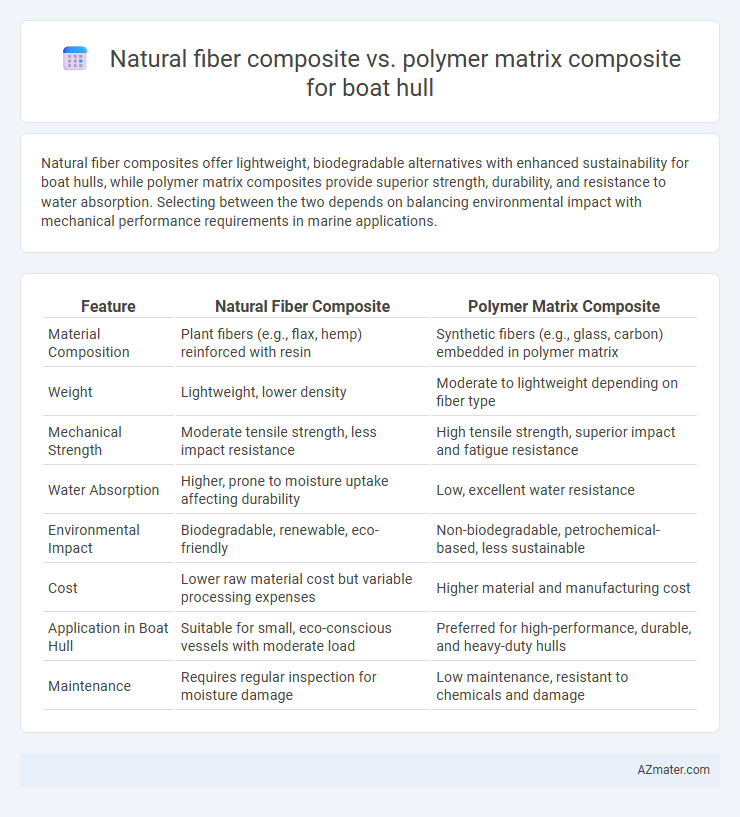
Natural fiber composites offer lightweight, biodegradable alternatives with enhanced sustainability for boat hulls, while polymer matrix composites provide superior strength, durability, and resistance to water absorption. Selecting between the two depends on balancing environmental impact with mechanical performance requirements in marine applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Natural Fiber Composite | Polymer Matrix Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plant fibers (e.g., flax, hemp) reinforced with resin | Synthetic fibers (e.g., glass, carbon) embedded in polymer matrix |
| Weight | Lightweight, lower density | Moderate to lightweight depending on fiber type |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength, less impact resistance | High tensile strength, superior impact and fatigue resistance |
| Water Absorption | Higher, prone to moisture uptake affecting durability | Low, excellent water resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable, eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, petrochemical-based, less sustainable |
| Cost | Lower raw material cost but variable processing expenses | Higher material and manufacturing cost |
| Application in Boat Hull | Suitable for small, eco-conscious vessels with moderate load | Preferred for high-performance, durable, and heavy-duty hulls |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspection for moisture damage | Low maintenance, resistant to chemicals and damage |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Boat hull materials significantly influence vessel performance, durability, and environmental impact. Natural fiber composites offer a sustainable alternative with benefits such as biodegradability, lower density, and reduced environmental footprint compared to traditional polymer matrix composites, which provide superior strength, chemical resistance, and long-term durability. Selecting between natural fiber composites and polymer matrix composites depends on factors like mechanical requirements, cost constraints, and ecological considerations in marine applications.
Overview of Natural Fiber Composites
Natural fiber composites for boat hulls utilize fibers like hemp, flax, and jute embedded in a polymer matrix, offering advantages such as biodegradability, reduced weight, and lower environmental impact compared to traditional composites. These composites exhibit good specific strength and stiffness, making them suitable for marine applications where sustainability and lightweight construction are critical. Challenges include moisture absorption and lower durability compared to synthetic fiber composites, which are mitigated through advanced treatments and hybridization techniques.
