using resin transfer molding and filament winding, offering streamlined production with lower costs and high scalability for mass production. Ceramic matrix armor panels require advanced processes like hot pressing and chemical vapor infiltration, which involve higher temperatures and precise control, resulting in increased manufacturing complexity and limited scalability. The scalability of glass fiber panels makes them suitable for large-scale deployment, whereas ceramic matrix panels are preferred in specialized, high-performance applications despite their more challenging production.
Future Trends in Armor Material Technologies
Glass fiber armor panels offer cost-effective lightweight protection but are gradually being outpaced by ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) due to their superior hardness, thermal stability, and ballistic resistance. Future trends in armor technology emphasize the integration of nanostructured ceramic matrices with hybrid fiber reinforcements, enhancing multi-hit performance and reducing weight without compromising durability. Advancements in additive manufacturing and material science are driving the development of customizable, scalable armor solutions that balance glass fiber's flexibility with ceramics' robust defense capabilities for next-generation combat and security applications.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Ceramic matrix for Armor panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com