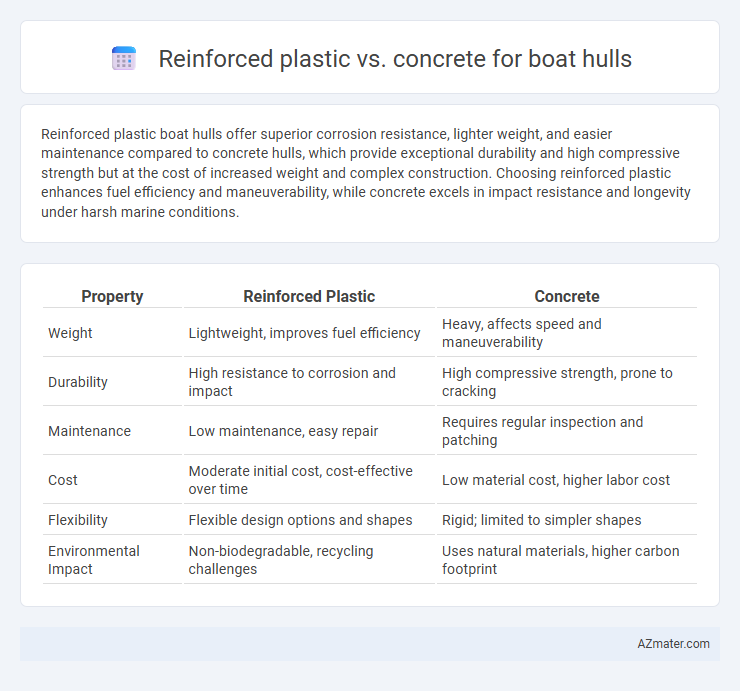
Reinforced plastic boat hulls offer superior corrosion resistance, lighter weight, and easier maintenance compared to concrete hulls, which provide exceptional durability and high compressive strength but at the cost of increased weight and complex construction. Choosing reinforced plastic enhances fuel efficiency and maneuverability, while concrete excels in impact resistance and longevity under harsh marine conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Reinforced Plastic | Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, improves fuel efficiency | Heavy, affects speed and maneuverability |
| Durability | High resistance to corrosion and impact | High compressive strength, prone to cracking |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy repair | Requires regular inspection and patching |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, cost-effective over time | Low material cost, higher labor cost |
| Flexibility | Flexible design options and shapes | Rigid; limited to simpler shapes |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recycling challenges | Uses natural materials, higher carbon footprint |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Reinforced plastic, commonly known as fiberglass, offers a lightweight and corrosion-resistant option for boat hulls, making it ideal for performance and ease of maintenance. Concrete hulls provide exceptional durability and strength with superior resistance to impact and abrasion but are significantly heavier and require complex construction techniques. Choosing between reinforced plastic and concrete depends on factors such as intended use, weight considerations, budget, and maintenance preferences.
Overview of Reinforced Plastic in Boat Construction
Reinforced plastic, commonly known as fiberglass, is a composite material used extensively in boat hull construction due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ease of molding into complex shapes. It combines plastic resins with glass fibers to achieve enhanced durability and flexibility, allowing boat designs to be lightweight yet robust for marine environments. This material offers superior maintenance efficiency compared to traditional concrete hulls, making it a preferred choice for recreational and commercial vessels.
Concrete as a Material for Boat Hulls
Concrete offers exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion, making it a robust material for boat hulls in harsh marine environments. Its high compressive strength and low maintenance requirements provide long-term cost savings compared to traditional materials. Additionally, modern fiber-reinforced concrete enhances flexibility and impact resistance, ensuring structural integrity and longevity for various marine vessels.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Reinforced plastic boat hulls offer high tensile strength and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for lightweight and flexible designs, while concrete hulls provide exceptional compressive strength and superior impact resistance but at the expense of increased weight. Durability-wise, reinforced plastic resists marine biofouling and UV degradation effectively, whereas concrete exhibits excellent longevity and low maintenance in harsh marine environments due to its robust structural composition. The choice between these materials depends on the specific performance requirements, with reinforced plastic favored for speed and maneuverability, and concrete preferred for heavy-duty, long-lasting vessels.
Weight Considerations: Reinforced Plastic vs Concrete
Reinforced plastic boat hulls offer significant weight advantages over concrete, enabling easier handling, faster speeds, and improved fuel efficiency. Concrete hulls, while robust and durable, are considerably heavier, which can lead to decreased maneuverability and increased fuel consumption. The lightweight nature of reinforced plastics also allows for more versatile design options and enhanced performance in various marine conditions.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Reinforced plastic boat hulls require less frequent maintenance compared to concrete hulls due to their resistance to corrosion and ease of cleaning, with gelcoat surfaces that resist algae and barnacle buildup. Concrete hulls, while highly durable and unlikely to suffer rot or corrosion, demand regular inspection for cracks and surface wear to prevent water intrusion and structural damage. Both materials offer long lifespans, but reinforced plastic hulls typically provide a maintenance-friendly option with lifespans exceeding 30 years, whereas well-maintained concrete hulls can last 50 years or more under proper care.
Cost Analysis of Reinforced Plastic and Concrete Hulls
Reinforced plastic boat hulls typically have lower initial material costs compared to concrete hulls, with fiberglass costing between $3 to $8 per pound, while concrete mixes range higher due to specialized additives and reinforcement requirements. Maintenance expenses for reinforced plastic are generally lower, as they resist corrosion and require fewer repairs, whereas concrete hulls may incur higher long-term costs from potential cracking and water infiltration. Overall, the cost efficiency of reinforced plastic hulls makes them more economically viable for small to medium-sized boats, while concrete hulls tend to be favored for larger crafts with specific structural needs despite higher upfront and maintenance costs.
Performance and Efficiency on Water
Reinforced plastic boat hulls offer superior corrosion resistance and lighter weight, enhancing fuel efficiency and maneuverability compared to traditional concrete hulls. Concrete hulls provide exceptional durability and strength but tend to be heavier, leading to reduced speed and higher fuel consumption. The choice between reinforced plastic and concrete hulls directly impacts performance metrics such as acceleration, top speed, and operational costs on water.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reinforced plastic boat hulls, primarily made from fiberglass and resin, generate significant non-biodegradable waste and rely on petroleum-based materials, posing long-term environmental disposal challenges. Concrete hulls, while energy-intensive during production, can incorporate recycled materials and offer greater durability and longevity, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated resource consumption. Sustainability considerations favor concrete hulls for their potential recyclability and extended lifecycle, contrasting with the environmental burden of reinforced plastic waste management.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Boat Hull
Reinforced plastic offers a lightweight, corrosion-resistant solution ideal for smaller, high-performance boats, enhancing fuel efficiency and maneuverability. Concrete hulls provide exceptional durability, fire resistance, and sound insulation, making them suitable for large, heavy-duty vessels despite increased weight. Selecting the right boat hull material depends on factors like vessel size, intended use, maintenance preferences, and performance requirements.
Infographic: Reinforced plastic vs Concrete for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com