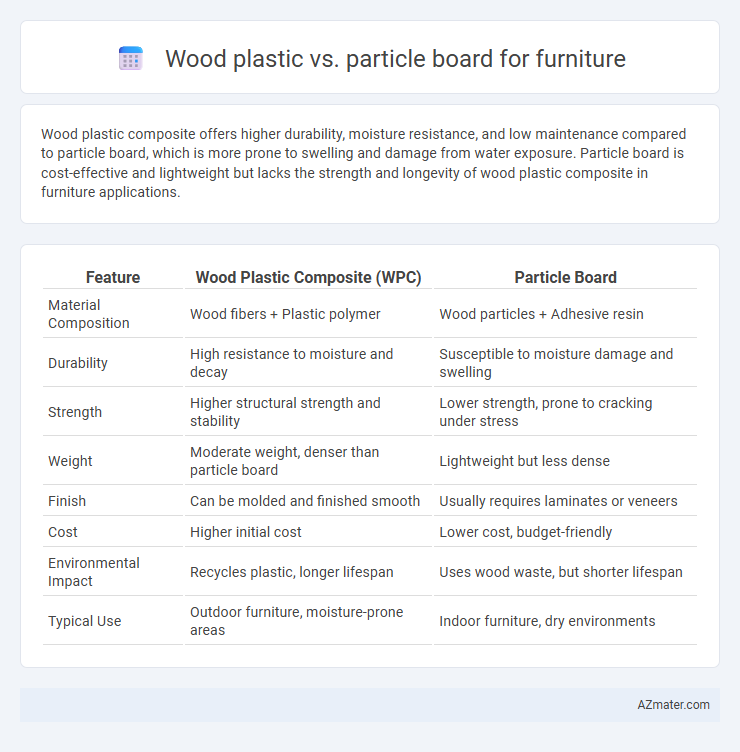
Wood plastic composite offers higher durability, moisture resistance, and low maintenance compared to particle board, which is more prone to swelling and damage from water exposure. Particle board is cost-effective and lightweight but lacks the strength and longevity of wood plastic composite in furniture applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) | Particle Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood fibers + Plastic polymer | Wood particles + Adhesive resin |
| Durability | High resistance to moisture and decay | Susceptible to moisture damage and swelling |
| Strength | Higher structural strength and stability | Lower strength, prone to cracking under stress |
| Weight | Moderate weight, denser than particle board | Lightweight but less dense |
| Finish | Can be molded and finished smooth | Usually requires laminates or veneers |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
| Environmental Impact | Recycles plastic, longer lifespan | Uses wood waste, but shorter lifespan |
| Typical Use | Outdoor furniture, moisture-prone areas | Indoor furniture, dry environments |
Introduction to Wood Plastic and Particle Board
Wood plastic composite (WPC) furniture combines wood fibers with thermoplastics, offering enhanced durability, moisture resistance, and low maintenance compared to traditional wood products. Particle board, composed of compressed wood chips and resin, provides a cost-effective solution with a smooth surface ideal for laminates but lacks the moisture resistance and structural strength of WPC. Both materials serve distinct purposes in furniture manufacturing, balancing factors like strength, cost, and environmental impact.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Wood plastic composite (WPC) furniture combines wood fibers or sawdust with thermoplastics such as polyethylene or polypropylene, creating a material resistant to moisture and decay through extrusion or injection molding processes. Particle board consists of wood chips, sawdust, and resin bonded under heat and pressure, resulting in a dense, uniform panel commonly used for indoor furniture with limited moisture resistance. WPC manufacturing involves blending and melting wood fibers with plastic polymers to achieve durability and weather resistance, whereas particle board relies on mechanical pressing of wood particles with adhesive resins for affordability and ease of machining.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Wood plastic composites (WPC) offer superior durability compared to particle board due to their resistance to moisture, rot, and insect damage, making them ideal for outdoor and high-humidity environments. Particle board, composed of wood chips and resin, tends to swell and deteriorate when exposed to water, resulting in reduced strength and shortened lifespan. WPC demonstrates higher tensile strength and impact resistance, supporting heavier loads and sustained use in furniture applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wood plastic composites (WPC) offer a more sustainable alternative to particle board by incorporating recycled plastics and wood fibers, reducing landfill waste and conserving natural resources. Particle board, typically made from wood chips and synthetic resins, often involves formaldehyde-based adhesives that can off-gas harmful chemicals and have lower recyclability. WPC's durability and resistance to moisture increase furniture lifespan, promoting long-term environmental benefits compared to the less durable particle board.
Moisture and Termite Resistance
Wood plastic composite (WPC) furniture exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to particle board, making it ideal for humid environments or outdoor use. Particle board tends to absorb water quickly, leading to swelling, warping, and reduced structural integrity. WPC also offers enhanced termite resistance due to its synthetic polymer content, whereas particle board, made from compressed wood fibers, is highly susceptible to termite damage.
Cost and Affordability
Wood plastic composites generally cost more than particle board due to the use of recycled plastics and enhanced durability, making them a longer-term investment for furniture. Particle board remains the most affordable option, widely used for budget-friendly furniture despite being less resistant to moisture and wear. For cost-conscious buyers seeking economical furniture solutions, particle board offers the least upfront expense, while wood plastic composites provide better value over time through increased lifespan and maintenance savings.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Options
Wood plastic composites (WPC) offer a smoother surface finish with enhanced resistance to moisture and scratches, making them ideal for modern furniture designs requiring durability and low maintenance. Particle board, often coated with laminates or veneers, provides a versatile aesthetic with numerous patterns and textures, but its surface durability is lower and prone to damage from moisture. WPC delivers a consistent, sleek look with limited customization, while particle board allows extensive decorative options but may require careful handling to preserve the finish.
Applications in Furniture Design
Wood plastic composite (WPC) is ideal for outdoor and moisture-prone furniture applications due to its durability, water resistance, and low maintenance compared to particle board. Particle board is commonly used in indoor furniture design like cabinets and shelving where cost efficiency and smooth surfaces for veneers are prioritized over moisture resistance. Designers often select WPC for patio furniture and bathroom vanities, while particle board suits bedroom furniture and office desks requiring smooth finishes and affordability.
Maintenance and Longevity
Wood plastic composites offer superior resistance to moisture, decay, and pests compared to particle board, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and enhanced longevity. Particle board tends to absorb water, leading to swelling, warping, and reduced durability, necessitating frequent repairs or replacements. Choosing wood plastic materials significantly extends furniture lifespan, especially in humid or high-traffic environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Wood plastic composites offer superior moisture resistance and durability compared to particle board, making them ideal for outdoor or high-humidity environments. Particle board is more cost-effective, lightweight, and easier to work with, suitable for indoor furniture where budget and ease of customization are priorities. Selecting between wood plastic and particle board depends on factors like exposure to moisture, budget constraints, and desired longevity of the furniture.
Infographic: Wood plastic vs Particle board for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com