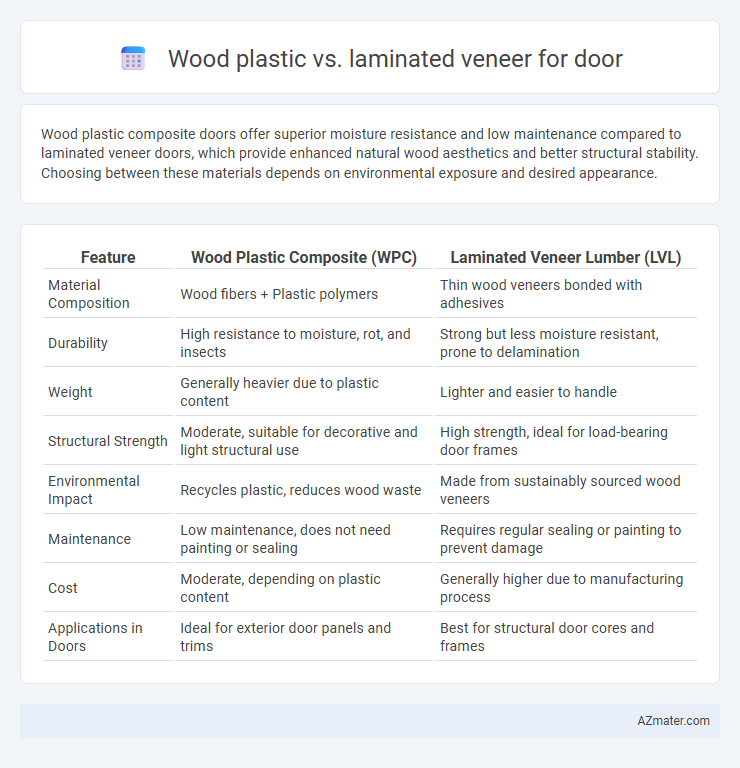
Wood plastic composite doors offer superior moisture resistance and low maintenance compared to laminated veneer doors, which provide enhanced natural wood aesthetics and better structural stability. Choosing between these materials depends on environmental exposure and desired appearance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) | Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood fibers + Plastic polymers | Thin wood veneers bonded with adhesives |
| Durability | High resistance to moisture, rot, and insects | Strong but less moisture resistant, prone to delamination |
| Weight | Generally heavier due to plastic content | Lighter and easier to handle |
| Structural Strength | Moderate, suitable for decorative and light structural use | High strength, ideal for load-bearing door frames |
| Environmental Impact | Recycles plastic, reduces wood waste | Made from sustainably sourced wood veneers |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, does not need painting or sealing | Requires regular sealing or painting to prevent damage |
| Cost | Moderate, depending on plastic content | Generally higher due to manufacturing process |
| Applications in Doors | Ideal for exterior door panels and trims | Best for structural door cores and frames |
Introduction to Door Material Choices
Wood plastic composites (WPC) offer durability and resistance to moisture, making them ideal for exterior door applications. Laminated veneer lumber (LVL), crafted from multiple layers of wood veneers, provides superior strength and stability, suitable for structural door frames and interior doors. Selecting between WPC and LVL depends on factors like weather resistance, structural requirements, and desired aesthetic finish.
What is Wood Plastic Composite (WPC)?
Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) is a durable material made by combining wood fibers or flour with thermoplastics such as polyethylene or polypropylene, resulting in enhanced strength and resistance to moisture, decay, and insects. WPC offers superior low maintenance and environmental benefits compared to Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL), which is composed of thin wood layers glued together, providing high structural strength but requiring periodic sealing and protection against water damage. For doors, WPC delivers improved longevity and weather resistance, making it ideal for outdoor or high-humidity environments where laminated veneer doors may deteriorate faster due to swelling or delamination.
Understanding Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL)
Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) is engineered wood made by layering thin wood veneers with adhesives, offering superior strength and uniformity compared to wood plastic composites. LVL provides excellent load-bearing capacity and stability, making it ideal for structural door components requiring durability and precise dimensions. Unlike wood plastic, LVL maintains natural wood aesthetics while resisting warping and moisture-related deformation in door applications.
Durability: Wood Plastic vs Laminated Veneer
Wood plastic composite doors offer superior durability compared to laminated veneer doors due to their resistance to moisture, insects, and warping, making them ideal for high-humidity environments. Laminated veneer doors, while aesthetically pleasing with their natural wood appearance, are more prone to surface damage and delamination over time when exposed to heavy wear or moisture. The synthetic composition of wood plastic materials enhances long-term performance and reduces maintenance needs compared to the more fragile laminated veneer surface.
Moisture and Termite Resistance Comparison
Wood plastic composite doors exhibit superior moisture resistance due to their synthetic polymer content, which prevents water absorption and swelling, making them ideal for damp environments. Laminated veneer doors, while stronger structurally, tend to absorb moisture over time, leading to potential warping and delamination if not properly sealed. In terms of termite resistance, wood plastic composites inherently resist termite damage as the plastic content is indigestible to insects, whereas laminated veneer doors require chemical treatments to protect against termite infestation.
Design and Aesthetic Options
Wood plastic composites (WPC) offer a modern, versatile design with smooth finishes and the ability to mimic natural wood grains, delivering durability alongside aesthetic appeal. Laminated veneer doors provide rich, authentic wood textures with a wide range of veneer patterns and colors, offering a classic, elegant look suitable for traditional or upscale interiors. Both materials support customization, but laminated veneer excels in warmth and natural beauty, while WPC emphasizes low maintenance and contemporary styling.
Strength and Structural Integrity
Wood plastic composite doors offer enhanced strength due to the combination of robust polymers and wood fibers, resulting in superior resistance to impact and moisture compared to laminated veneer doors. Laminated veneer doors consist of multiple thin wood layers bonded under heat and pressure, providing excellent dimensional stability but lower impact resistance. For applications requiring high structural integrity and durability, wood plastic composites outperform laminated veneers by resisting warping, cracking, and environmental degradation.
Cost Analysis: WPC vs Laminated Veneer
Wood plastic composite (WPC) doors generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to laminated veneer doors, making them a budget-friendly option for many homeowners. Laminated veneer doors tend to have higher material and manufacturing costs due to the natural wood veneer and intricate lamination process, impacting the overall price. Long-term cost efficiency favors WPC doors because of their low maintenance and resistance to moisture, reducing repair and replacement expenses over time.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Wood plastic composite (WPC) doors leverage recycled plastics and wood fibers, reducing deforestation and landfill waste while offering long-lasting durability that minimizes replacement frequency. Laminated veneer doors use thin layers of wood glued together, optimizing wood use but often rely on adhesives that may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs), impacting indoor air quality and environmental health. Overall, WPC doors present a more sustainable choice due to their use of recycled materials and lower environmental footprint in production and disposal.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Door
Wood plastic composites offer superior moisture resistance and durability, making them ideal for exterior doors exposed to harsh weather conditions. Laminated veneer, made from thin wood layers bonded under heat and pressure, provides a natural wood appearance with enhanced stability and reduced warping. Choosing the best material depends on application requirements: wood plastic suits low-maintenance, weather-resistant needs, while laminated veneer excels in aesthetic appeal and structural integrity for indoor doors.
Infographic: Wood plastic vs Laminated veneer for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com