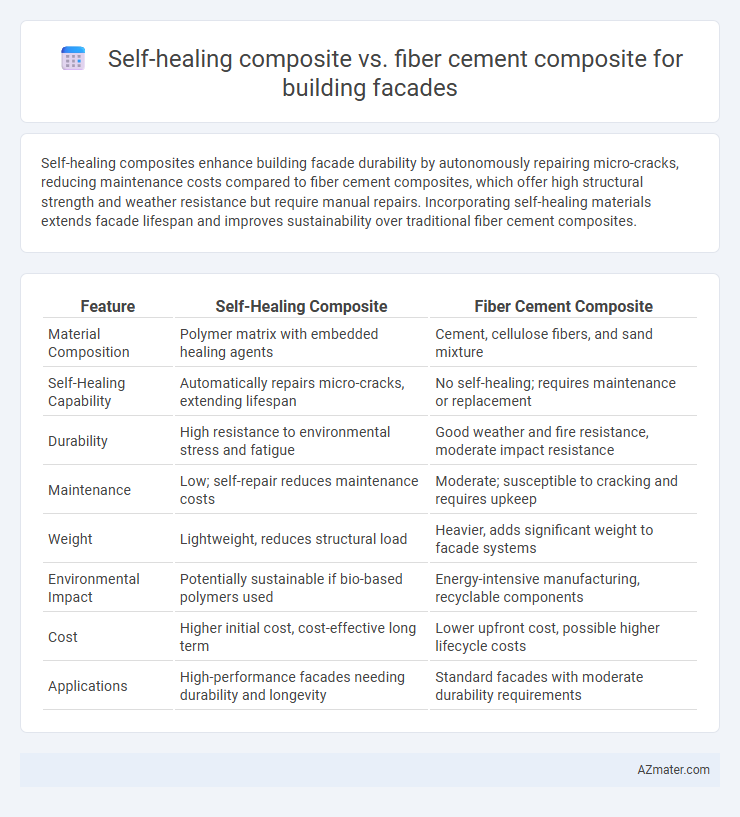
Self-healing composites enhance building facade durability by autonomously repairing micro-cracks, reducing maintenance costs compared to fiber cement composites, which offer high structural strength and weather resistance but require manual repairs. Incorporating self-healing materials extends facade lifespan and improves sustainability over traditional fiber cement composites.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Healing Composite | Fiber Cement Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymer matrix with embedded healing agents | Cement, cellulose fibers, and sand mixture |
| Self-Healing Capability | Automatically repairs micro-cracks, extending lifespan | No self-healing; requires maintenance or replacement |
| Durability | High resistance to environmental stress and fatigue | Good weather and fire resistance, moderate impact resistance |
| Maintenance | Low; self-repair reduces maintenance costs | Moderate; susceptible to cracking and requires upkeep |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces structural load | Heavier, adds significant weight to facade systems |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially sustainable if bio-based polymers used | Energy-intensive manufacturing, recyclable components |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, cost-effective long term | Lower upfront cost, possible higher lifecycle costs |
| Applications | High-performance facades needing durability and longevity | Standard facades with moderate durability requirements |
Introduction to Building Facade Materials
Self-healing composites for building facades incorporate microcapsules or vascular networks that enable autonomous repair of cracks, significantly enhancing durability and reducing maintenance costs. Fiber cement composites combine Portland cement and cellulose fibers, offering fire resistance, weather durability, and tensile strength vital for exterior cladding. Both materials address facade longevity but differ in their mechanisms: self-healing composites actively restore structural integrity, whereas fiber cement composites offer passive robustness through material composition.
Overview of Self-Healing Composites
Self-healing composites incorporate microcapsules or vascular networks containing healing agents that activate upon damage, promoting autonomous repair and extending facade durability. These materials significantly reduce maintenance costs and improve structural integrity compared to traditional fiber cement composites, which rely on external interventions to address cracks and wear. Advances in polymer-based self-healing systems facilitate adaptability to various climatic conditions, making them a cutting-edge solution for sustainable building facades.
