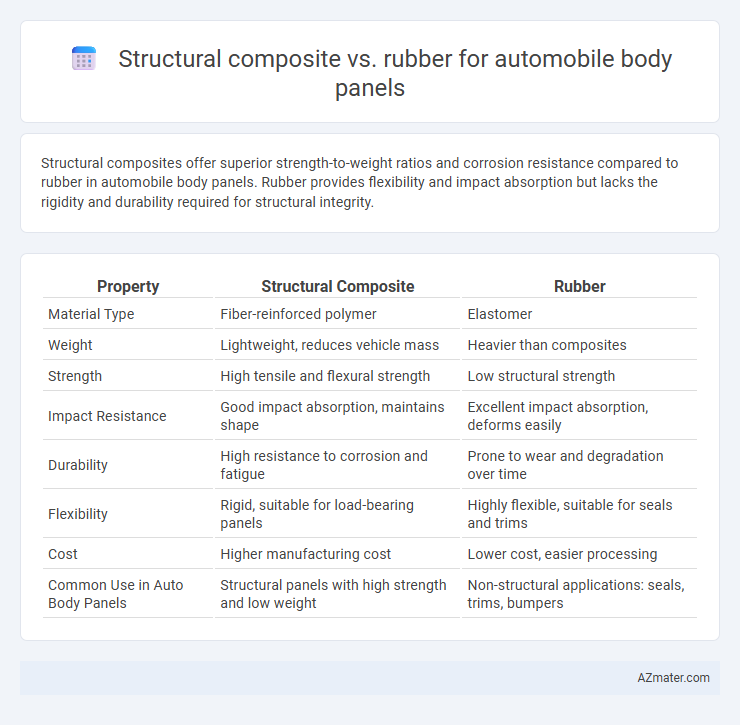
Structural composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance compared to rubber in automobile body panels. Rubber provides flexibility and impact absorption but lacks the rigidity and durability required for structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Structural Composite | Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Fiber-reinforced polymer | Elastomer |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces vehicle mass | Heavier than composites |
| Strength | High tensile and flexural strength | Low structural strength |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact absorption, maintains shape | Excellent impact absorption, deforms easily |
| Durability | High resistance to corrosion and fatigue | Prone to wear and degradation over time |
| Flexibility | Rigid, suitable for load-bearing panels | Highly flexible, suitable for seals and trims |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, easier processing |
| Common Use in Auto Body Panels | Structural panels with high strength and low weight | Non-structural applications: seals, trims, bumpers |
Introduction to Automobile Body Panel Materials
Automobile body panels utilize materials such as structural composites and rubber, each offering distinct properties tailored to automotive design requirements. Structural composites provide high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance, enhancing vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. Rubber materials contribute flexibility, impact absorption, and noise reduction, improving occupant comfort and durability in body panel applications.
Overview of Structural Composites
Structural composites for automobile body panels consist of fiber-reinforced polymers that combine high strength, low weight, and excellent durability, outperforming traditional rubber materials in impact resistance and stiffness. These composites enhance vehicle fuel efficiency by reducing overall mass while maintaining structural integrity and improving crashworthiness. Advanced manufacturing techniques enable precise molding and customization, making structural composites a preferred choice for high-performance, lightweight automotive body panels.
Rubber as a Body Panel Material
Rubber as a body panel material offers exceptional flexibility, impact resistance, and noise dampening properties, making it ideal for absorbing shocks and reducing vibrations in automobile manufacturing. Unlike structural composites, rubber panels provide superior weather resistance and corrosion protection, enhancing vehicle durability and longevity. Additionally, rubber's lightweight nature contributes to overall fuel efficiency while simplifying repairs and replacements compared to composites.
Weight Comparison: Structural Composite vs Rubber
Structural composites used in automobile body panels offer significant weight reduction compared to rubber, typically weighing 30-50% less due to their high strength-to-weight ratio. Composites such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers enable vehicle manufacturers to improve fuel efficiency and handling by decreasing overall vehicle mass. In contrast, rubber panels tend to be heavier and less stiff, limiting their effectiveness in weight-sensitive applications.
Impact Resistance and Crash Safety
Structural composites offer superior impact resistance and crash safety compared to rubber due to their higher strength-to-weight ratio and energy absorption capabilities. Composite materials such as carbon fiber and fiberglass reduce deformation upon impact, effectively dissipating crash forces to protect passengers. In contrast, rubber panels provide limited structural support, primarily absorbing minor vibrations and impacts but failing to contribute significantly to crash energy management.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Structural composites offer superior durability and weather resistance compared to rubber, as they resist corrosion, UV degradation, and temperature fluctuations more effectively. Rubber panels tend to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to sunlight and harsh weather, leading to cracking and loss of elasticity. The engineered fiber reinforcement within composites provides enhanced mechanical strength and long-term performance for automobile body panels in diverse environmental conditions.
Manufacturing Processes and Costs
Structural composites for automobile body panels typically involve advanced manufacturing processes such as resin transfer molding, compression molding, or automated fiber placement, which require significant capital investment and skilled labor. Rubber panels, on the other hand, are produced using simpler methods like injection molding or extrusion, resulting in lower tooling and production costs. While structural composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance, their higher manufacturing complexity leads to increased production expenses compared to rubber counterparts.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Potential
Structural composites offer superior design flexibility for automobile body panels due to their ability to be molded into complex shapes, providing enhanced aerodynamic efficiency and unique styling options. Rubber panels, while less adaptable in form, excel in impact absorption and weather resistance but limit aesthetic potential with simpler, more utilitarian designs. Choosing structural composites enables manufacturers to achieve intricate textures, glossy finishes, and lightweight yet strong panels, key attributes for modern automotive design innovation.
Environmental Sustainability and Recycling
Structural composites for automobile body panels offer superior environmental sustainability through lightweight design, which reduces fuel consumption and lowers CO2 emissions during vehicle operation. These composites often incorporate recyclable fibers and resins, enabling more efficient end-of-life material recovery compared to traditional rubber panels. Rubber panels, while flexible and impact-resistant, pose recycling challenges due to complex vulcanization and limited recyclability, leading to higher environmental impact in disposal and less circular reuse potential.
Choosing the Right Material for Future Automobiles
Structural composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for lightweight, fuel-efficient automobile body panels. Rubber provides excellent impact absorption and flexibility, enhancing crash safety and vibration damping in automotive applications. Selecting the right material depends on balancing durability, weight reduction, cost efficiency, and manufacturing processes to meet future automobile performance and sustainability goals.
Infographic: Structural composite vs Rubber for Automobile body panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com