Understanding Polymer Matrix Composites
Polymer matrix composites (PMCs) for boat hulls combine a polymer resin matrix with reinforcing fibers such as glass or carbon, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance ideal for marine environments. The matrix binds the fibers, transferring loads and protecting them from environmental damage, while enhancing impact resistance and durability in harsh seawater conditions. Compared to natural fiber composites, PMCs exhibit better mechanical properties, water resistance, and long-term performance critical for structural integrity in boat hull applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Natural fiber composites exhibit lower tensile strength and stiffness compared to polymer matrix composites, which typically feature superior mechanical properties such as higher impact resistance and fatigue durability essential for boat hull applications. The density of natural fiber composites is significantly less, offering weight reduction benefits, but polymer matrix composites provide enhanced water resistance and dimensional stability under marine conditions. Mechanical performance variability in natural fiber composites arises from fiber type and treatment, whereas polymer matrix composites deliver consistent strength and longevity, making them preferable for structurally demanding hull designs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Natural fiber composites for boat hulls offer significant environmental benefits due to their biodegradability, renewable sourcing, and lower carbon footprint compared to traditional polymer matrix composites made from non-renewable petroleum-based resins. The life cycle analysis reveals that natural fiber composites reduce greenhouse gas emissions and waste generation during production and end-of-life disposal, enhancing sustainability in marine applications. Polymer matrix composites, while durable and strong, pose challenges in recycling and contribute to long-term environmental pollution through microplastic release and extended degradation periods.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Natural fiber composites offer a cost-effective alternative to polymer matrix composites for boat hulls, primarily due to lower raw material prices and reduced energy consumption during production. The affordability of natural fibers such as flax, hemp, or jute significantly reduces overall manufacturing expenses compared to synthetic fibers like fiberglass or carbon fiber embedded in polymer matrices. Despite slightly lower mechanical properties, natural fiber composites provide a competitive balance of cost savings and adequate performance, making them economically attractive for budget-conscious boat manufacturing.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Natural fiber composites for boat hulls offer enhanced biodegradability and reduced environmental impact but generally exhibit lower durability compared to polymer matrix composites, which provide superior resistance to water absorption, UV radiation, and mechanical stress. Polymer matrix composites require less frequent maintenance due to their higher corrosion resistance and structural integrity under harsh marine conditions. Maintaining natural fiber composites often involves protective coatings and more regular inspections to prevent deterioration from moisture and microbial attack.
Weight Considerations in Hull Design
Natural fiber composites offer significant weight reduction in boat hull design due to their lower density compared to traditional polymer matrix composites, improving fuel efficiency and maneuverability. The inherent lightweight nature of fibers like flax, hemp, and jute reduces overall hull mass without compromising structural integrity. However, polymer matrix composites often provide superior strength-to-weight ratios, making them preferable when higher load-bearing capacity is critical.
Performance in Marine Environments
Natural fiber composites, composed of fibers like flax or jute embedded in bio-resins, offer enhanced biodegradability and reduced environmental impact for boat hulls but typically exhibit lower mechanical strength and moisture resistance compared to polymer matrix composites. Polymer matrix composites, often based on epoxy or polyester resins combined with glass or carbon fibers, provide superior durability, hydrolytic stability, and resistance to saltwater degradation, ensuring longer service life and better structural integrity in marine environments. Performance in marine conditions heavily favors polymer matrix composites due to their enhanced resistance to corrosion, UV exposure, and osmotic blistering, critical for maintaining hull reliability and safety.
Future Trends in Boat Hull Composite Materials
Natural fiber composites are gaining traction in boat hull construction due to their sustainability, biodegradability, and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional polymer matrix composites. Advances in hybrid composites combining natural fibers with polymer matrices enhance mechanical properties and durability while maintaining eco-friendliness. Future trends emphasize the development of high-performance, bio-based resins and innovative fiber treatments to increase water resistance and longevity for marine applications.
Infographic: Natural fiber composite vs Polymer matrix composite for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com