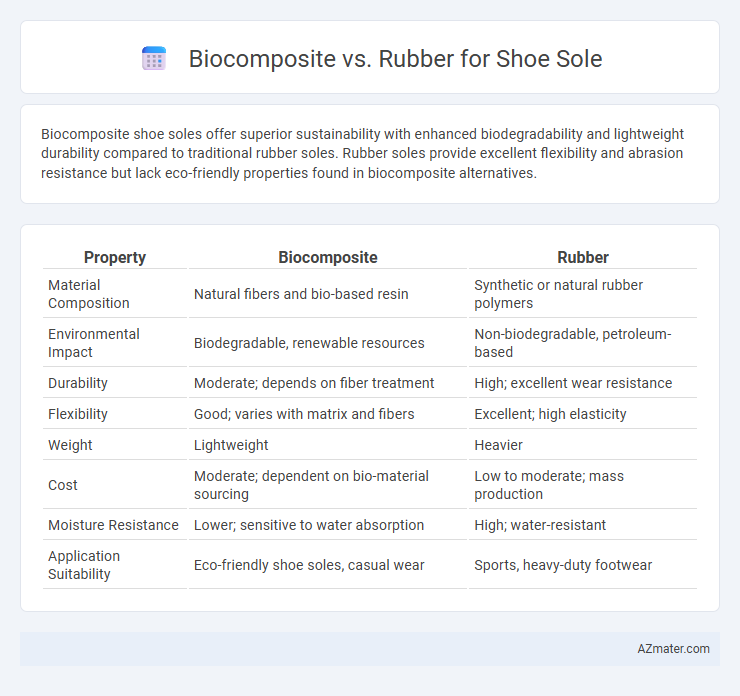
Biocomposite shoe soles offer superior sustainability with enhanced biodegradability and lightweight durability compared to traditional rubber soles. Rubber soles provide excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance but lack eco-friendly properties found in biocomposite alternatives.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biocomposite | Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers and bio-based resin | Synthetic or natural rubber polymers |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable resources | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Durability | Moderate; depends on fiber treatment | High; excellent wear resistance |
| Flexibility | Good; varies with matrix and fibers | Excellent; high elasticity |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Cost | Moderate; dependent on bio-material sourcing | Low to moderate; mass production |
| Moisture Resistance | Lower; sensitive to water absorption | High; water-resistant |
| Application Suitability | Eco-friendly shoe soles, casual wear | Sports, heavy-duty footwear |
Introduction to Shoe Sole Materials
Shoe sole materials significantly impact durability, comfort, and environmental footprint, with biocomposites and rubber being prominent options. Biocomposites combine natural fibers like hemp or flax with polymers, offering lightweight and biodegradable advantages. Rubber, traditionally sourced from natural or synthetic origins, provides excellent flexibility, abrasion resistance, and shock absorption for various footwear applications.
What Are Biocomposites?
Biocomposites are innovative materials composed of natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute combined with bio-based or synthetic polymers, offering enhanced sustainability and biodegradability compared to traditional rubber. These materials provide comparable durability, flexibility, and shock absorption qualities essential for shoe soles while significantly reducing environmental impact through renewable resources and lower carbon footprints. The use of biocomposites in footwear manufacturing aligns with growing demand for eco-friendly alternatives without compromising performance and comfort.
Understanding Traditional Rubber Soles
Traditional rubber soles, typically made from natural or synthetic rubber, offer excellent durability, flexibility, and slip resistance, making them a popular choice for footwear. Natural rubber sourced from latex sap provides superior elasticity and wear resistance, while synthetic variants, like styrene-butadiene rubber, enhance performance under diverse environmental conditions. The manufacturing process of rubber soles involves vulcanization, which improves strength and elasticity, but environmental concerns over non-biodegradability have prompted exploration of sustainable alternatives such as biocomposites.
Environmental Impact: Biocomposite vs Rubber
Biocomposite shoe soles significantly reduce environmental impact by utilizing renewable natural fibers and biodegradable polymers, lowering carbon emissions and waste in comparison to traditional rubber soles, which often derive from non-renewable petroleum resources. Rubber production, especially synthetic variants, contributes to deforestation, habitat loss, and chemical pollution, whereas biocomposites promote sustainable sourcing and easier end-of-life composting or recycling. Life cycle assessments reveal biocomposites offer superior eco-efficiency, supporting circular economy principles and reducing ecological footprints in footwear manufacturing.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Biocomposite shoe soles, composed of natural fibers and biodegradable polymers, offer enhanced environmental sustainability alongside competitive durability. Rubber soles provide superior abrasion resistance and flexibility, making them ideal for high-impact activities and prolonged wear. Performance-wise, rubber excels in traction and shock absorption, whereas biocomposites are improving rapidly to balance strength with eco-friendly properties.
Comfort and Flexibility Factors
Biocomposite shoe soles offer enhanced breathability and improved cushioning due to natural fiber reinforcements and biodegradable polymers, promoting superior comfort during extended wear. Rubber soles provide excellent flexibility and shock absorption, benefiting durability and dynamic movement but may retain heat and moisture, potentially reducing overall comfort. The choice between biocomposite and rubber depends on balancing eco-friendly materials with performance needs for optimal flexibility and wearer comfort.
Cost Analysis: Biocomposite vs Rubber Soles
Biocomposite shoe soles generally offer a cost advantage over traditional rubber soles due to lower raw material expenses and reduced reliance on petroleum-based components. Manufacturing processes for biocomposite soles often require less energy and can utilize agricultural byproducts, further decreasing overall production costs. Rubber soles, while durable, tend to incur higher costs related to material extraction, processing, and environmental compliance.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Biocomposite shoe soles utilize natural fibers combined with biodegradable polymers, requiring specialized compounding and injection molding processes that emphasize eco-friendly material sourcing and lower carbon emissions. Rubber soles depend on established vulcanization techniques involving synthetic or natural rubber, offering proven scalability with high-volume production capabilities and consistent durability. Manufacturing biocomposites faces challenges in uniform fiber dispersion and material variability, limiting mass adoption, whereas rubber's extensive industry infrastructure supports cost-effective large-scale manufacturing.
Innovations in Sustainable Footwear
Biocomposite materials for shoe soles offer significant sustainability advantages by incorporating renewable resources such as plant fibers and biodegradable polymers, reducing reliance on petroleum-based rubber. Recent innovations in biocomposite technology enhance durability, flexibility, and comfort, matching or surpassing traditional rubber performance while lowering environmental impact through biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint. These advancements position biocomposites as a forward-thinking alternative in sustainable footwear design, supporting eco-conscious consumer demand and circular economy principles.
Future Trends in Shoe Sole Materials
Biocomposite materials are rapidly gaining traction over traditional rubber in shoe sole manufacturing due to their sustainability, biodegradability, and reduced environmental footprint. Innovations in biopolymer blends and natural fiber reinforcements are driving developments in lightweight, durable, and eco-friendly soles that meet performance standards. The future trend emphasizes circular economy principles, pushing brands to adopt biocomposites for enhanced recyclability and consumer demand for green products.
Infographic: Biocomposite vs Rubber for Shoe Sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com