Sandwich structure boat hulls offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional plastic hulls, improving durability and fuel efficiency. Plastic hulls provide cost-effective manufacturing and corrosion resistance but typically lack the stiffness and energy absorption capabilities of sandwich composites.
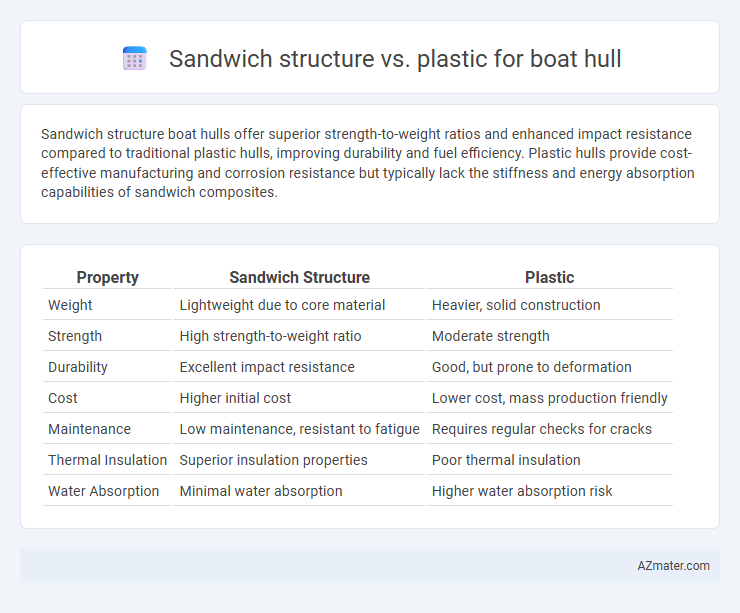
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sandwich Structure | Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight due to core material | Heavier, solid construction |
| Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio | Moderate strength |
| Durability | Excellent impact resistance | Good, but prone to deformation |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, mass production friendly |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, resistant to fatigue | Requires regular checks for cracks |
| Thermal Insulation | Superior insulation properties | Poor thermal insulation |
| Water Absorption | Minimal water absorption | Higher water absorption risk |
Introduction to Boat Hull Construction Materials
Boat hull construction materials significantly impact performance, durability, and maintenance. Sandwich structures, typically consisting of a lightweight core like foam or balsa wood between two fiberglass or carbon fiber skins, offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional plastic hulls. Plastic hulls, often made from polyethylene or ABS, provide cost-effective, corrosion-resistant options but generally lack the rigidity and structural benefits found in sandwich composite designs.
Understanding Sandwich Structure in Boat Hulls
Sandwich structures in boat hulls consist of a lightweight core material, such as foam or balsa, bonded between two layers of fiberglass or composite skins, providing enhanced strength-to-weight ratio and improved impact resistance compared to traditional plastic hulls. This design optimizes stiffness and durability while reducing overall weight, resulting in better fuel efficiency and performance. Understanding the mechanical advantages and material properties of sandwich construction helps boat designers create hulls that balance rigidity, buoyancy, and durability for marine environments.
Key Properties of Plastic Hulls
Plastic hulls offer high impact resistance, excellent corrosion resistance, and low maintenance requirements, making them ideal for harsh marine environments. Their inherent flexibility allows them to absorb shocks better than rigid sandwich structures, reducing the risk of cracks or structural damage. However, plastic hulls typically have lower stiffness and strength-to-weight ratios compared to sandwich composite materials, which may affect performance in high-speed or heavy-load applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
A sandwich structure boat hull, composed of a lightweight core material like foam or honeycomb between two fiber-reinforced composite skins, offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional plastic hulls. Plastic hulls, typically made from polyethylene or fiberglass-reinforced plastic, provide good durability and resistance to corrosion but are generally heavier and less rigid, leading to lower structural performance under stress. Sandwich constructions excel in distributing loads and resisting deformation, which results in longer service life and better fatigue resistance in marine environments.
Weight and Performance Analysis
Sandwich structure boat hulls typically offer superior weight-to-strength ratios compared to traditional plastic hulls, resulting in enhanced buoyancy and fuel efficiency. The core materials, such as foam or honeycomb, combined with composite skins, provide high stiffness and impact resistance while maintaining low weight. In contrast, plastic hulls are heavier and less rigid, potentially compromising speed and maneuverability during performance-intensive operations.
Cost Factors: Sandwich Structure vs Plastic
Sandwich structure boat hulls typically incur higher initial costs due to the use of composite materials like fiberglass or carbon fiber combined with core materials such as foam or balsa wood, whereas plastic hulls, commonly made from polyethylene or fiberglass-reinforced plastic, offer lower manufacturing expenses. Maintenance costs for sandwich structures may be greater because damage repair often requires specialized skills and materials, while plastic hulls provide easier and more cost-effective repairs due to their uniform material composition. Over the boat's lifespan, sandwich structures deliver superior strength-to-weight ratios and durability, potentially reducing long-term operational costs despite higher upfront investment compared to plastic hulls.
Maintenance and Lifespan Considerations
Sandwich structure boat hulls, consisting of a core material like foam or balsa between fiberglass layers, offer enhanced stiffness and impact resistance, reducing maintenance frequency compared to traditional solid plastic hulls. Plastic hulls, typically made from polyethylene, are highly durable and resist corrosion but may require more frequent inspections for surface abrasion and UV degradation. Lifespan of sandwich structures generally exceeds that of plastic hulls by several years due to their superior structural integrity and resistance to delamination under marine conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sandwich structures, typically composed of a core material such as foam or balsa wood bonded between fiberglass or carbon fiber skins, offer improved strength-to-weight ratios, reducing fuel consumption and associated carbon emissions for boats. In contrast, traditional plastic hulls, often made from non-recyclable fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP), present significant environmental challenges due to their production processes and end-of-life disposal issues, including landfill accumulation and microplastic pollution. Sustainable alternatives in sandwich construction, like natural fiber cores and bio-based resins, enhance recyclability and reduce ecological footprints, making sandwich structures more favorable for eco-conscious boat manufacturing.
Suitable Applications for Each Material
Sandwich structures are ideal for high-performance boat hulls requiring lightweight strength, such as racing yachts and sailboats, due to their superior stiffness and impact resistance. Plastic hulls, commonly made from fiberglass-reinforced polymers, suit recreational and fishing boats where durability and lower cost are priorities. Sandwich construction excels in applications demanding enhanced thermal insulation and noise reduction, while plastics provide easier repairability and mass production efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Hull Structure
Sandwich structure boat hulls offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, improved impact resistance, and enhanced thermal insulation compared to traditional plastic hulls, making them ideal for high-performance and long-range vessels. Plastic hulls provide cost-effective manufacturing, excellent corrosion resistance, and ease of repair, suitable for smaller, recreational boats or budget-conscious buyers. Selecting the right hull structure depends on balancing performance requirements, budget constraints, durability needs, and maintenance expectations specific to the intended boating application.
Infographic: Sandwich structure vs Plastic for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com