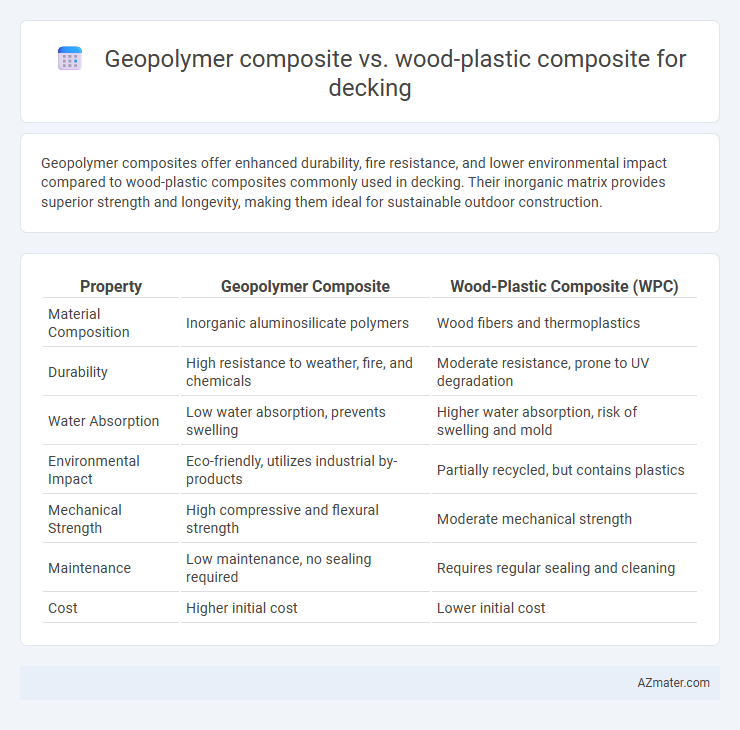
Geopolymer composites offer enhanced durability, fire resistance, and lower environmental impact compared to wood-plastic composites commonly used in decking. Their inorganic matrix provides superior strength and longevity, making them ideal for sustainable outdoor construction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Geopolymer Composite | Wood-Plastic Composite (WPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Inorganic aluminosilicate polymers | Wood fibers and thermoplastics |
| Durability | High resistance to weather, fire, and chemicals | Moderate resistance, prone to UV degradation |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption, prevents swelling | Higher water absorption, risk of swelling and mold |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, utilizes industrial by-products | Partially recycled, but contains plastics |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive and flexural strength | Moderate mechanical strength |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, no sealing required | Requires regular sealing and cleaning |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
Introduction to Decking Materials
Geopolymer composites offer enhanced durability and environmental resistance compared to traditional wood-plastic composites, making them an innovative choice for decking materials. Wood-plastic composites, blending wood fibers with thermoplastics, provide natural aesthetics and moderate resistance to moisture and decay. Selecting between these materials depends on factors such as load-bearing capacity, weather resilience, and sustainability requirements for outdoor decking applications.
Overview of Geopolymer Composites
Geopolymer composites for decking consist of inorganic polymers formed by the reaction of aluminosilicate materials with alkaline solutions, offering exceptional durability, fire resistance, and low environmental impact compared to traditional materials. These composites exhibit high compressive strength, resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and chemical degradation, making them ideal for outdoor applications. The eco-friendly nature of geopolymers, derived from industrial byproducts like fly ash or slag, promotes sustainable construction with reduced carbon footprint relative to wood-plastic composites.
Understanding Wood-Plastic Composites
Wood-plastic composites (WPCs) blend natural wood fibers with thermoplastic materials such as polyethylene or polypropylene, offering enhanced durability and low maintenance for decking applications. Their resistance to rot, insect damage, and UV degradation makes them a popular alternative to traditional wood, while their moldability allows for diverse design options. Compared to geopolymer composites, WPCs provide better aesthetic appeal and flexibility but may exhibit lower fire resistance and structural strength.
Comparative Strength and Durability
Geopolymer composites exhibit superior compressive and tensile strength compared to wood-plastic composites (WPC), making them more resistant to heavy loads and structural stresses commonly encountered in decking applications. The inherent chemical inertness and fire resistance of geopolymer materials significantly enhance durability, reducing degradation from moisture, UV exposure, and biological attack, whereas WPCs are prone to fungal growth and swelling over time. Long-term performance studies indicate that geopolymer composites maintain structural integrity and surface appearance longer than WPCs, offering a more sustainable solution for outdoor decking with minimal maintenance requirements.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Geopolymer composites offer superior weather resistance compared to wood-plastic composites (WPC), exhibiting excellent resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, which reduces warping, cracking, and decay. The inorganic nature of geopolymer composites enhances their longevity, often exceeding 50 years in outdoor environments, whereas WPC decking typically lasts 20 to 30 years due to its vulnerability to mold, rot, and insect damage. This durability makes geopolymer composites a more sustainable choice for long-term decking applications in harsh weather conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer composites for decking offer significantly lower carbon footprints compared to wood-plastic composites (WPC), as they utilize industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, reducing landfill waste and conserving natural resources. Wood-plastic composites, while incorporating recycled wood fibers and plastics, often rely on virgin plastic resins and can contribute to microplastic pollution over time. The durability and resistance to weathering of geopolymer composites enhance their lifecycle sustainability by lowering maintenance frequency and material replacement, supporting long-term environmental benefits.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Geopolymer composite decking offers superior installation ease due to its lightweight nature and uniform dimensions, reducing labor time compared to wood-plastic composite (WPC) that often requires pre-drilling and additional fasteners. Maintenance of geopolymer composites is minimal, demanding only occasional cleaning without the need for sealing or staining, unlike WPC which can suffer from surface fading, mold growth, and requires periodic sealing to maintain appearance. The inherent durability and resistance to moisture, insects, and UV degradation in geopolymer composites further lower long-term upkeep costs relative to wood-plastic composites.
Aesthetic Versatility and Design
Geopolymer composites offer superior aesthetic versatility for decking due to their ability to mimic natural stone and concrete textures while providing customizable color options that resist fading and staining. In contrast, wood-plastic composites primarily replicate natural wood grain but may show wear and discoloration over time, limiting long-term design appeal. The structural integrity and design flexibility of geopolymer composites allow architects and designers to create unique, modern decking solutions that blend seamlessly with various architectural styles.
Cost Analysis and Value
Geopolymer composites offer higher durability and fire resistance compared to wood-plastic composites (WPC), often justifying their initial higher cost through extended lifespan and reduced maintenance expenses. WPC typically provides a lower upfront investment with easier installation, appealing for budget-conscious projects, but may incur greater long-term costs due to susceptibility to moisture damage and UV degradation. Evaluating total cost of ownership, geopolymer composites deliver superior value in high-demand, weather-exposed decking applications by minimizing replacement and repair frequency.
Future Trends in Composite Decking
Geopolymer composites for decking are gaining attention due to their superior durability, fire resistance, and eco-friendly manufacturing processes compared to traditional wood-plastic composites (WPC). Future trends indicate a shift towards using geopolymer composites that incorporate industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, enhancing sustainability and mechanical performance while reducing carbon footprint. Innovations in nanotechnology and advanced curing methods are expected to further improve the structural integrity and weather resistance of geopolymer decking materials, positioning them as a next-generation alternative in the composite decking market.
Infographic: Geopolymer composite vs Wood-plastic composite for Decking
 azmater.com
azmater.com