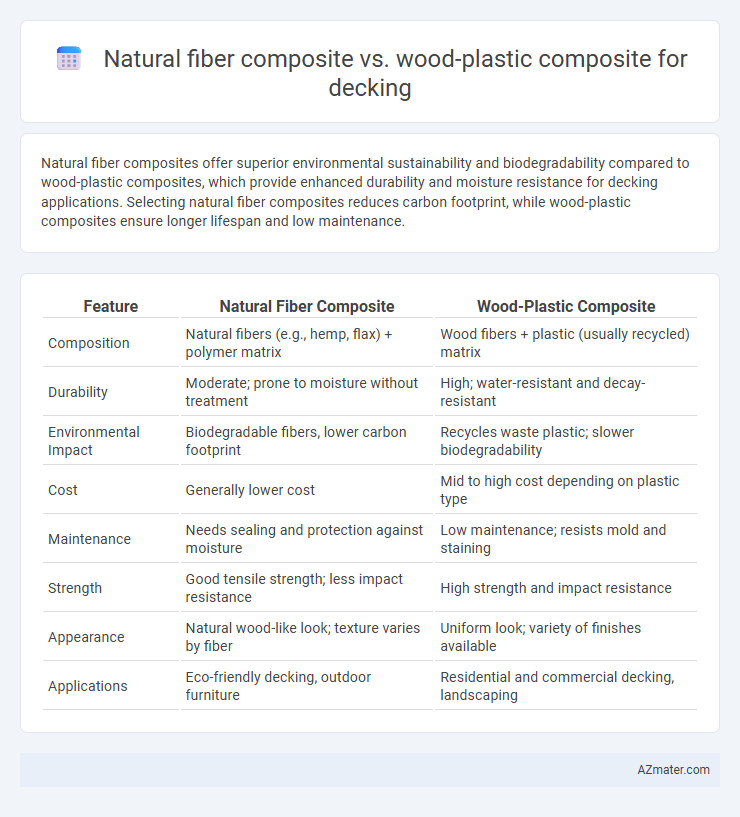
Natural fiber composites offer superior environmental sustainability and biodegradability compared to wood-plastic composites, which provide enhanced durability and moisture resistance for decking applications. Selecting natural fiber composites reduces carbon footprint, while wood-plastic composites ensure longer lifespan and low maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Natural Fiber Composite | Wood-Plastic Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Natural fibers (e.g., hemp, flax) + polymer matrix | Wood fibers + plastic (usually recycled) matrix |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to moisture without treatment | High; water-resistant and decay-resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable fibers, lower carbon footprint | Recycles waste plastic; slower biodegradability |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Mid to high cost depending on plastic type |
| Maintenance | Needs sealing and protection against moisture | Low maintenance; resists mold and staining |
| Strength | Good tensile strength; less impact resistance | High strength and impact resistance |
| Appearance | Natural wood-like look; texture varies by fiber | Uniform look; variety of finishes available |
| Applications | Eco-friendly decking, outdoor furniture | Residential and commercial decking, landscaping |
Introduction to Decking Material Options
Natural fiber composites, made from renewable resources like hemp, flax, or jute combined with polymers, offer superior biodegradability and lower environmental impact compared to traditional materials. Wood-plastic composites (WPCs) blend wood fibers with plastic resins, providing enhanced durability, resistance to moisture, and reduced maintenance requirements. Choosing between these decking materials depends on factors such as sustainability goals, budget, and desired performance characteristics.
What Are Natural Fiber Composites?
Natural fiber composites are materials made by reinforcing a polymer matrix with natural fibers such as hemp, flax, jute, or kenaf, offering high strength-to-weight ratios and biodegradability. These composites provide superior moisture resistance and thermal insulation compared to traditional wood-plastic composites, making them ideal for sustainable decking applications. The renewable nature of natural fibers contributes to lower carbon footprints and improved environmental performance in construction materials.
Understanding Wood-Plastic Composites
Wood-plastic composites (WPCs) combine thermoplastics with wood fibers or flour to create durable, low-maintenance decking materials resistant to rot, moisture, and insect damage. WPCs offer superior dimensional stability and weather resistance compared to natural fiber composites, making them ideal for outdoor applications. Their engineered structure allows customization in texture and color, providing aesthetic flexibility alongside long-term performance benefits.
Material Composition and Sustainability
Natural fiber composites for decking consist primarily of renewable fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute combined with bio-based or recyclable resins, offering enhanced biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint. Wood-plastic composites (WPC) integrate wood flour or fibers with thermoplastics like polyethylene or polypropylene, providing durability but typically relying on non-renewable plastics that may impact recyclability. Sustainability advantages of natural fiber composites include lower energy consumption during production and improved end-of-life compostability, whereas WPCs emphasize maintenance reduction and resource efficiency but face challenges in biodegradation and plastic waste management.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Natural fiber composites exhibit higher tensile strength and better resistance to impact compared to wood-plastic composites, making them suitable for heavy-load decking applications. Wood-plastic composites, however, provide superior moisture resistance and are less prone to fungal decay, enhancing long-term durability in wet environments. Both materials offer a balance of mechanical performance and environmental resilience, but natural fiber composites excel in structural strength while wood-plastic composites optimize weathering durability.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Natural fiber composites for decking offer superior biodegradability but tend to absorb moisture, leading to reduced weather resistance and shorter longevity compared to wood-plastic composites. Wood-plastic composites provide enhanced resistance to UV exposure, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, resulting in greater durability and extended lifespan in outdoor environments. The integration of synthetic polymers in wood-plastic composites improves dimensional stability and reduces maintenance requirements, making them more suitable for long-term decking applications.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Natural fiber composites offer superior aesthetic appeal for decking with their authentic wood-like texture and rich, organic color variations that enhance outdoor environments. They provide greater design flexibility due to their ability to be molded into intricate shapes and customized finishes, allowing for unique decking patterns and styles. Wood-plastic composites, while durable, typically have a more uniform appearance and limited customization options, often resulting in less visually dynamic decking surfaces.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Natural fiber composites offer easier installation due to their lighter weight and greater flexibility, allowing for quicker cutting and fitting without specialized tools. Maintenance involves regular cleaning to prevent mold and mildew buildup, but these composites generally resist staining and require no sealing or painting. Wood-plastic composites, being denser and heavier, may demand more effort during installation, including pre-drilling and specialized fasteners; they require periodic cleaning and occasional sealing to maintain their appearance and prevent surface cracking.
Environmental Impact and Eco-Friendliness
Natural fiber composites for decking use renewable materials like hemp or flax, offering superior biodegradability and lower carbon footprint compared to wood-plastic composites (WPCs), which combine wood fibers with non-biodegradable plastics. WPCs often rely on recycled plastics, reducing landfill waste, but their production involves higher energy consumption and potential microplastic release during degradation. Choosing natural fiber composites supports sustainable resource use and enhances deck recyclability, making them a more environmentally friendly option in outdoor construction.
Cost Comparison and Value for Money
Natural fiber composites typically offer a lower material cost compared to wood-plastic composites, making them a more budget-friendly option for decking projects. Wood-plastic composites provide enhanced durability and lower maintenance requirements, which can translate into better long-term value despite a higher upfront price. Evaluating cost per lifespan, wood-plastic composites often deliver superior return on investment due to their resistance to moisture, insects, and weathering.
Infographic: Natural fiber composite vs Wood-plastic composite for Decking
 azmater.com
azmater.com