What is Fiber Cement Composite?
Fiber cement composite is a durable building material composed of cement reinforced with cellulose fibers, providing enhanced strength and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, fire, and pests. It offers excellent dimensional stability and low maintenance, making it a popular choice for building facades. Unlike self-healing composites, fiber cement does not possess intrinsic self-repairing capabilities but excels in long-term structural integrity and weather resistance.
Structural Performance Comparison
Self-healing composites for building facades exhibit enhanced crack resistance and durability through autonomous damage repair mechanisms, significantly improving structural integrity under cyclic loading conditions. Fiber cement composites provide high tensile strength and fire resistance but lack the intrinsic ability to recover from micro-cracks, leading to progressive degradation over time. Comparative studies show that self-healing composites maintain higher load-bearing capacity and reduce maintenance costs, making them a superior choice for long-term facade performance.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Self-healing composites for building facades exhibit enhanced durability by autonomously repairing microcracks, significantly extending service life compared to traditional fiber cement composites, which rely on passive material strength. Fiber cement composites offer high resistance to weathering and impact but lack self-repair capabilities, leading to gradual deterioration under environmental stress. The integration of self-healing mechanisms in composite materials can increase the longevity of facades by reducing maintenance frequency and mitigating crack propagation caused by thermal and mechanical loads.
Maintenance and Repair Needs
Self-healing composites for building facades significantly reduce maintenance and repair needs by autonomously sealing cracks and preventing moisture infiltration, extending facade longevity. Fiber cement composites, while durable and resistant to weathering, require regular maintenance such as repainting, sealing, and potential crack repairs to maintain performance and aesthetic appeal. The integration of self-healing technology in composites offers cost-effective, long-term facade solutions by minimizing manual interventions and repair frequency compared to traditional fiber cement materials.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Self-healing composites for building facades significantly enhance sustainability by extending material lifespan and reducing maintenance frequency, thereby lowering resource consumption and waste generation compared to traditional fiber cement composites. Fiber cement composites, while durable and fire-resistant, involve energy-intensive manufacturing processes and release silica dust, raising environmental and health concerns. The integration of self-healing mechanisms in composites not only minimizes facade deterioration but also supports circular economy principles by promoting material reuse and reducing carbon footprint.
Aesthetic Versatility and Design Options
Self-healing composites offer unparalleled aesthetic versatility with their ability to autonomously repair surface damage, maintaining pristine facade appearance over time, ideal for dynamic architectural designs. Fiber cement composites provide extensive design options through diverse textures and color finishes, mimicking natural materials like wood and stone while ensuring durability and low maintenance. Architects prioritize self-healing composites for longevity and seamless facade integrity, whereas fiber cement composites excel in customizable finishes and traditional aesthetic appeal.
Cost Considerations for Facade Projects
Self-healing composites generally incur higher upfront costs compared to fiber cement composites due to advanced materials and manufacturing processes, but they offer long-term savings by reducing maintenance and repair expenses through automatic crack repair. Fiber cement composites present a more budget-friendly initial investment with well-established production techniques and widespread availability, yet they may lead to higher lifecycle costs owing to susceptibility to damage and periodic maintenance requirements. Considering total cost of ownership, self-healing composites can be more economical for facade projects demanding durability and reduced upkeep, while fiber cement remains a cost-effective choice for projects with tight initial budgets.
Choosing the Right Composite for Your Building
Self-healing composites offer enhanced durability by autonomously repairing micro-cracks, reducing maintenance costs and extending facade lifespan. Fiber cement composites provide excellent weather resistance, fire retardancy, and structural strength, making them ideal for harsh climates and load-bearing applications. Selecting the right composite depends on project requirements such as longevity, environmental conditions, and maintenance budget to optimize facade performance and sustainability.
Infographic: Self-healing composite vs Fiber cement composite for Building facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com