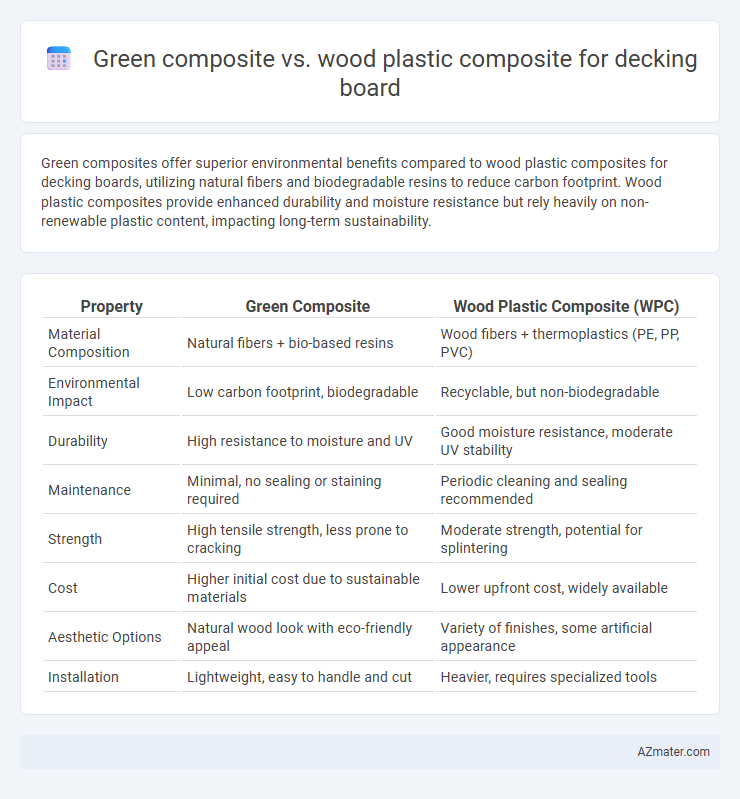
Green composites offer superior environmental benefits compared to wood plastic composites for decking boards, utilizing natural fibers and biodegradable resins to reduce carbon footprint. Wood plastic composites provide enhanced durability and moisture resistance but rely heavily on non-renewable plastic content, impacting long-term sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Green Composite | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers + bio-based resins | Wood fibers + thermoplastics (PE, PP, PVC) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | Recyclable, but non-biodegradable |
| Durability | High resistance to moisture and UV | Good moisture resistance, moderate UV stability |
| Maintenance | Minimal, no sealing or staining required | Periodic cleaning and sealing recommended |
| Strength | High tensile strength, less prone to cracking | Moderate strength, potential for splintering |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to sustainable materials | Lower upfront cost, widely available |
| Aesthetic Options | Natural wood look with eco-friendly appeal | Variety of finishes, some artificial appearance |
| Installation | Lightweight, easy to handle and cut | Heavier, requires specialized tools |
Introduction to Decking Materials
Green composites for decking boards often utilize natural fibers combined with biodegradable resins, offering enhanced environmental benefits and superior biodegradability compared to traditional materials. Wood plastic composites (WPCs) blend wood fibers with plastic polymers, providing durability, resistance to moisture, and low maintenance requirements ideal for outdoor applications. Both materials serve as sustainable alternatives to pure wood, with green composites emphasizing eco-friendliness and WPCs focusing on longevity and structural integrity.
What Are Green Composites?
Green composites are eco-friendly materials made from natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute combined with biodegradable or recyclable resins, offering sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional composites. In decking boards, green composites provide superior biodegradability and lower carbon footprint while maintaining strength and durability similar to wood plastic composites (WPCs). Unlike WPCs, which blend wood fibers with plastic resins, green composites minimize plastic use, enhancing their appeal for environmentally conscious outdoor decking projects.
Overview of Wood Plastic Composites (WPC)
Wood Plastic Composites (WPC) are engineered materials combining wood fibers and thermoplastic polymers, offering enhanced durability and low maintenance for decking applications. WPCs exhibit superior resistance to moisture, rot, and insect damage compared to traditional wood, making them ideal for outdoor environments. Their versatility allows for various finishes and textures, providing aesthetic appeal while reducing environmental impact through the use of recycled materials.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green composites, made from natural fibers combined with biodegradable resins, typically offer superior environmental benefits over wood plastic composites (WPC) by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and enhancing biodegradability. WPCs, composed mainly of recycled plastics and wood fibers, provide durability and resistance but often face challenges in end-of-life disposal due to non-biodegradable plastic content. Lifecycle assessments show green composites have lower carbon emissions and a smaller ecological footprint, promoting sustainable decking solutions with reduced environmental impact.
Material Composition and Sources
Green composites typically combine natural fibers like jute, hemp, or flax with bio-based resins, offering enhanced biodegradability and lower environmental impact compared to traditional materials. Wood plastic composites (WPC) consist of wood fibers or flour blended with thermoplastics such as polyethylene or polypropylene, usually sourced from recycled plastics and wood byproducts, providing durability and resistance to moisture. The material composition of green composites is largely renewable and compostable, while WPC relies on a hybrid of organic and synthetic components, influencing the sustainability and lifecycle of decking boards.
Durability and Lifecycle Performance
Green composite decking offers superior durability compared to traditional wood plastic composites (WPC) due to its enhanced resistance to moisture, UV exposure, and microbial decay, extending its lifecycle significantly. While wood plastic composites may suffer from surface scratching and fading over time, green composites maintain structural integrity and aesthetic appeal for 25-30 years with minimal maintenance. Lifecycle assessments indicate green composite decking reduces environmental impact through sustainable materials and longer service life, making it a more resilient and eco-friendly option for outdoor applications.
Maintenance Requirements
Green composite decking boards require minimal maintenance, typically needing only regular cleaning with water and mild soap to prevent mold and mildew growth. Wood plastic composites (WPC) benefit from their resistance to rot and insect damage, but occasional cleaning and treatment with UV protectants help maintain their appearance and durability over time. Both materials outperform traditional wood in maintenance demands, significantly reducing the need for sealing, staining, or sanding.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Green composite decking boards offer a natural wood-like appearance with enhanced color retention and resistance to fading, providing consistent aesthetic appeal over time. Wood plastic composite (WPC) decking tends to have a more uniform texture and color but may lack the realistic grain patterns found in green composites. Both materials support diverse design options, yet green composite decking allows for more sophisticated finishes and customizations, appealing to homeowners seeking premium visual impact.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Green composite decking boards typically have a higher upfront cost compared to wood plastic composite (WPC) due to their eco-friendly materials and advanced manufacturing processes. Over the long term, green composites offer better durability, resistance to weathering, and lower maintenance expenses, which can result in greater value for homeowners and contractors. WPC decking often requires more frequent repairs or replacements, increasing overall lifecycle costs despite its initial affordability.
Choosing the Right Composite for Your Deck
Green composite decking boards, made from recycled and sustainable materials, offer superior environmental benefits and resistance to moisture compared to traditional wood plastic composites (WPC), which blend wood fibers and plastic for durability and low maintenance. When choosing the right composite for your deck, consider factors such as weather resistance, lifespan, maintenance requirements, and environmental impact; green composites typically excel in biodegradability and eco-friendliness, while WPCs provide better structural strength and color retention. Evaluating local climate conditions and budget constraints will help determine whether the eco-conscious green composite or the robust wood plastic composite best suits your decking needs.
Infographic: Green composite vs Wood plastic composite for Decking board
 azmater.com
azmater.com