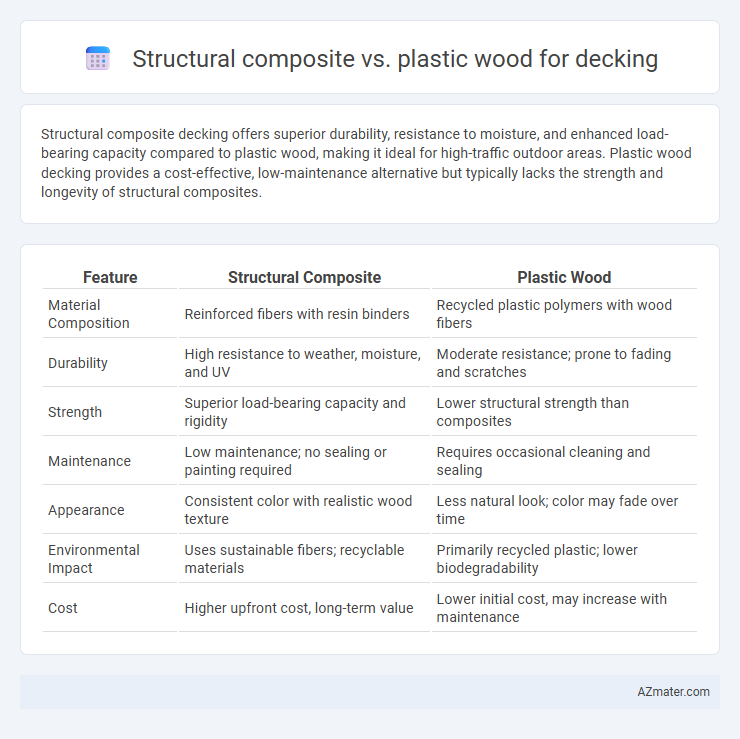
Structural composite decking offers superior durability, resistance to moisture, and enhanced load-bearing capacity compared to plastic wood, making it ideal for high-traffic outdoor areas. Plastic wood decking provides a cost-effective, low-maintenance alternative but typically lacks the strength and longevity of structural composites.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Structural Composite | Plastic Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Reinforced fibers with resin binders | Recycled plastic polymers with wood fibers |
| Durability | High resistance to weather, moisture, and UV | Moderate resistance; prone to fading and scratches |
| Strength | Superior load-bearing capacity and rigidity | Lower structural strength than composites |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; no sealing or painting required | Requires occasional cleaning and sealing |
| Appearance | Consistent color with realistic wood texture | Less natural look; color may fade over time |
| Environmental Impact | Uses sustainable fibers; recyclable materials | Primarily recycled plastic; lower biodegradability |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost, long-term value | Lower initial cost, may increase with maintenance |
Understanding Structural Composite Decking
Structural composite decking is engineered from a blend of wood fibers and polymer resins, offering enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to moisture compared to traditional plastic wood decking. Unlike plastic wood, which primarily uses recycled plastics, structural composite decking provides superior load-bearing capacity and reduced expansion or contraction under weather changes. This material is ideal for decking applications requiring long-term performance, minimal maintenance, and a natural wood appearance combined with advanced composite technology.
What is Plastic Wood Decking?
Plastic wood decking is a type of decking material made primarily from recycled plastics, offering high resistance to moisture, rot, and insect damage. Unlike structural composite decking, which blends wood fibers and plastic resins for enhanced strength and a wood-like appearance, plastic wood decking is typically 100% plastic, providing lower maintenance and longer durability. This material is ideal for environments prone to humidity and requires minimal sealing or staining compared to traditional wood or composite options.
Material Composition: Structural Composite vs Plastic Wood
Structural composite decking consists of a blend of wood fibers and thermoplastics, creating a material that combines the strength and natural appearance of wood with enhanced durability and resistance to moisture, rot, and insects. Plastic wood decking, made entirely from recycled or virgin plastic resins, offers superior water resistance and low maintenance but lacks the wood grain texture and rigidity provided by wood fibers in composites. The integration of wood fibers in structural composites contributes to greater structural integrity and a more authentic aesthetic compared to the uniform, synthetic surface of plastic wood.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Structural composite decking offers superior durability compared to plastic wood, featuring enhanced resistance to moisture, rot, and insect damage, making it ideal for long-term outdoor use. Plastic wood decking, while resistant to termites and water, tends to degrade faster under intense UV exposure and may warp or crack over time. The lifespan of structural composite decking typically ranges from 25 to 30 years, significantly outlasting plastic wood decking, which generally lasts around 10 to 15 years depending on environmental conditions.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Material
Structural composite decking requires minimal maintenance, needing only occasional cleaning with soap and water to prevent mold and dirt buildup, and it resists fading, staining, and insect damage. Plastic wood decking demands similar low maintenance, as it does not rot, splinter, or attract termites, but periodic cleaning is necessary to avoid surface mold and grime accumulation. Both materials outperform traditional wood by eliminating the need for regular sealing, staining, or painting, making them durable and hassle-free options for long-term decking use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Structural composite decking, made from wood fibers and recycled plastics, offers enhanced durability and reduces reliance on virgin timber, promoting sustainable resource use and decreasing landfill waste. Plastic wood decking, primarily composed of recycled polyethylene, contributes significantly to plastic waste reduction but may have a larger carbon footprint due to petroleum-based components. When evaluating environmental impact, structural composites generally balance resource efficiency and recyclability better, supporting long-term sustainability in decking applications.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Structural composite decking generally has a higher upfront cost compared to plastic wood due to its enhanced durability and structural integrity. Long-term expenses for structural composite decking tend to be lower as it requires minimal maintenance, resists rot, and offers greater longevity, reducing replacement and repair costs over time. Plastic wood may have a lower initial price but often incurs higher maintenance costs and shorter lifespan, impacting overall cost-effectiveness in deck installation.
Aesthetic Differences and Design Options
Structural composite decking offers a sleek, uniform appearance with a wide range of color and texture options that mimic natural wood grain, providing a modern and polished look for outdoor spaces. Plastic wood decking, often made from recycled materials, typically has a more uniform color but can lack the nuanced texture and rich aesthetic variety found in composite materials. Design flexibility is greater with structural composites due to their ability to be molded into intricate patterns and shapes, allowing for customized decking layouts and decorative elements.
Slip Resistance and Safety Factors
Structural composites offer superior slip resistance due to their textured surfaces and embedded anti-slip additives, enhancing safety on wet or icy decking. Plastic wood, while lower in maintenance, can become slippery when wet unless treated with slip-resistant coatings, posing potential safety hazards. Choosing structural composite decking improves overall stability and reduces accident risks compared to untreated plastic wood options.
Choosing the Right Decking Material for Your Needs
Structural composite decking offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for high-traffic or load-bearing applications. Plastic wood decking provides excellent weather resistance and low maintenance, suitable for environments prone to moisture and insects. Assess load requirements, environmental conditions, maintenance preferences, and budget to select the most appropriate decking material for long-term performance and aesthetic appeal.
Infographic: Structural composite vs Plastic wood for Decking
 azmater.com
azmater.com