Foam core composites offer superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties ideal for construction panels, while polymer matrix composites provide enhanced mechanical strength and durability. Choosing between foam core and polymer matrix composites depends on balancing insulation performance with structural requirements.
Table of Comparison
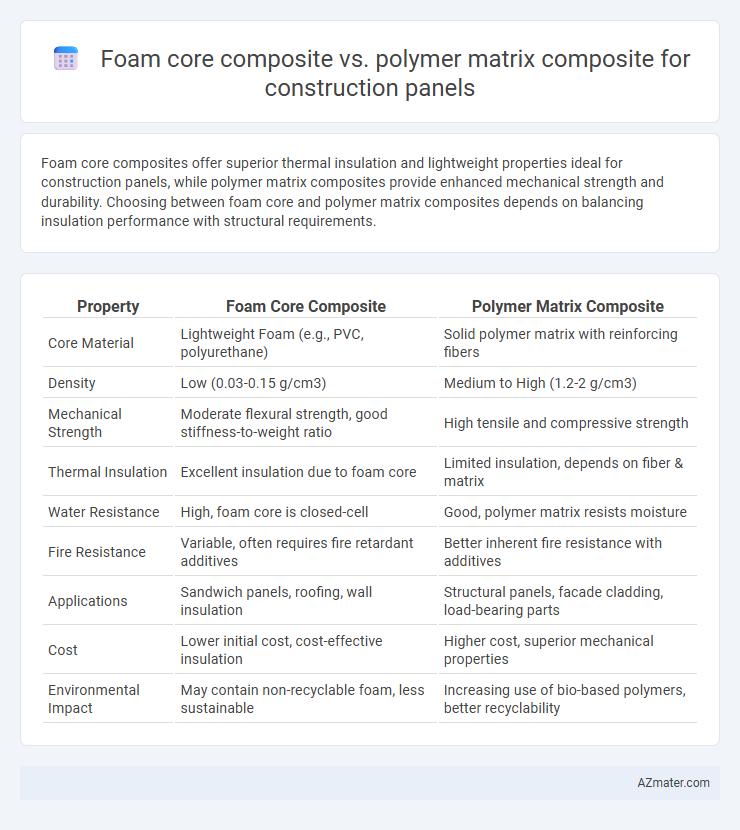
| Property | Foam Core Composite | Polymer Matrix Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Core Material | Lightweight Foam (e.g., PVC, polyurethane) | Solid polymer matrix with reinforcing fibers |
| Density | Low (0.03-0.15 g/cm3) | Medium to High (1.2-2 g/cm3) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate flexural strength, good stiffness-to-weight ratio | High tensile and compressive strength |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent insulation due to foam core | Limited insulation, depends on fiber & matrix |
| Water Resistance | High, foam core is closed-cell | Good, polymer matrix resists moisture |
| Fire Resistance | Variable, often requires fire retardant additives | Better inherent fire resistance with additives |
| Applications | Sandwich panels, roofing, wall insulation | Structural panels, facade cladding, load-bearing parts |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, cost-effective insulation | Higher cost, superior mechanical properties |
| Environmental Impact | May contain non-recyclable foam, less sustainable | Increasing use of bio-based polymers, better recyclability |
Introduction to Composite Materials in Construction
Foam core composites and polymer matrix composites are essential materials in modern construction panels, offering enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and improved thermal insulation. Foam core composites consist of a lightweight core material sandwiched between two composite face sheets, providing superior stiffness and energy absorption. Polymer matrix composites integrate high-performance fibers within a polymer resin, delivering exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion, making both ideal for structural and architectural applications.
Overview of Foam Core Composites
Foam core composites consist of a lightweight core material, typically polyurethane or polystyrene foam, sandwiched between two layers of fiber-reinforced polymer skins, providing high stiffness-to-weight ratios ideal for construction panels. These composites offer excellent thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and structural performance, making them effective for wall and roofing applications. Their ease of fabrication and durability contribute to reduced construction time and enhanced energy efficiency in building projects.
Fundamentals of Polymer Matrix Composites
Foam core composites typically consist of a lightweight foam core sandwiched between polymer matrix composite (PMC) face sheets, offering high stiffness-to-weight ratios ideal for construction panels. Polymer matrix composites are comprised of reinforcing fibers embedded in a polymer resin matrix, which provides superior mechanical strength, durability, and resistance to environmental degradation. The fundamental advantage of PMCs lies in their ability to tailor fiber orientation and matrix properties, resulting in enhanced load-bearing capacity and corrosion resistance critical for structural applications.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Foam core composites exhibit lightweight properties with high thermal insulation and excellent impact absorption, making them suitable for energy-efficient construction panels. Polymer matrix composites offer superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and durability, providing enhanced load-bearing capacity and longevity in structural applications. Both materials balance stiffness and weight, but foam core composites prioritize insulation and cushioning, while polymer matrix composites focus on structural integrity and resistance to environmental degradation.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capacity
Foam core composites exhibit high stiffness-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for lightweight construction panels with moderate load-bearing requirements, while polymer matrix composites (PMCs) offer superior tensile strength and impact resistance suitable for high-load structural applications. The closed-cell foam core in foam core composites provides excellent thermal insulation and energy absorption but may suffer from lower shear strength compared to the continuous fiber reinforcement in PMCs. Polymer matrix composites demonstrate enhanced durability and resistance to environmental degradation, resulting in longer service life for load-bearing construction panels under cyclic or dynamic loads.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Efficiency
Foam core composites exhibit superior thermal insulation efficiency due to their low thermal conductivity, making them ideal for reducing heat transfer in construction panels. Polymer matrix composites offer enhanced acoustic insulation by effectively dampening sound vibrations and reducing noise transmission. Combining foam cores with polymer matrix layers can optimize both thermal and acoustic insulation performance in building applications.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Foam core composites offer superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties but generally exhibit lower durability and weather resistance compared to polymer matrix composites, which are engineered with reinforced fibers like glass or carbon for enhanced structural integrity and superior resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. Polymer matrix composites maintain mechanical properties and resist weather-induced degradation over extended periods, making them ideal for exterior construction panels exposed to harsh climates. Their ability to resist corrosion, delamination, and impact damage surpasses foam core alternatives, resulting in longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs in demanding environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis and Lifecycle Considerations
Foam core composites typically offer lower initial costs due to cheaper core materials and simpler manufacturing processes, making them attractive for budget-conscious construction panels. Polymer matrix composites, while generally more expensive upfront, provide superior durability, chemical resistance, and structural performance, which can result in longer lifecycles and reduced maintenance expenses. Lifecycle cost analysis often favors polymer matrix composites for applications requiring sustained load-bearing capacity and environmental resilience, despite higher initial investments.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Foam core composites offer lightweight structural support with improved thermal insulation, reducing energy consumption in buildings and enhancing sustainability. Polymer matrix composites, typically derived from synthetic resins, pose environmental challenges due to non-biodegradable polymers and reliance on fossil fuels, impacting end-of-life disposal and carbon footprint. Choosing foam core composites with bio-based or recyclable materials significantly lowers environmental impact compared to conventional polymer matrix composites in construction panels.
Applications and Future Trends in Construction Panels
Foam core composites offer exceptional thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making them ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes and interior partition panels in modern construction. Polymer matrix composites provide superior mechanical strength and durability, suited for structural panels that require high load-bearing capacity and resistance to environmental degradation. Future trends in construction panels emphasize the integration of sustainable materials, enhanced fire retardancy, and smart sensor embedding to improve building performance and longevity.
Infographic: Foam core composite vs Polymer matrix composite for Construction panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com