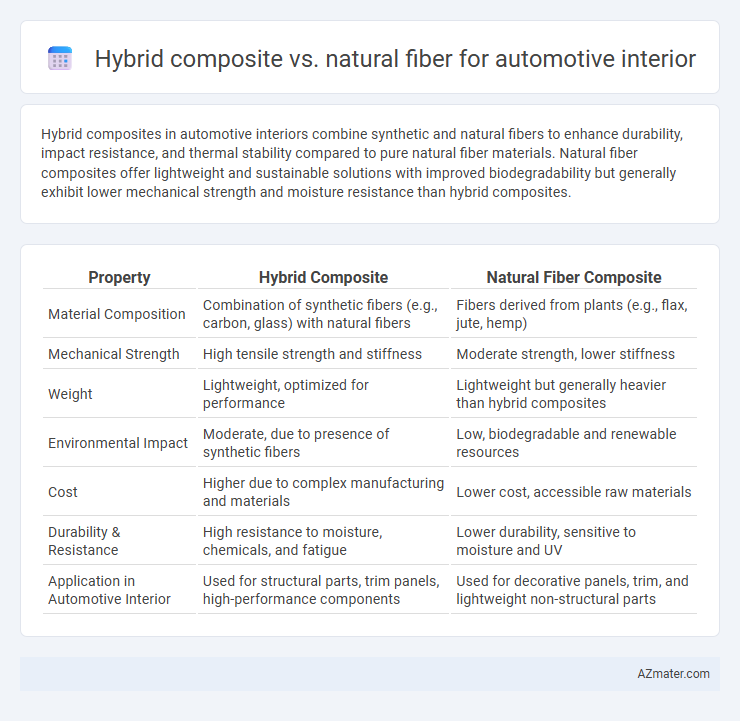
Hybrid composites in automotive interiors combine synthetic and natural fibers to enhance durability, impact resistance, and thermal stability compared to pure natural fiber materials. Natural fiber composites offer lightweight and sustainable solutions with improved biodegradability but generally exhibit lower mechanical strength and moisture resistance than hybrid composites.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hybrid Composite | Natural Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Combination of synthetic fibers (e.g., carbon, glass) with natural fibers | Fibers derived from plants (e.g., flax, jute, hemp) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and stiffness | Moderate strength, lower stiffness |
| Weight | Lightweight, optimized for performance | Lightweight but generally heavier than hybrid composites |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate, due to presence of synthetic fibers | Low, biodegradable and renewable resources |
| Cost | Higher due to complex manufacturing and materials | Lower cost, accessible raw materials |
| Durability & Resistance | High resistance to moisture, chemicals, and fatigue | Lower durability, sensitive to moisture and UV |
| Application in Automotive Interior | Used for structural parts, trim panels, high-performance components | Used for decorative panels, trim, and lightweight non-structural parts |
Introduction to Automotive Interior Materials
Automotive interior materials are evolving towards lightweight, durable, and sustainable solutions, with hybrid composites and natural fibers emerging as key contenders. Hybrid composites combine synthetic fibers like carbon or glass with natural fibers such as flax or hemp, offering enhanced mechanical properties and weight reduction crucial for fuel efficiency. Natural fibers alone provide biodegradability and low cost but often lack the strength and durability required for demanding automotive interior applications compared to hybrid composites.
What are Hybrid Composites?
Hybrid composites in automotive interiors combine natural fibers such as flax, hemp, or jute with synthetic fibers like glass or carbon to enhance mechanical performance and durability. These materials offer improved strength-to-weight ratios, better impact resistance, and thermal stability compared to purely natural fiber composites. The synergy between natural and synthetic components in hybrid composites enables lightweight, eco-friendly, and cost-effective solutions ideal for reducing vehicle emissions and improving fuel efficiency.
Overview of Natural Fiber Composites
Natural fiber composites for automotive interiors offer lightweight, renewable alternatives to traditional materials, improving fuel efficiency and reducing environmental impact. These composites typically combine fibers like flax, hemp, or jute with polymer matrices, providing excellent vibration damping and thermal insulation properties. Their biodegradability and cost-effectiveness make them increasingly popular for door panels, dashboards, and trim components in eco-conscious vehicle manufacturing.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Hybrid composites used in automotive interiors offer superior mechanical properties such as enhanced tensile strength, impact resistance, and stiffness compared to natural fiber composites. Natural fibers like hemp, flax, and jute provide lightweight and environmentally friendly options but typically exhibit lower durability and mechanical stability under stress conditions. The combination of synthetic fibers with natural fibers in hybrid composites achieves an optimized balance of strength, flexibility, and weight, making them preferable for high-performance automotive interior applications.
Weight and Fuel Efficiency Implications
Hybrid composites combining synthetic fibers with natural fibers offer improved strength-to-weight ratios compared to purely natural fiber materials, reducing overall vehicle weight and enhancing fuel efficiency. Natural fiber composites are lighter than traditional materials like glass fiber composites, but hybrids optimize mechanical properties without significantly increasing weight, supporting better energy consumption. Weight reduction through hybrid composites directly contributes to lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions, aligning with automotive industry goals for sustainability and performance.
Thermal and Acoustic Performance
Hybrid composites exhibit superior thermal insulation and acoustic dampening properties compared to natural fibers, making them ideal for automotive interior applications where temperature regulation and noise reduction are critical. Natural fibers, while eco-friendly and lightweight, typically have lower thermal resistance and sound absorption coefficients, which can limit their effectiveness in high-performance automotive environments. Optimizing the blend of synthetic and natural fibers within hybrid composites can enhance overall thermal conductivity and acoustic attenuation, improving passenger comfort and vehicle efficiency.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hybrid composites in automotive interiors combine synthetic fibers with natural fibers to enhance durability while reducing environmental impact compared to purely synthetic materials. Natural fiber composites, derived from renewable resources like flax, hemp, and jute, offer superior biodegradability and lower carbon footprints, contributing significantly to sustainability goals. The integration of natural fibers in hybrid composites optimizes resource efficiency, lowers emissions during manufacturing, and promotes recyclability, aligning with automotive industry trends toward eco-friendly materials.
Cost Analysis: Hybrid vs. Natural Fiber
Hybrid composites often present higher initial costs due to complex manufacturing processes and the use of synthetic fibers combined with natural materials. Natural fibers typically offer cost advantages as they are renewable, lightweight, and require less energy-intensive processing, which reduces raw material expenses and overall production costs. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, including durability and maintenance, is crucial for determining the most economical choice for automotive interior applications.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Hybrid composites offer enhanced strength and durability for automotive interiors but require complex processing techniques such as controlled curing cycles and precise fiber alignment. Natural fibers provide lightweight, sustainable options with easier manufacturing through conventional molding and lower energy consumption but may face challenges in moisture absorption and variability in quality. Balancing the processing demands and performance characteristics is crucial for optimizing cost-efficiency and material longevity in automotive interior applications.
Future Trends in Automotive Interior Materials
Hybrid composite materials, combining synthetic fibers with natural fibers like hemp or flax, are gaining traction in automotive interiors due to their enhanced strength-to-weight ratio and improved sustainability profile. Future trends emphasize the integration of bio-based resins and advanced manufacturing techniques such as resin transfer molding to optimize durability and reduce carbon footprint. Rising consumer demand for eco-friendly vehicles drives innovation in hybrid composites, positioning them as a key material for next-generation automotive interior designs.
Infographic: Hybrid composite vs Natural fiber for Automotive interior
 azmater.com
azmater.com