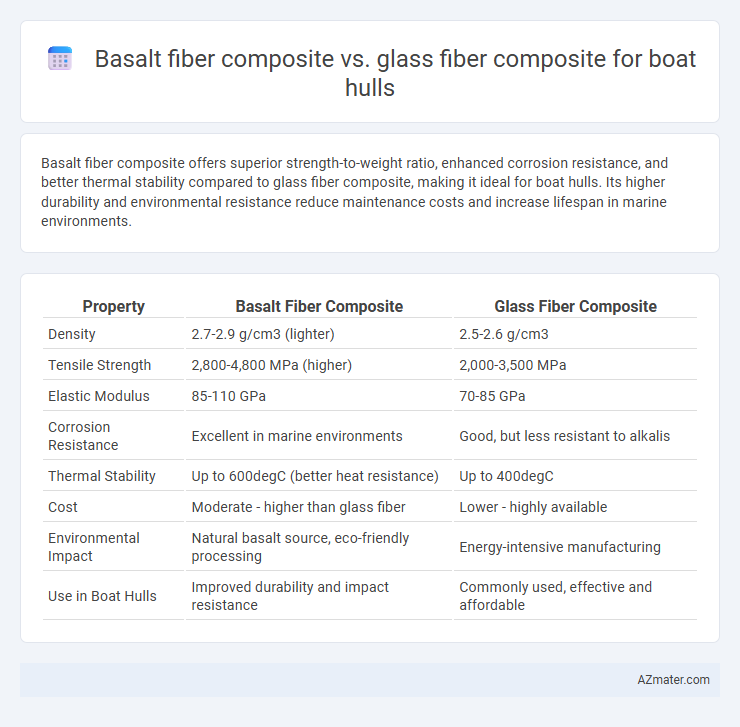
Basalt fiber composite offers superior strength-to-weight ratio, enhanced corrosion resistance, and better thermal stability compared to glass fiber composite, making it ideal for boat hulls. Its higher durability and environmental resistance reduce maintenance costs and increase lifespan in marine environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Basalt Fiber Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2.7-2.9 g/cm3 (lighter) | 2.5-2.6 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 2,800-4,800 MPa (higher) | 2,000-3,500 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 85-110 GPa | 70-85 GPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in marine environments | Good, but less resistant to alkalis |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 600degC (better heat resistance) | Up to 400degC |
| Cost | Moderate - higher than glass fiber | Lower - highly available |
| Environmental Impact | Natural basalt source, eco-friendly processing | Energy-intensive manufacturing |
| Use in Boat Hulls | Improved durability and impact resistance | Commonly used, effective and affordable |
Introduction to Basalt Fiber and Glass Fiber Composites
Basalt fiber composites, derived from volcanic basalt rocks, offer superior chemical resistance, higher tensile strength, and enhanced thermal stability compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Glass fiber composites, widely used in boat hull manufacturing, provide cost-effective performance with good mechanical properties but are prone to corrosion and lower impact resistance. The choice between basalt and glass fiber composites significantly influences hull durability, weight, and maintenance requirements in marine applications.
Key Material Properties: Basalt vs Glass Fiber
Basalt fiber composites offer superior corrosion resistance and higher tensile strength compared to glass fiber composites, making them more durable for boat hull applications exposed to harsh marine environments. The thermal stability of basalt fibers also surpasses that of glass fibers, providing enhanced performance under fluctuating temperature conditions typical at sea. Furthermore, basalt fibers exhibit better impact resistance and vibration damping, contributing to improved overall hull integrity and longevity.
Comparative Strength and Durability in Marine Environments
Basalt fiber composites offer superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to traditional glass fiber composites, making them highly effective for boat hull construction. Their enhanced chemical stability and natural resistance to saltwater corrosion provide greater durability in harsh marine environments, reducing maintenance needs over time. Glass fiber composites, while cost-effective, tend to absorb more moisture and degrade faster under prolonged marine exposure, leading to potential structural weaknesses.
Weight and Density Impact on Boat Hull Performance
Basalt fiber composite offers a lower density of approximately 2.7 g/cm3 compared to glass fiber composite's density of around 2.5 g/cm3, resulting in a slightly heavier material but with enhanced mechanical properties. The increased weight of basalt fiber composites contributes to improved hull stiffness and impact resistance, which can enhance boat durability and safety in rough marine conditions. In contrast, glass fiber composites, being lighter, provide better fuel efficiency and speed but may sacrifice some strength and longevity under heavy loads.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance Differences
Basalt fiber composites exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to glass fiber composites, making them highly suitable for boat hulls exposed to harsh marine environments. The inherent chemical stability of basalt fibers provides enhanced resistance to acids, alkalis, and saltwater, reducing degradation and maintenance frequency. In contrast, glass fiber composites are more susceptible to chemical attack and osmotic blistering, which can compromise hull integrity over time.
Fatigue Life and Long-Term Reliability
Basalt fiber composites exhibit superior fatigue life compared to glass fiber composites, making them highly suitable for boat hull applications exposed to cyclic loading and harsh marine environments. Their enhanced long-term reliability stems from better resistance to moisture, UV degradation, and chemical corrosion, which significantly reduces maintenance costs and extends service intervals. Studies demonstrate that basalt fiber composites maintain structural integrity over extended periods, providing a durable alternative to traditional glass fiber composites in marine construction.
Manufacturing Process and Ease of Fabrication
Basalt fiber composites offer a more environmentally friendly manufacturing process compared to glass fiber composites, requiring lower energy consumption during fiber production. The basalt fibers exhibit better compatibility with resin systems, resulting in improved wetting and easier layup during fabrication of boat hulls. Glass fiber composites remain popular due to established supply chains and cost-effectiveness, but basalt fiber composites provide enhanced handling and reduced tooling wear, facilitating smoother fabrication workflows.
Cost Analysis: Basalt Fiber vs Glass Fiber
Basalt fiber composites typically cost 10-20% more than glass fiber composites due to higher raw material and processing expenses, but offer superior mechanical properties and durability. Glass fiber composites remain popular in boat hull construction because of their lower initial cost and widespread availability, making them a budget-friendly choice for mass production. Evaluating long-term expenses, basalt fiber composites can reduce maintenance and repair costs due to better corrosion resistance and impact strength, potentially offsetting the initial price difference.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Basalt fiber composites outperform glass fiber composites in environmental impact due to their natural volcanic rock origin, which requires less energy-intensive processing and produces fewer emissions. Basalt fibers offer improved sustainability with higher recyclability and lower toxicity compared to traditional glass fibers, which rely on raw materials like silica sand and soda ash extracted through energy-heavy methods. Boats constructed with basalt fiber composites exhibit longer life cycles and reduced carbon footprints, making them a greener choice for sustainable marine applications.
Application Case Studies in Boat Hull Construction
Basalt fiber composite demonstrates superior mechanical properties and corrosion resistance compared to glass fiber composite in boat hull construction, making it ideal for high-performance vessels exposed to harsh marine environments. Case studies reveal basalt fiber composites reduce overall hull weight by up to 20%, enhancing fuel efficiency and maneuverability while maintaining structural integrity. Glass fiber composites remain prevalent in cost-sensitive projects due to their established manufacturing processes and lower material costs despite comparatively lower durability and impact resistance.
Infographic: Basalt fiber composite vs Glass fiber composite for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com