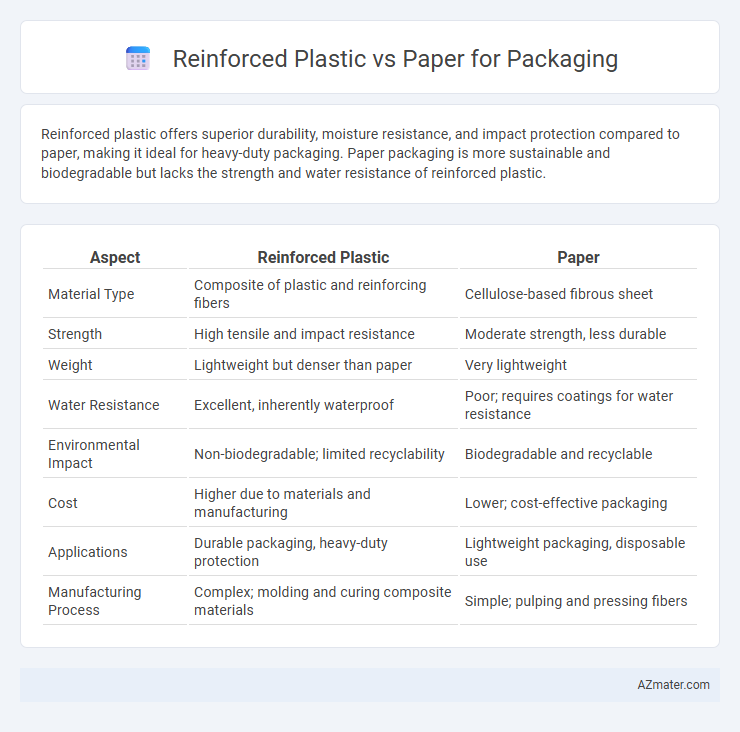
Reinforced plastic offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and impact protection compared to paper, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging. Paper packaging is more sustainable and biodegradable but lacks the strength and water resistance of reinforced plastic.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reinforced Plastic | Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Composite of plastic and reinforcing fibers | Cellulose-based fibrous sheet |
| Strength | High tensile and impact resistance | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Weight | Lightweight but denser than paper | Very lightweight |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, inherently waterproof | Poor; requires coatings for water resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable; limited recyclability | Biodegradable and recyclable |
| Cost | Higher due to materials and manufacturing | Lower; cost-effective packaging |
| Applications | Durable packaging, heavy-duty protection | Lightweight packaging, disposable use |
| Manufacturing Process | Complex; molding and curing composite materials | Simple; pulping and pressing fibers |
Introduction to Packaging Materials
Reinforced plastic packaging offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and tensile strength compared to traditional paper packaging, making it ideal for heavy-duty and long-term storage applications. Paper packaging, while biodegradable and sustainable, typically lacks the robustness and barrier properties required for protecting sensitive or heavy products. Selecting the appropriate material depends on balancing environmental impact with functional performance needs in packaging design.
Overview of Reinforced Plastic Packaging
Reinforced plastic packaging offers superior strength and durability compared to traditional materials, making it ideal for heavy-duty and long-term storage applications. This type of packaging incorporates embedded fibers or fabrics within the plastic matrix to enhance resistance to impact, moisture, and environmental stressors, ensuring product protection during transportation and handling. Its lightweight nature combined with high tensile strength reduces overall shipping costs while maintaining excellent barrier properties against contaminants.
Overview of Paper-Based Packaging
Paper-based packaging offers a sustainable alternative to reinforced plastic with its renewable, biodegradable, and recyclable properties. It is commonly used in food containers, cartons, and wrapping materials due to its lightweight nature and ease of printability, enhancing brand communication. Despite lower moisture resistance and durability compared to reinforced plastics, innovations in coating and lamination have improved its performance for various packaging applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Reinforced plastic offers significantly higher tensile strength and resistance to tearing compared to paper, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging applications. Its durability under moisture, chemicals, and abrasion ensures longer lifespan and better protection for contents during transit. Paper packaging, while biodegradable and cost-effective, generally lacks the robustness and water resistance required for extended or rough handling.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reinforced plastic packaging offers enhanced durability and protection but poses significant challenges in environmental impact due to its limited recyclability and persistence in landfills. Paper packaging, derived from renewable resources, is generally biodegradable and easier to recycle, significantly reducing its ecological footprint. Sustainable packaging strategies favor paper for its lower carbon emissions and compostability, while efforts to improve reinforced plastic recycling are crucial to mitigate long-term environmental harm.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Reinforced plastic packaging offers higher durability and reusability, often resulting in lower long-term costs compared to paper alternatives that have lower initial costs but reduced lifespan. The economic considerations favor reinforced plastic in industries requiring heavy-duty protection and repeated handling, where its resistance to moisture and wear reduces replacement frequency. Paper packaging remains cost-effective for short-term, lightweight applications but may incur higher expenses due to its limited durability and susceptibility to environmental factors.
Customizability and Branding Opportunities
Reinforced plastic offers superior customizability through its versatility in shapes, colors, and finishes, allowing brands to create highly distinctive packaging designs that enhance visual appeal and durability. Paper packaging provides eco-friendly branding opportunities with ease of printing and embossing options, supporting sustainable brand messaging and consumer engagement. Both materials enable tailored packaging solutions, but reinforced plastic stands out for long-lasting brand visibility, while paper emphasizes environmental responsibility.
Regulatory Compliance and Food Safety
Reinforced plastic packaging meets stringent regulatory compliance standards such as FDA and EFSA regulations for food safety, ensuring it is non-toxic and resistant to contamination. Paper packaging, while biodegradable and recyclable, often requires additional coatings or treatments to meet similar food safety standards, potentially complicating regulatory approval. Both materials must comply with migration limits and hygiene protocols to guarantee consumer protection in food packaging applications.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Reinforced plastic packaging is perceived by consumers as durable and protective, offering superior resistance to moisture and physical damage compared to traditional paper packaging. Market trends indicate a growing preference for eco-friendly solutions, driving innovation in recyclable reinforced plastics that balance sustainability with strength. Consumer demand increasingly favors packaging that combines environmental responsibility with functional performance, pushing brands to invest in advanced materials that reduce environmental impact while ensuring product integrity.
Future Prospects: Reinforced Plastic vs Paper
Reinforced plastic offers superior durability and moisture resistance compared to paper, making it ideal for long-term packaging solutions in industries such as automotive and electronics. Paper packaging, favored for its biodegradability and recyclability, aligns with increasing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for sustainable materials. Future prospects indicate a growing trend toward hybrid materials combining reinforced plastic's strength with paper's eco-friendly properties to meet both performance and environmental standards.
Infographic: Reinforced plastic vs Paper for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com