Green composites, made from renewable natural fibers and biodegradable resins, offer superior environmental benefits and lower carbon footprints compared to basalt composites, which are derived from volcanic rock and provide exceptional mechanical strength and fire resistance. For construction panels, green composites prioritize sustainability and lightweight properties, while basalt composites excel in durability and thermal insulation.
Table of Comparison
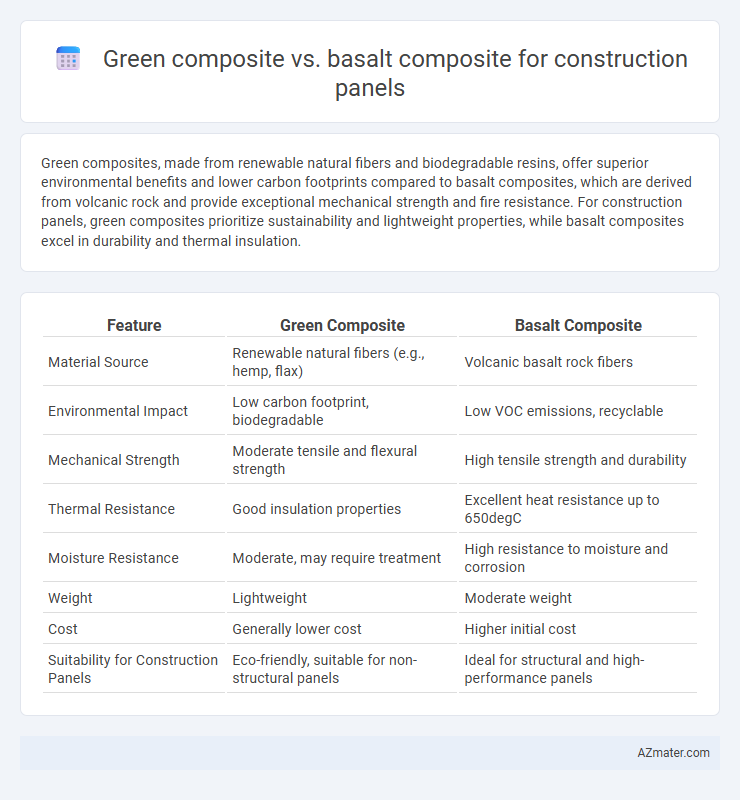
| Feature | Green Composite | Basalt Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable natural fibers (e.g., hemp, flax) | Volcanic basalt rock fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | Low VOC emissions, recyclable |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile and flexural strength | High tensile strength and durability |
| Thermal Resistance | Good insulation properties | Excellent heat resistance up to 650degC |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, may require treatment | High resistance to moisture and corrosion |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate weight |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher initial cost |
| Suitability for Construction Panels | Eco-friendly, suitable for non-structural panels | Ideal for structural and high-performance panels |
Introduction to Composite Materials in Construction
Composite materials in construction combine two or more distinct substances to achieve enhanced mechanical and thermal properties. Green composites utilize natural fibers like hemp or flax embedded in bio-based resins, offering sustainability and biodegradability with adequate strength for interior panels. Basalt composites incorporate fibers from volcanic rock, delivering superior fire resistance, durability, and mechanical performance, making them suitable for exterior and structural applications.
Overview of Green Composites
Green composites for construction panels combine natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute with bio-based or recyclable resins, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional materials. These composites provide enhanced biodegradability, lower carbon footprints, and improved thermal insulation compared to synthetic counterparts. Their growing application in building facades and interior panels supports eco-friendly construction practices while maintaining mechanical strength and durability.
Overview of Basalt Composites
Basalt composites, derived from natural volcanic rock, offer superior thermal resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent durability compared to traditional construction materials. Their eco-friendly profile and resistance to corrosion and fire make them ideal for sustainable construction panels. The cost-effective production process and enhanced mechanical properties position basalt composites as a competitive alternative to both green and conventional composites in structural applications.
Material Composition and Sourcing
Green composites typically combine natural fibers such as flax, hemp, or jute with bio-based or recycled polymer matrices, offering renewable sourcing and lower environmental impact. Basalt composites use fibers derived from volcanic basalt rock, providing high strength and thermal stability while relying on abundant, naturally occurring raw materials. Both materials emphasize sustainable sourcing, but green composites leverage agricultural byproducts, whereas basalt composites utilize mineral-based resources extracted through energy-efficient processes.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Green composites, typically reinforced with natural fibers such as hemp or flax, exhibit lower tensile strength and stiffness compared to basalt composites but offer superior biodegradability and reduced environmental impact. Basalt composites demonstrate higher mechanical properties with tensile strengths up to 2.8 GPa and excellent impact resistance, making them suitable for load-bearing construction panels requiring durability and fire resistance. The elastic modulus of basalt composites ranges between 80-100 GPa, significantly outperforming green composites, which generally have moduli around 20-40 GPa, highlighting their structural advantages in construction applications.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Green composites, typically made from natural fibers like jute or hemp combined with bio-based resins, exhibit significantly lower carbon footprints and biodegradability compared to basalt composites, which are derived from volcanic rock fibers requiring energy-intensive processing. Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) highlight that basalt composites offer enhanced durability and fire resistance but impose higher embodied energy and greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing. Sustainable construction panels increasingly favor green composites for their renewable material sources and reduced ecological toxicity, aligning with stringent environmental regulations and circular economy principles.
Durability and Lifecycle Performance
Green composites made from natural fibers like hemp or flax exhibit strong biodegradability but may face challenges in moisture resistance and UV stability, potentially affecting long-term durability. Basalt composites offer superior mechanical strength, excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, and enhanced thermal stability, contributing to a longer lifecycle and reduced maintenance costs in construction panels. Lifecycle performance analysis shows basalt composites generally outperform green composites in durability under harsh environmental conditions, promoting better structural integrity over time.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Green composites typically offer lower raw material costs due to the use of natural fibers like hemp or flax, reducing overall expenses compared to basalt composites, which rely on more energy-intensive basalt fiber production. Basalt composites, while often more expensive upfront, provide superior durability and fire resistance, potentially lowering long-term maintenance and replacement costs in construction panels. Economic considerations must balance initial investment against lifecycle savings, with green composites favored for budget-sensitive projects and basalt composites justified by performance-driven applications.
Application Suitability for Construction Panels
Green composites, typically made from natural fibers like hemp or flax combined with bio-based resins, offer excellent thermal insulation and environmental sustainability for construction panels, making them ideal for eco-friendly building projects. Basalt composites, derived from volcanic rock fibers, deliver superior mechanical strength, fire resistance, and durability, which suit high-load-bearing and fire-sensitive construction applications. Selection depends on the project's performance requirements, with green composites prioritized for sustainable, low-impact buildings and basalt composites favored for structurally demanding or high-safety environments.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Green composite construction panels, utilizing natural fibers like hemp or flax, promise enhanced environmental sustainability through reduced carbon footprints and biodegradability, aligning with increasing regulatory demands for eco-friendly materials. Basalt composite panels, derived from volcanic rock, offer superior fire resistance, durability, and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-performance building envelopes in future urban developments. Innovations in hybrid composites combining basalt fibers with bio-based resins are advancing, aiming to optimize strength-to-weight ratios while minimizing environmental impact, indicating significant growth potential in sustainable construction markets.
Infographic: Green composite vs Basalt composite for Construction panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com