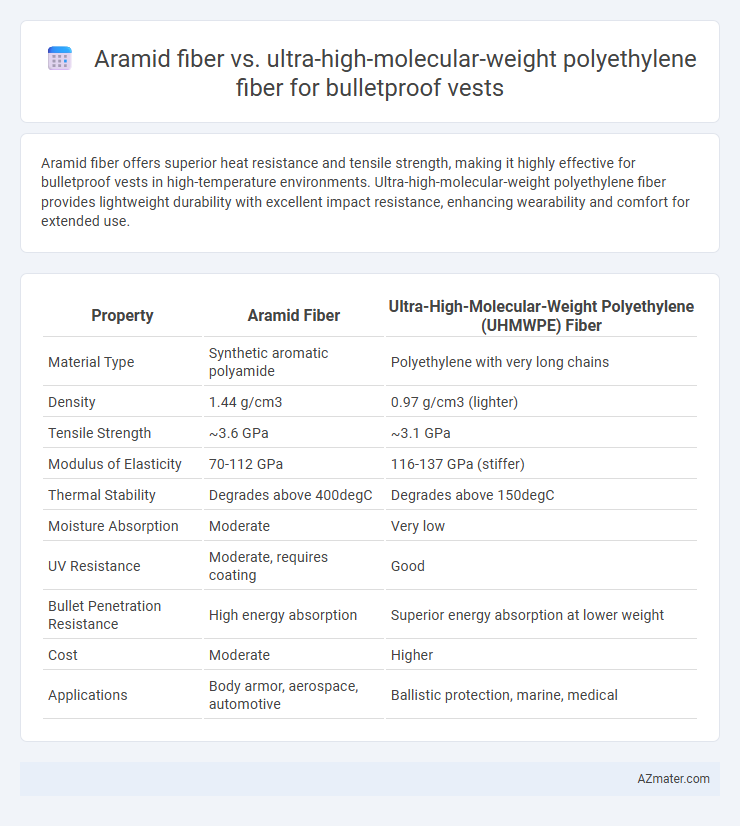
Aramid fiber offers superior heat resistance and tensile strength, making it highly effective for bulletproof vests in high-temperature environments. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene fiber provides lightweight durability with excellent impact resistance, enhancing wearability and comfort for extended use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid Fiber | Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic aromatic polyamide | Polyethylene with very long chains |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 0.97 g/cm3 (lighter) |
| Tensile Strength | ~3.6 GPa | ~3.1 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 70-112 GPa | 116-137 GPa (stiffer) |
| Thermal Stability | Degrades above 400degC | Degrades above 150degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate | Very low |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, requires coating | Good |
| Bullet Penetration Resistance | High energy absorption | Superior energy absorption at lower weight |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Applications | Body armor, aerospace, automotive | Ballistic protection, marine, medical |
Introduction to Bulletproof Vest Materials
Aramid fiber and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber are leading materials in bulletproof vest manufacturing due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and impact resistance. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer high tensile strength and thermal stability, making them effective in dissipating ballistic energy. UHMWPE fibers provide lower weight and higher resistance to moisture and chemicals, enhancing wearer comfort while maintaining superior ballistic protection.
What is Aramid Fiber?
Aramid fiber is a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers known for their exceptional tensile strength and lightweight nature, making them ideal for bulletproof vests. Commonly recognized under trade names like Kevlar and Twaron, aramid fibers provide superior ballistic protection by efficiently absorbing and dissipating kinetic energy from projectiles. Compared to ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers, aramid fibers offer higher thermal stability and resistance to degradation, crucial for maintaining durability in various combat environments.
What is Ultra-high-molecular-weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Fiber?
Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber is a lightweight, synthetic polymer characterized by extremely long molecular chains, providing superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance. UHMWPE fibers, such as Dyneema and Spectra, offer higher energy absorption per unit weight compared to aramid fibers, making them ideal for bulletproof vests requiring ballistic resistance and impact durability. Its low density and chemical inertness enhance wearer comfort and longevity in protective gear applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Aramid fiber, commonly known as Kevlar, exhibits exceptional tensile strength ranging from 2.9 to 3.6 GPa, making it highly effective for bulletproof vests. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber offers even higher tensile strength, typically around 2.4 to 3.1 GPa, combined with lower density, resulting in lighter protective gear. Both materials provide excellent toughness and impact resistance, but UHMWPE fibers generally deliver superior energy absorption and stiffness, enhancing ballistic protection without significantly increasing weight.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Aramid fiber, known for its lightweight and high tensile strength, offers excellent flexibility and breathability, making it ideal for contouring to the body in bulletproof vests. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber is even lighter in weight compared to aramid, providing superior strength-to-weight ratio, but it tends to be less flexible and more rigid, potentially reducing wearer comfort. The choice between aramid and UHMWPE in ballistic vests hinges on balancing UHMWPE's weight benefits with aramid's superior flexibility for ergonomic performance.
Ballistic Protection Performance
Aramid fiber offers excellent ballistic protection due to its high tensile strength and thermal stability, making it resistant to high-velocity projectiles and sharp objects commonly encountered in bulletproof vests. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber provides superior energy absorption and lighter weight compared to aramid fibers, enhancing wearer mobility while maintaining high ballistic resistance. Both materials are widely used in ballistic armor, but UHMWPE typically delivers better multi-hit performance and resistance to water and chemicals, improving durability in harsh environments.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Aramid fiber offers exceptional durability with high tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion and heat, making it ideal for bulletproof vests requiring long-term performance under strenuous conditions. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber provides superior environmental resistance, exhibiting outstanding chemical and moisture resistance that enhances vest longevity in harsh environments. Both materials deliver robust protection, but aramid fibers excel in thermal stability while UHMWPE fibers outperform in resistance to humidity and corrosive substances.
Comfort and Wearability
Aramid fiber offers excellent heat resistance and maintains durability under high temperatures, but it tends to be heavier and less flexible, which may affect comfort during extended wear. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber is significantly lighter and provides superior flexibility and moisture resistance, enhancing breathability and wearability in bulletproof vests. The reduced weight and increased comfort of UHMWPE make it a preferred choice for users requiring agility and prolonged use without sacrificing ballistic performance.
Cost and Production Considerations
Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, typically offers a cost-effective solution with well-established production processes suited for bulletproof vests, resulting in widespread availability and consistent quality. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber, while generally more expensive due to advanced manufacturing techniques like gel spinning and thermal consolidation, provides superior strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to moisture. The choice between these materials depends on balancing upfront cost against performance requirements and production scalability within the ballistic protective gear industry.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Bulletproof Vests
Aramid fiber offers superior heat resistance and maintains strength under high temperatures, making it ideal for bulletproof vests exposed to varied combat conditions. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber provides exceptional tensile strength and is lighter in weight, enhancing mobility and comfort for extended wear. Choosing between aramid and UHMWPE fibers depends on balancing weight, thermal stability, and the specific threat level the bulletproof vest is designed to withstand.
Infographic: Aramid fiber vs Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene fiber for Bulletproof vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com