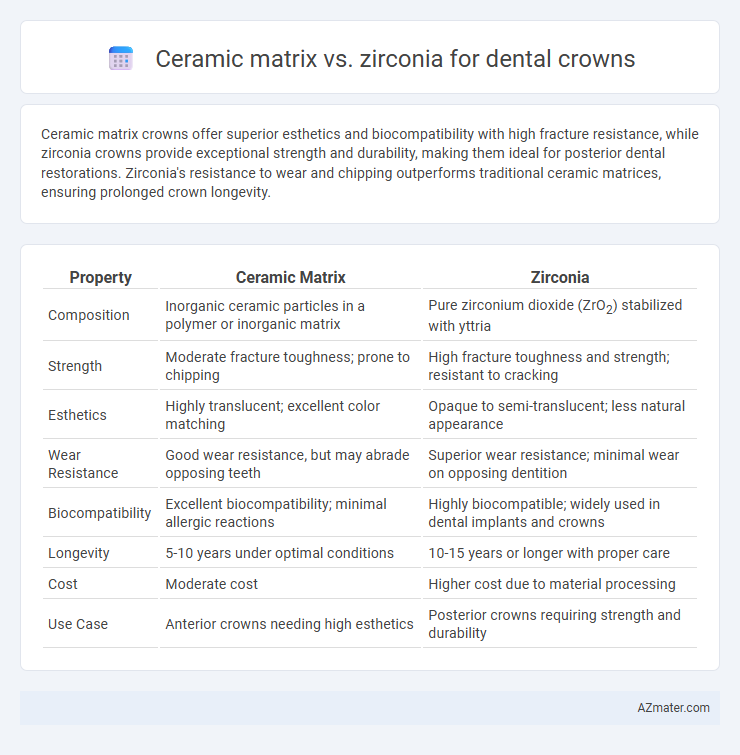
Ceramic matrix crowns offer superior esthetics and biocompatibility with high fracture resistance, while zirconia crowns provide exceptional strength and durability, making them ideal for posterior dental restorations. Zirconia's resistance to wear and chipping outperforms traditional ceramic matrices, ensuring prolonged crown longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Matrix | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Inorganic ceramic particles in a polymer or inorganic matrix | Pure zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) stabilized with yttria |
| Strength | Moderate fracture toughness; prone to chipping | High fracture toughness and strength; resistant to cracking |
| Esthetics | Highly translucent; excellent color matching | Opaque to semi-translucent; less natural appearance |
| Wear Resistance | Good wear resistance, but may abrade opposing teeth | Superior wear resistance; minimal wear on opposing dentition |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent biocompatibility; minimal allergic reactions | Highly biocompatible; widely used in dental implants and crowns |
| Longevity | 5-10 years under optimal conditions | 10-15 years or longer with proper care |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to material processing |
| Use Case | Anterior crowns needing high esthetics | Posterior crowns requiring strength and durability |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Dental crown materials primarily include ceramic matrix and zirconia, each offering distinct benefits for restoration durability and aesthetics. Ceramic matrix crowns provide excellent translucency and mimic natural tooth appearance, making them ideal for front teeth. Zirconia crowns feature superior strength and fracture resistance, suitable for molar restorations where durability is critical.
Overview of Ceramic Matrix Crowns
Ceramic matrix crowns are composed of a fine ceramic powder embedded within a glassy matrix, offering high esthetic appeal and natural translucency that mimic tooth enamel. These crowns provide excellent biocompatibility and resistance to wear, making them suitable for patients with metal allergies. Their structural composition allows for strong bonding to tooth structure, enhancing durability and longevity in dental restorations.
Understanding Zirconia Dental Crowns
Zirconia dental crowns offer exceptional strength and durability compared to traditional ceramic matrix crowns, making them ideal for posterior restorations where high masticatory forces are present. Zirconia's biocompatibility and resistance to wear also contribute to its growing popularity in dental applications, promoting long-term oral health and patient comfort. Advanced manufacturing techniques like CAD/CAM milling enhance the precision and aesthetic appeal of zirconia crowns, ensuring a natural look while maintaining superior mechanical properties.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Ceramic matrix crowns offer excellent aesthetics and moderate strength suitable for anterior teeth, while zirconia crowns provide superior strength and durability, making them ideal for posterior restorations with high occlusal forces. Zirconia demonstrates a flexural strength ranging from 900 to 1200 MPa, significantly higher than traditional ceramic matrices, which typically range between 300 to 500 MPa. This enhanced strength translates to greater resistance to fracture and chipping, ensuring longer-lasting dental crowns in demanding oral environments.
Aesthetics and Natural Appearance
Ceramic matrix dental crowns offer superior translucency and color-matching properties, closely mimicking the natural enamel's light reflection and enhancing aesthetics. Zirconia crowns provide high strength but can appear more opaque, sometimes resulting in a less natural appearance compared to ceramic. Modern advancements in zirconia shading and layering techniques have improved its aesthetics, yet ceramic matrix crowns remain the gold standard for achieving optimal natural look in restorative dentistry.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Ceramic matrix crowns, often composed of lithium disilicate, offer excellent biocompatibility with minimal risk of allergic reactions and promote healthy gum tissue integration, enhancing patient safety. Zirconia crowns, made from yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystals, exhibit superior strength and fracture resistance while maintaining high biocompatibility and low plaque accumulation. Both materials are well-tolerated, but zirconia's durability provides long-term safety advantages for patients requiring robust restorative solutions.
Longevity and Wear Resistance
Ceramic matrix dental crowns, often composed of lithium disilicate, offer excellent longevity due to their high flexural strength and resistance to crack propagation, making them suitable for long-term use. Zirconia crowns provide superior wear resistance and durability, with a toughness that resists chipping and fractures, extending the crown's lifespan in high-stress occlusal areas. Both materials demonstrate excellent biocompatibility and minimal opposing enamel wear, but zirconia's superior hardness enhances its performance in longevity and wear resistance compared to ceramic matrix crowns.
Suitability for Different Dental Cases
Ceramic matrix crowns offer excellent aesthetic appeal and biocompatibility, making them suitable for front teeth restorations where appearance is critical. Zirconia crowns provide superior strength and durability, ideal for molars and patients with heavy bite forces or bruxism. Selection depends on balancing the need for toughness in functional areas versus translucency and natural look in visible regions.
Cost Considerations and Insurance Coverage
Ceramic matrix dental crowns generally offer a more affordable option compared to zirconia crowns, with prices ranging between $800 and $1,500 per tooth, while zirconia crowns can cost $1,000 to $2,000 due to their superior strength and durability. Insurance coverage varies widely; many dental insurance plans partially cover ceramic crowns due to their cost-effectiveness, whereas zirconia crowns often face limited or no coverage, which impacts out-of-pocket expenses. Patients should verify their specific dental plan benefits and consider long-term savings from zirconia's longevity when evaluating cost versus insurance reimbursement.
Choosing the Right Crown: Factors to Consider
Ceramic matrix crowns offer superior esthetics and biocompatibility, making them ideal for patients prioritizing natural appearance and metal allergies. Zirconia crowns provide exceptional strength and durability, suitable for molars subjected to high bite forces and bruxism patients. Selecting the right crown involves assessing factors such as tooth location, occlusal load, esthetic demands, and individual health considerations to ensure optimal functionality and longevity.
Infographic: Ceramic matrix vs Zirconia for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com