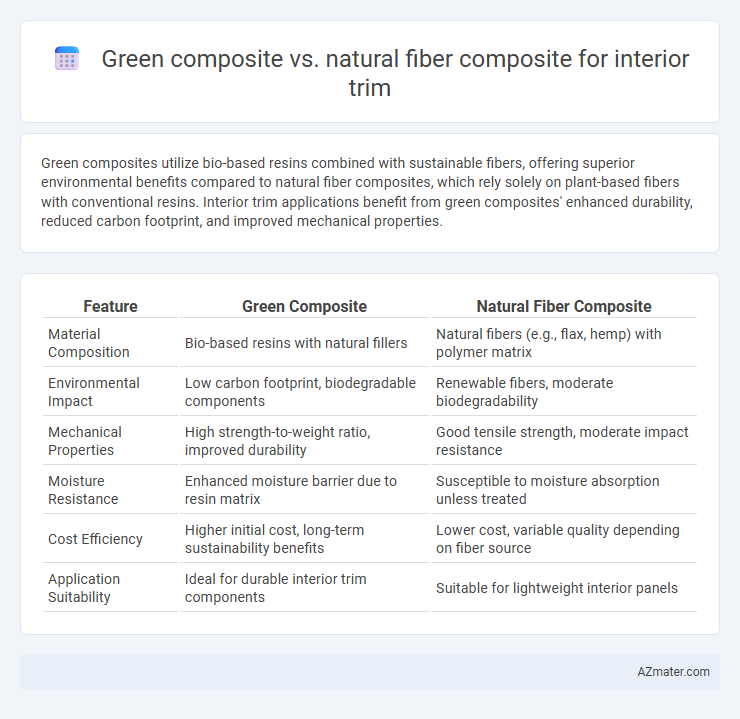
Green composites utilize bio-based resins combined with sustainable fibers, offering superior environmental benefits compared to natural fiber composites, which rely solely on plant-based fibers with conventional resins. Interior trim applications benefit from green composites' enhanced durability, reduced carbon footprint, and improved mechanical properties.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Composite | Natural Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Bio-based resins with natural fillers | Natural fibers (e.g., flax, hemp) with polymer matrix |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable components | Renewable fibers, moderate biodegradability |
| Mechanical Properties | High strength-to-weight ratio, improved durability | Good tensile strength, moderate impact resistance |
| Moisture Resistance | Enhanced moisture barrier due to resin matrix | Susceptible to moisture absorption unless treated |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial cost, long-term sustainability benefits | Lower cost, variable quality depending on fiber source |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for durable interior trim components | Suitable for lightweight interior panels |
Introduction to Green Composites and Natural Fiber Composites
Green composites combine natural fibers with biodegradable or recyclable polymer matrices, offering environmentally friendly alternatives for interior trim applications. Natural fiber composites specifically utilize fibers like flax, jute, or hemp embedded in thermoplastic or thermoset resins to achieve lightweight, durable, and sustainable material properties. These composites reduce carbon footprint and improve recyclability compared to conventional synthetic composites, making them ideal for eco-conscious interior design innovations.
Material Composition and Sources
Green composites for interior trim often combine bio-based resins with natural fibers such as kenaf, hemp, or flax, offering a sustainable alternative with reduced environmental impact. Natural fiber composites primarily utilize plant-derived fibers like jute, sisal, or coir embedded in polymer matrices, balancing durability and lightweight performance. Material composition in green composites emphasizes renewable, recyclable content sourced from agricultural by-products or fast-growing plants, enhancing eco-friendly attributes in automotive and furniture interior applications.
Manufacturing Processes
Green composites for interior trim typically utilize bio-based resins combined with natural fibers, requiring specialized manufacturing processes such as compression molding or resin transfer molding to ensure proper fiber wetting and matrix curing. Natural fiber composites often involve simpler processes like hand lay-up or vacuum bagging but may face challenges in achieving consistent fiber dispersion and moisture resistance. Advanced techniques integrating thermoplastic matrices with natural fibers improve production efficiency and enhance mechanical properties for automotive and furniture interior trims.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Green composites composed of bio-based resins and natural fibers exhibit significantly lower carbon footprints compared to conventional natural fiber composites that often use petroleum-based resins. The biodegradability of green composites enhances end-of-life disposal options, reducing landfill accumulation and environmental pollution. Sustainable sourcing of raw materials like agricultural residues or fast-growing plants in green composites promotes renewable resource cycles, supporting circular economy principles in interior trim manufacturing.
Mechanical and Physical Properties
Green composites offer superior mechanical properties such as higher tensile strength and stiffness compared to natural fiber composites, making them ideal for durable interior trim applications. The physical properties of green composites include enhanced moisture resistance and better dimensional stability, which reduce warping and degradation over time. Natural fiber composites excel in lightweight characteristics and biodegradability but often suffer from lower impact strength and moisture barrier performance, limiting their long-term use in interior environments.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
Green composites offer superior design flexibility due to their customizable formulations and ability to be molded into complex shapes, making them ideal for innovative interior trim applications. Natural fiber composites provide a wide range of aesthetic options with their unique textures and organic appearance, appealing to eco-conscious consumers seeking authentic, natural finishes. Both materials support sustainable design goals while enabling diverse interior trim styles that combine environmental benefits with visual appeal.
Performance in Automotive Interior Trim
Green composites exhibit superior sustainability and moderate mechanical properties, making them suitable for automotive interior trim focused on environmental impact reduction. Natural fiber composites offer enhanced vibration damping and lightweight characteristics, improving passenger comfort and fuel efficiency in vehicles. Both materials provide adequate strength and aesthetic versatility, but green composites often outperform in biodegradability while natural fiber composites excel in cost-effectiveness and ease of processing.
Cost Analysis and Market Trends
Green composites, combining bio-based resins with recycled fibers, typically offer a cost advantage over natural fiber composites due to more stable supply chains and scalable production methods. Market trends indicate growing demand for green composites in interior trim applications driven by automotive and furniture sectors' push for sustainability and regulatory incentives. Natural fiber composites remain valued for lightweight properties but face higher variability in raw material costs and processing challenges, affecting their overall market competitiveness.
Challenges and Limitations
Green composites for interior trim face challenges including high moisture absorption, leading to reduced mechanical properties and dimensional instability. Natural fiber composites often suffer from poor interfacial bonding with polymer matrices, resulting in lower impact resistance and durability issues. Processing difficulties such as fiber variability and thermal degradation limit consistent quality and scalability in automotive interior applications.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Green composites based on bio-based resins and natural fiber composites using flax or hemp show significant promise for lightweight, sustainable interior trim applications. Innovations in nanocellulose reinforcement and enhanced resin compatibility are improving mechanical performance and durability, addressing traditional limitations. Future prospects include scalable manufacturing techniques and smart composites integrating sensor technologies for improved safety and customization in automotive and aerospace interiors.
Infographic: Green composite vs Natural fiber composite for Interior trim
 azmater.com
azmater.com