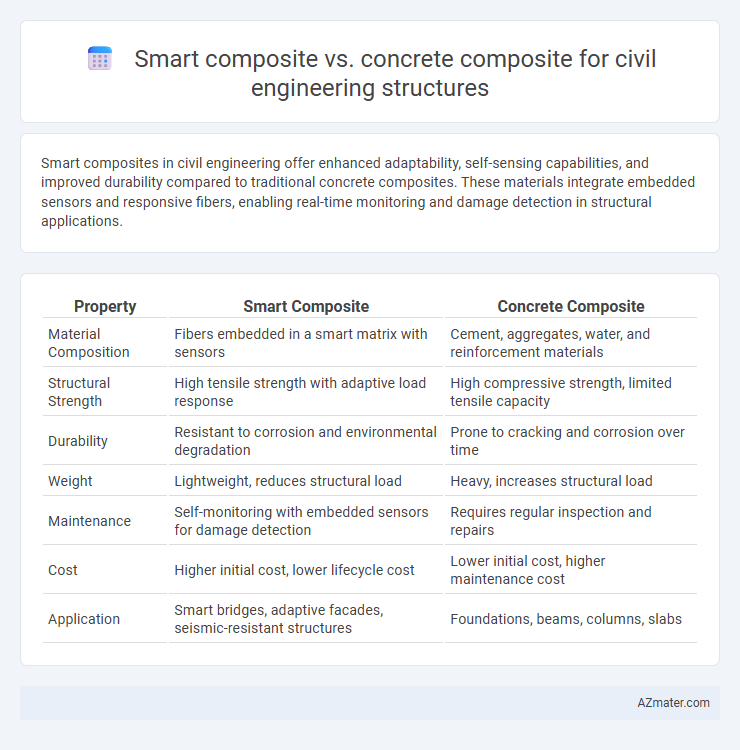
Smart composites in civil engineering offer enhanced adaptability, self-sensing capabilities, and improved durability compared to traditional concrete composites. These materials integrate embedded sensors and responsive fibers, enabling real-time monitoring and damage detection in structural applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Smart Composite | Concrete Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Fibers embedded in a smart matrix with sensors | Cement, aggregates, water, and reinforcement materials |
| Structural Strength | High tensile strength with adaptive load response | High compressive strength, limited tensile capacity |
| Durability | Resistant to corrosion and environmental degradation | Prone to cracking and corrosion over time |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces structural load | Heavy, increases structural load |
| Maintenance | Self-monitoring with embedded sensors for damage detection | Requires regular inspection and repairs |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower lifecycle cost | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance cost |
| Application | Smart bridges, adaptive facades, seismic-resistant structures | Foundations, beams, columns, slabs |
Introduction to Composite Materials in Civil Engineering
Smart composites in civil engineering integrate advanced materials like shape memory alloys and fiber optics to enhance structural responsiveness and durability, whereas traditional concrete composites combine cement, aggregates, and reinforcement for strength and stability. Composite materials improve load distribution, crack resistance, and overall performance, making them essential for modern infrastructure. Innovations in smart composites enable real-time monitoring and adaptive repair, advancing the longevity and safety of civil engineering structures.
Definition and Composition of Smart Composites
Smart composites in civil engineering are advanced materials integrating sensors, actuators, and responsive fibers within a matrix to enable real-time structural health monitoring and adaptive response capabilities. Their composition typically includes a combination of fiber-reinforced polymers (FRP) embedded with piezoelectric sensors, shape memory alloys, or carbon nanotubes to provide multifunctionality beyond traditional load-bearing performance. Concrete composites, by contrast, consist primarily of cementitious matrices reinforced with aggregates and fibers, designed mainly for enhanced mechanical strength and durability without active sensing or adaptive functions.
Overview of Concrete Composites
Concrete composites combine cementitious materials with fibers or additives to enhance mechanical properties such as strength, durability, and crack resistance. Smart composites integrate sensors or responsive materials within concrete to enable real-time monitoring and adaptive responses to environmental changes or structural stresses. The development of these advanced composites aims to improve structural performance, longevity, and safety in civil engineering applications.
Mechanical Properties: Smart vs Concrete Composites
Smart composites exhibit enhanced mechanical properties such as superior tensile strength, higher impact resistance, and improved fatigue durability compared to traditional concrete composites. The integration of smart materials like fiber optics and piezoelectric sensors in smart composites enables real-time health monitoring and adaptive load management, which conventional concrete composites lack. These advancements result in smarter infrastructure with extended service life, reduced maintenance costs, and greater structural reliability in civil engineering applications.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Smart composites in civil engineering offer enhanced durability compared to traditional concrete composites due to their superior resistance to environmental degradation, including corrosion, moisture infiltration, and thermal stress. Advanced materials like fiber-reinforced polymers (FRP) in smart composites provide extended longevity by preventing crack propagation and reducing maintenance needs over the structure's lifespan. Concrete composites, while cost-effective and widely used, often suffer from issues like carbonation and chloride-induced corrosion, leading to reduced service life compared to the adaptive and resilient properties of smart composite alternatives.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capacity
Smart composites in civil engineering structures exhibit enhanced structural performance and superior load-bearing capacity compared to traditional concrete composites due to their adaptive properties and high strength-to-weight ratio. These materials improve durability by mitigating crack propagation and resisting environmental degradation, resulting in extended service life. Concrete composites, while cost-effective and widely used, typically demonstrate lower tensile strength and flexibility, limiting their load-bearing efficiency under dynamic or heavy loads.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Smart composites in civil engineering structures offer superior cost efficiency through reduced maintenance requirements and longer service life compared to traditional concrete composites. Concrete composites generally involve higher initial material and labor costs but may require frequent repairs, increasing life-cycle expenses. Economic considerations favor smart composites for projects emphasizing sustainability and long-term financial savings.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Smart composites in civil engineering offer enhanced sustainability through improved durability and reduced material usage, leading to lower carbon footprints compared to traditional concrete composites. Concrete composites often rely on high cement content, contributing significantly to CO2 emissions during production, whereas smart composites incorporate recycled fibers and eco-friendly resins that minimize environmental impact. The integration of self-healing and energy-efficient properties in smart composites further extends structural lifespan, reducing resource consumption and waste generation over time.
Applications in Modern Civil Engineering Structures
Smart composites, incorporating sensors and responsive materials, enable real-time monitoring and adaptive performance improvements in civil engineering structures, enhancing durability and safety. Concrete composites, combining traditional concrete with fibers or additives, provide superior strength, toughness, and resistance to environmental degradation, making them ideal for load-bearing elements like bridges and high-rise buildings. Integrating smart composite technology with concrete composites optimizes structural health management and lifecycle sustainability in modern infrastructure projects.
Future Trends and Innovations in Composite Technology
Smart composites in civil engineering structures integrate sensors and responsive materials for real-time monitoring and adaptive performance, enhancing durability and safety beyond traditional concrete composites. Advances in nanomaterials and self-healing technologies are driving innovations, enabling structures to autonomously repair damage and extend service life. Future trends emphasize sustainability through eco-friendly composites and multifunctional materials that combine load-bearing capacity with environmental sensing and energy efficiency.
Infographic: Smart composite vs Concrete composite for Civil engineering structure
 azmater.com
azmater.com