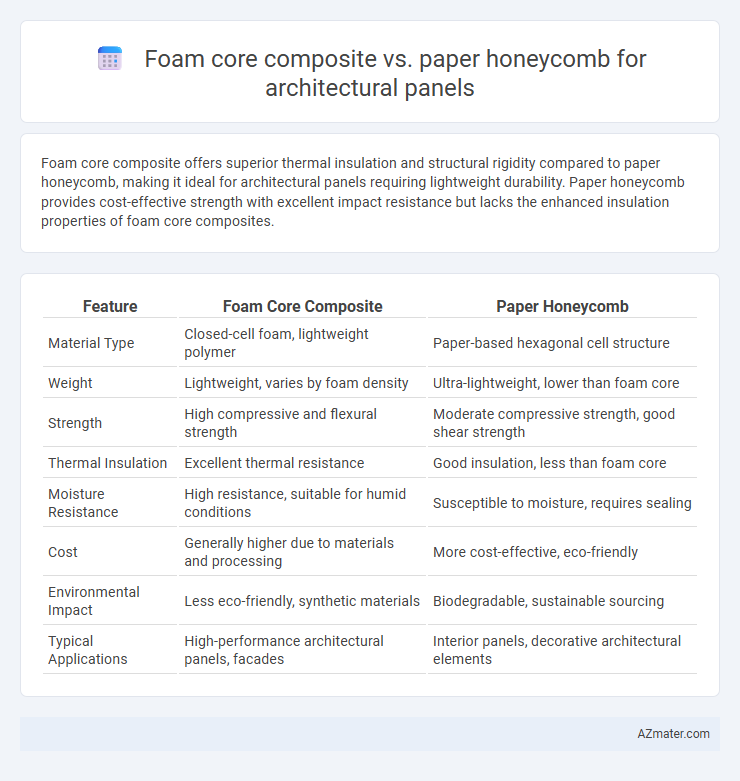
Foam core composite offers superior thermal insulation and structural rigidity compared to paper honeycomb, making it ideal for architectural panels requiring lightweight durability. Paper honeycomb provides cost-effective strength with excellent impact resistance but lacks the enhanced insulation properties of foam core composites.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Foam Core Composite | Paper Honeycomb |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Closed-cell foam, lightweight polymer | Paper-based hexagonal cell structure |
| Weight | Lightweight, varies by foam density | Ultra-lightweight, lower than foam core |
| Strength | High compressive and flexural strength | Moderate compressive strength, good shear strength |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent thermal resistance | Good insulation, less than foam core |
| Moisture Resistance | High resistance, suitable for humid conditions | Susceptible to moisture, requires sealing |
| Cost | Generally higher due to materials and processing | More cost-effective, eco-friendly |
| Environmental Impact | Less eco-friendly, synthetic materials | Biodegradable, sustainable sourcing |
| Typical Applications | High-performance architectural panels, facades | Interior panels, decorative architectural elements |
Introduction to Architectural Panel Core Materials
Architectural panel core materials such as foam core composite and paper honeycomb offer distinct performance characteristics crucial for structural efficiency and aesthetic appeal. Foam core composites provide superior rigidity, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation, making them ideal for environments requiring durability and lightweight strength. Paper honeycomb cores, valued for their eco-friendliness and high strength-to-weight ratio, excel in sustainable design applications while maintaining cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication.
Overview of Foam Core Composite Panels
Foam core composite panels consist of a lightweight, rigid foam core sandwiched between two durable facings, offering excellent thermal insulation and high strength-to-weight ratio for architectural applications. These panels provide superior impact resistance, moisture resistance, and dimensional stability compared to traditional paper honeycomb cores, making them ideal for exterior cladding and interior wall systems. Foam core composites also support various finishes and designs, enhancing aesthetic versatility while maintaining structural integrity in building envelopes.
Understanding Paper Honeycomb Core Panels
Paper honeycomb core panels offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios due to their hexagonal cell structure, providing superior load distribution and impact resistance for architectural applications. Unlike foam core composites, paper honeycomb cores are environmentally sustainable, made from recycled materials and easily recyclable after use, making them ideal for green building projects. Their enhanced rigidity and dimensional stability ensure long-lasting performance in wall cladding, ceilings, and partitions without adding significant weight.
Structural Performance Comparison
Foam core composites exhibit superior structural performance in architectural panels due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent impact resistance, making them ideal for load-bearing applications. Paper honeycomb cores provide efficient stiffness and weight reduction but generally offer lower compressive strength and durability when subjected to prolonged stress or moisture exposure. The choice between foam core and paper honeycomb depends on specific architectural requirements, balancing factors like mechanical strength, environmental resistance, and cost efficiency.
Weight and Density Differences
Foam core composite panels offer significantly lower density, typically around 50-100 kg/m3, compared to paper honeycomb cores which range from 60-200 kg/m3, making foam cores substantially lighter for architectural applications. The reduced weight of foam core composites enhances ease of installation and reduces structural load without compromising panel strength. This weight advantage is critical in large-scale facades where minimizing dead load improves overall building efficiency and performance.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Foam core composite panels exhibit superior thermal insulation with low thermal conductivity, effectively reducing heat transfer in architectural applications. Paper honeycomb panels provide excellent acoustic insulation due to their unique cellular structure, which dampens sound waves and minimizes noise transmission. When choosing between the two, foam core composites excel in maintaining energy efficiency, while paper honeycomb panels offer enhanced sound absorption for quieter indoor environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Foam core composites often utilize petrochemical-based materials that pose challenges for recycling and contribute more significantly to environmental pollution compared to paper honeycomb, which is typically made from renewable and biodegradable paper fibers. Paper honeycomb panels offer superior sustainability due to their low embodied energy and ease of recycling, making them a preferable choice for eco-conscious architectural applications. The reduced carbon footprint of paper honeycomb also aligns closely with green building standards and LEED certification requirements.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Foam core composites typically offer higher upfront costs due to advanced materials and manufacturing processes compared to paper honeycomb panels, which use lightweight, sustainable, and low-cost paper cores. In terms of lifecycle costs, foam core panels provide superior durability, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation, potentially reducing maintenance and replacement expenses over long-term architectural applications. Paper honeycomb panels excel economically in large-scale, budget-sensitive projects where rapid installation and recyclability justify their moderate performance and shorter lifespan.
Applications in Modern Architecture
Foam core composite panels offer superior insulation, lightweight strength, and moisture resistance, making them ideal for exterior cladding and interior partitions in modern architecture. Paper honeycomb panels provide excellent structural support with eco-friendly, recyclable materials, often used in sustainable design projects and lightweight interior applications. Both materials enhance building performance but are selected based on specific needs such as thermal efficiency versus environmental impact.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Core for Your Project
Foam core composites offer superior lightweight strength and thermal insulation, making them ideal for architectural panels requiring enhanced durability and energy efficiency. Paper honeycomb cores provide an eco-friendly, cost-effective option with excellent compressive strength suited for non-structural or temporary installations. Selecting the right core depends on balancing project-specific factors such as load requirements, environmental impact, budget constraints, and long-term performance goals.
Infographic: Foam core composite vs Paper honeycomb for Architectural panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com