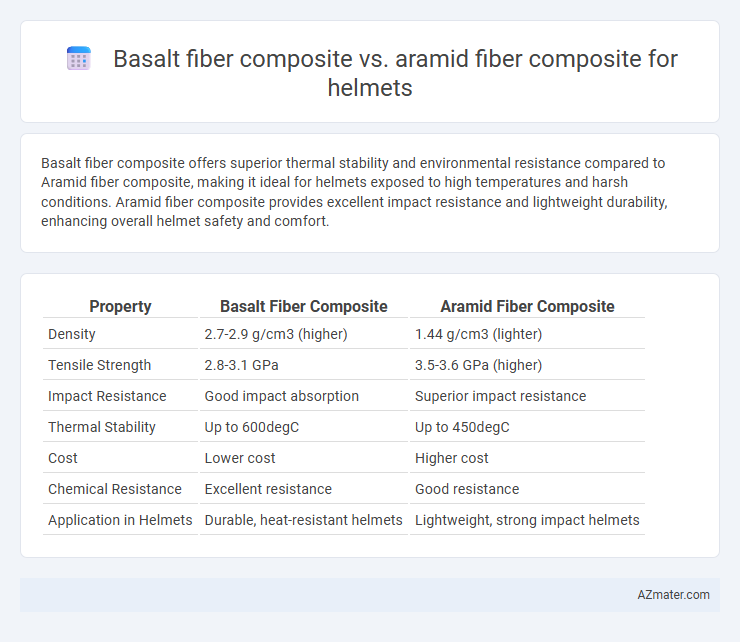
Basalt fiber composite offers superior thermal stability and environmental resistance compared to Aramid fiber composite, making it ideal for helmets exposed to high temperatures and harsh conditions. Aramid fiber composite provides excellent impact resistance and lightweight durability, enhancing overall helmet safety and comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Basalt Fiber Composite | Aramid Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2.7-2.9 g/cm3 (higher) | 1.44 g/cm3 (lighter) |
| Tensile Strength | 2.8-3.1 GPa | 3.5-3.6 GPa (higher) |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact absorption | Superior impact resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 600degC | Up to 450degC |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance | Good resistance |
| Application in Helmets | Durable, heat-resistant helmets | Lightweight, strong impact helmets |
Introduction to Helmet Composite Materials
Basalt fiber composite offers superior thermal stability and environmental resistance compared to aramid fiber composite, making it an excellent choice for helmet construction where heat and impact resistance are critical. Aramid fiber composites, such as Kevlar, deliver high tensile strength and exceptional energy absorption, enhancing ballistic and impact protection in helmets. Both materials provide lightweight alternatives to traditional composites, optimizing helmet performance through enhanced durability and wearer comfort.
Overview of Basalt Fiber Composites
Basalt fiber composites for helmets offer superior impact resistance and thermal stability due to their natural volcanic rock origin, providing enhanced durability compared to traditional fibers. These composites exhibit excellent vibration damping and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for protective gear subjected to harsh conditions. Their eco-friendly production process and cost-effectiveness also contribute to growing preference over aramid fiber composites in helmet manufacturing.
Overview of Aramid Fiber Composites
Aramid fiber composites, known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior impact resistance, are widely used in helmet manufacturing to enhance protection and durability. These composites exhibit excellent thermal stability and resistance to abrasion, making them ideal for high-performance safety gear. Compared to basalt fiber composites, aramid fibers offer better energy absorption and tensile strength, crucial for mitigating violent impacts during collisions.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Basalt fiber composites exhibit higher tensile strength and superior abrasion resistance compared to aramid fiber composites, enhancing helmet impact performance and longevity. Aramid fibers offer excellent energy absorption and are highly resistant to thermal degradation, contributing to improved durability under extreme conditions. The combination of basalt's stiffness and aramid's toughness results in helmets with optimized mechanical properties for strength and durability.
Weight and Comfort Comparison
Basalt fiber composite offers a lower density of approximately 2.7 g/cm3 compared to aramid fiber's density near 1.44 g/cm3, resulting in a heavier helmet with basalt but enhanced stiffness and impact resistance. Aramid fiber composites, such as Kevlar, provide superior comfort due to their flexibility and excellent energy absorption, making helmets lighter and more comfortable for extended wear. The choice between basalt and aramid fiber composites balances the trade-off between basalt's increased weight with structural rigidity and aramid's lighter weight with optimized comfort.
Impact Resistance and Energy Absorption
Basalt fiber composites exhibit superior impact resistance due to their high tensile strength and excellent vibration damping properties, making them ideal for helmet applications requiring enhanced safety. Aramid fiber composites, such as Kevlar, offer exceptional energy absorption and flexibility, effectively dissipating impact forces and preventing penetration. Both materials provide robust protection, but basalt fibers demonstrate better durability against repeated impacts, while aramid fibers excel in lightweight energy absorption performance.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Basalt fiber composites exhibit superior thermal resistance with a decomposition temperature exceeding 800degC, making them ideal for helmets subjected to extreme heat, while aramid fiber composites typically withstand temperatures up to 400degC before degradation. Chemically, basalt fibers demonstrate excellent resistance to alkalis, acids, and solvents, thereby enhancing helmet longevity in harsh environments, whereas aramid fibers are more susceptible to degradation from strong acids and ultraviolet exposure. The combined thermal stability and chemical inertness of basalt fiber composites provide enhanced protective performance for helmets in rigorous operational conditions.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturing Considerations
Basalt fiber composites offer a cost-effective alternative to aramid fiber composites in helmet manufacturing due to lower raw material costs and easier processing techniques, which reduce production expenses. Their superior thermal stability and chemical resistance simplify molding and curing, minimizing manufacturing complexities compared to aramid fibers that require more stringent handling conditions. While aramid composites excel in impact resistance, basalt fiber composites provide a balanced performance-cost ratio, making them attractive for economical helmet production without significant compromises in safety standards.
Environmental Sustainability and Recycling
Basalt fiber composites offer enhanced environmental sustainability due to their natural volcanic rock origin, reducing reliance on synthetic materials and promoting eco-friendly sourcing. They exhibit easier recycling processes compared to aramid fiber composites, as basalt fibers can be mechanically reclaimed and reused with less chemical degradation. Aramid fibers, derived from petrochemicals, present challenges in recycling and contribute to greater environmental impact through energy-intensive production and limited recyclability in helmet manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Composite for Helmets
Basalt fiber composites offer excellent impact resistance, thermal stability, and environmental sustainability, making them suitable for helmets requiring high durability and safety. Aramid fiber composites provide superior tensile strength and energy absorption, ideal for helmets that prioritize lightweight protection and ballistic resistance. Selecting the right composite depends on specific helmet performance criteria, balancing factors such as impact resistance, weight, cost, and environmental impact.
Infographic: Basalt fiber composite vs Aramid fiber composite for Helmet
 azmater.com
azmater.com