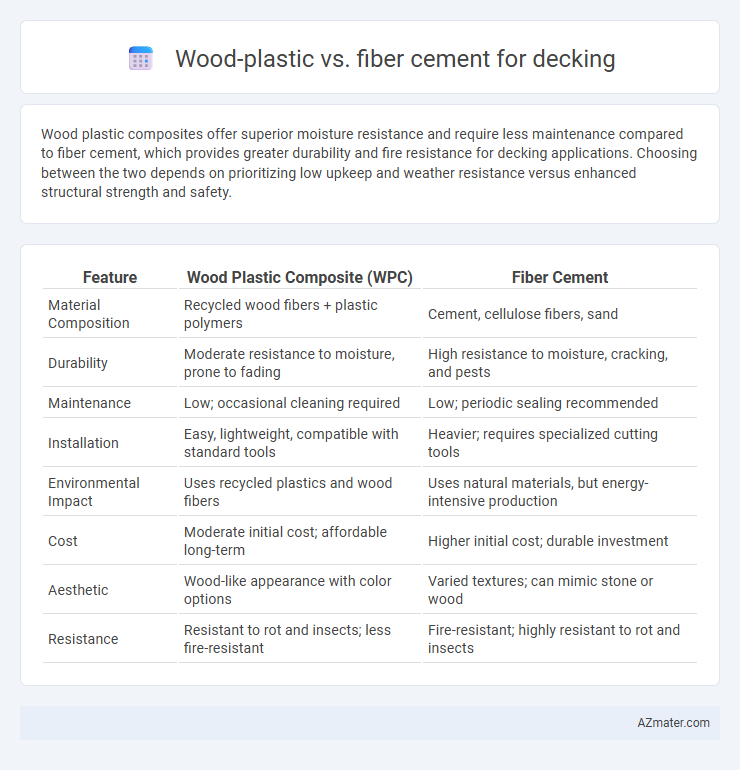
Wood plastic composites offer superior moisture resistance and require less maintenance compared to fiber cement, which provides greater durability and fire resistance for decking applications. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing low upkeep and weather resistance versus enhanced structural strength and safety.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) | Fiber Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Recycled wood fibers + plastic polymers | Cement, cellulose fibers, sand |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to moisture, prone to fading | High resistance to moisture, cracking, and pests |
| Maintenance | Low; occasional cleaning required | Low; periodic sealing recommended |
| Installation | Easy, lightweight, compatible with standard tools | Heavier; requires specialized cutting tools |
| Environmental Impact | Uses recycled plastics and wood fibers | Uses natural materials, but energy-intensive production |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; affordable long-term | Higher initial cost; durable investment |
| Aesthetic | Wood-like appearance with color options | Varied textures; can mimic stone or wood |
| Resistance | Resistant to rot and insects; less fire-resistant | Fire-resistant; highly resistant to rot and insects |
Introduction: Comparing Wood Plastic and Fiber Cement Decking
Wood plastic composite decking combines recycled wood fibers and plastic to offer durability, low maintenance, and resistance to moisture and insects. Fiber cement decking consists of cement reinforced with cellulose fibers, providing exceptional strength, fire resistance, and a natural wood appearance. Both materials differ in texture, longevity, and environmental impact, making the choice dependent on specific performance and aesthetic preferences.
Composition and Material Overview
Wood plastic composite decking combines recycled wood fibers and plastic resins, creating a durable, low-maintenance material resistant to rot and insect damage. Fiber cement decking is made from a blend of cement, silica, cellulose fibers, and sand, offering exceptional strength, fire resistance, and moisture durability. Both materials provide eco-friendly alternatives to traditional wood but differ significantly in texture, weight, and installation requirements.
Durability and Lifespan
Wood plastic composite decking offers notable resistance to rot, insect damage, and warping, with a typical lifespan of 25 to 30 years when properly maintained. Fiber cement decking provides superior durability against moisture, fire, and impact, often lasting 30 to 50 years due to its mineral-based composition. Both materials outperform traditional wood in longevity, but fiber cement generally delivers a longer lifespan and higher durability in extreme weather conditions.
Maintenance Requirements
Wood plastic composite (WPC) decking requires minimal maintenance, typically needing only occasional cleaning with soap and water to prevent dirt buildup and mildew. Fiber cement decking demands more frequent upkeep due to its susceptibility to surface cracking and moisture absorption, often requiring periodic sealing and repainting to maintain durability and appearance. The low-maintenance nature of WPC makes it a preferred choice for homeowners seeking long-term ease of care.
Installation Process and Complexity
Wood plastic composite (WPC) decking offers a simpler installation process compared to fiber cement boards due to its lighter weight and ability to be cut with standard woodworking tools. Fiber cement requires specialized cutting equipment like carbide blades and protective gear to handle silica dust, increasing complexity and installation time. The mechanical fastening system of WPC is often more straightforward, while fiber cement demands precise alignment and sealing to prevent moisture penetration.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Wood plastic composite decking offers a natural wood-like appearance with a variety of textures and colors that mimic cedar, redwood, and tropical hardwoods, providing versatile design options for modern or traditional styles. Fiber cement decking features a more uniform, smooth finish available in multiple contemporary colors, ideal for clean, minimalist aesthetics and can be painted or stained for further customization. Both materials provide durable, low-maintenance solutions, but wood plastic composite excels in replicating the organic look of wood, while fiber cement allows for bold design choices with its sleek, consistent surface.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wood plastic composite (WPC) decking utilizes recycled plastics and wood fibers, reducing landfill waste and conserving natural timber resources, making it a more sustainable option compared to traditional materials. Fiber cement decking, made from cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, offers durability and resistance to moisture, but its production involves high energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Choosing WPC decking supports circular economy principles, while fiber cement decking's environmental footprint depends heavily on manufacturing processes and sourcing of raw materials.
Cost Comparison: Initial and Long-term
Wood plastic composite decking typically has a higher initial cost ranging from $5 to $13 per square foot compared to fiber cement, which costs around $3 to $8 per square foot. Fiber cement offers lower upfront expenses but may incur higher long-term maintenance costs due to potential cracking and moisture damage. Wood plastic composite provides durability with minimal upkeep, ultimately reducing long-term expenses despite the steeper initial investment.
Performance in Various Climates
Wood plastic composites (WPC) for decking offer excellent resistance to moisture, rot, and insect damage, making them ideal for humid and wet climates. Fiber cement decking provides superior durability against extreme temperature fluctuations and UV exposure, minimizing warping and cracking in both hot and cold environments. Both materials require minimal maintenance, but fiber cement excels in fire resistance, while WPC delivers better thermal comfort under direct sunlight.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Decking Material
Wood plastic composites (WPC) offer enhanced durability and low maintenance, resisting rot and insect damage, making them ideal for long-lasting outdoor decks. Fiber cement provides superior strength, fire resistance, and a natural wood appearance, suitable for areas requiring robust and fireproof materials. Selecting the right decking material depends on climate, desired aesthetics, maintenance preferences, and budget, with WPC favored for moisture-prone environments and fiber cement preferred for high-heat or fire-risk locations.
Infographic: Wood plastic vs Fiber cement for Decking
 azmater.com
azmater.com