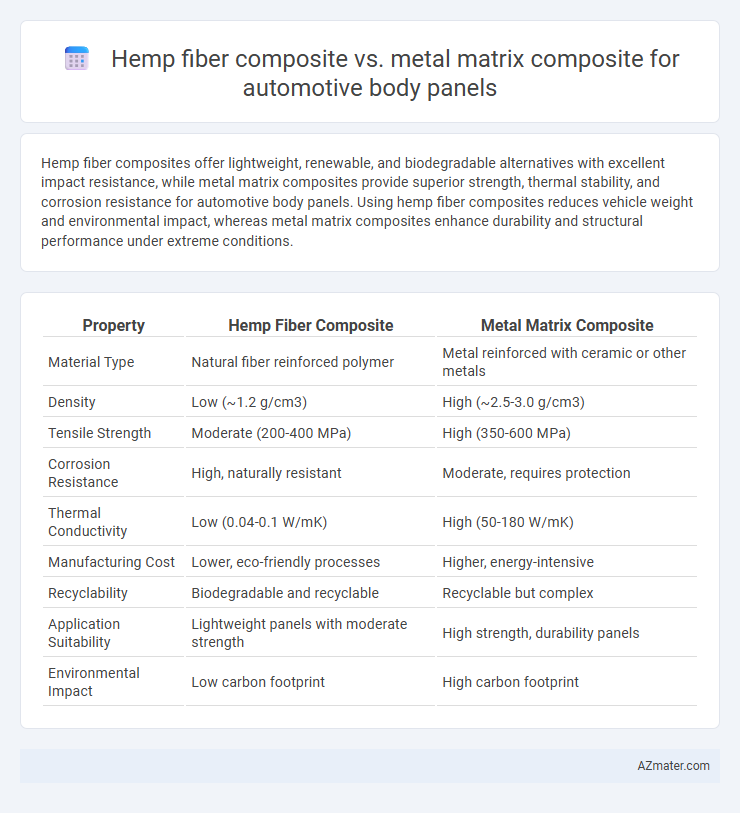
Hemp fiber composites offer lightweight, renewable, and biodegradable alternatives with excellent impact resistance, while metal matrix composites provide superior strength, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance for automotive body panels. Using hemp fiber composites reduces vehicle weight and environmental impact, whereas metal matrix composites enhance durability and structural performance under extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber Composite | Metal Matrix Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural fiber reinforced polymer | Metal reinforced with ceramic or other metals |
| Density | Low (~1.2 g/cm3) | High (~2.5-3.0 g/cm3) |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate (200-400 MPa) | High (350-600 MPa) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, naturally resistant | Moderate, requires protection |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.04-0.1 W/mK) | High (50-180 W/mK) |
| Manufacturing Cost | Lower, eco-friendly processes | Higher, energy-intensive |
| Recyclability | Biodegradable and recyclable | Recyclable but complex |
| Application Suitability | Lightweight panels with moderate strength | High strength, durability panels |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint | High carbon footprint |
Introduction to Automotive Body Panel Materials
Automotive body panels demand materials that balance strength, weight, and durability to enhance vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. Hemp fiber composites offer lightweight, renewable alternatives with excellent vibration damping and corrosion resistance compared to traditional metal matrix composites known for superior mechanical strength and heat resistance. Selecting between hemp fiber and metal matrix composites depends on prioritizing environmental impact, cost, and specific performance requirements in automotive design.
Overview of Hemp Fiber Composites
Hemp fiber composites are gaining traction in automotive body panels due to their lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, and eco-friendly properties compared to traditional metal matrix composites. These composites are primarily composed of natural hemp fibers embedded in polymer matrices, offering excellent vibration damping, thermal insulation, and biodegradability. Their lower carbon footprint and cost-effectiveness make hemp fiber composites a sustainable alternative, promoting reduced vehicle weight and improved fuel efficiency in automotive applications.
Overview of Metal Matrix Composites
Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs) for automotive body panels combine lightweight metal alloys, such as aluminum or magnesium, with reinforcing materials like ceramic particles or fibers to enhance strength, stiffness, and thermal resistance. MMCs offer superior mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability compared to traditional metals, enabling improved fuel efficiency and durability in automotive applications. Their higher production cost and complexity are balanced by performance benefits in high-stress environments and potential weight reductions.
Material Properties: Strength and Durability
Hemp fiber composites offer lightweight properties with moderate tensile strength ranging from 200 to 400 MPa, providing good impact resistance and enhanced vibration damping suitable for automotive body panels. Metal matrix composites (MMCs), typically composed of aluminum reinforced with ceramic particles, exhibit superior strength exceeding 500 MPa and exceptional durability under high-stress conditions, ensuring long-term structural integrity. While hemp fiber composites contribute to reduced vehicle weight and sustainability, MMCs deliver higher mechanical performance and resistance to wear, making them ideal for critical load-bearing automotive applications.
Weight Comparison: Lightweight Advantages
Hemp fiber composites offer significant lightweight advantages over metal matrix composites for automotive body panels, typically reducing weight by up to 40-50%, which enhances fuel efficiency and lowers emissions. The natural fibers in hemp composites contribute to a lower density while maintaining sufficient mechanical strength for structural applications. In contrast, metal matrix composites are generally heavier due to their metal content, making hemp-based composites a preferable choice for weight-sensitive automotive designs.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Hemp fiber composites offer significant environmental benefits over metal matrix composites in automotive body panels due to their renewable and biodegradable nature, reducing landfill waste and carbon emissions during production. The cultivation of hemp requires less energy and water compared to metal extraction and processing, leading to a smaller ecological footprint throughout the vehicle lifecycle. Metal matrix composites, while providing superior mechanical strength, involve energy-intensive mining and manufacturing processes, contributing to higher greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion.
Cost Analysis and Manufacturing Processes
Hemp fiber composites offer significant cost advantages over metal matrix composites (MMCs) due to lower raw material expenses and energy-efficient manufacturing processes such as compression molding and resin infusion, which require less specialized equipment and lower temperatures. In contrast, MMCs involve complex casting or powder metallurgy techniques with high energy consumption and costly alloying elements like aluminum or titanium, leading to increased production costs. Manufacturing hemp fiber composites also benefits from faster cycle times and reduced tooling wear, making them economically attractive for automotive body panels where weight reduction and sustainability are prioritized.
Impact Resistance and Crash Performance
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior impact resistance and energy absorption compared to traditional metal matrix composites, making them ideal for automotive body panels designed to enhance crash performance. The natural fibers in hemp composites provide improved toughness and reduced weight, contributing to better vehicle safety and fuel efficiency. Metal matrix composites, while strong and rigid, tend to be heavier and less effective at dissipating impact energy during collisions.
Corrosion, Aging, and Maintenance
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to metal matrix composites, which are prone to oxidation and require protective coatings to prevent rust. Hemp composites demonstrate enhanced aging properties due to their natural fiber structure, maintaining mechanical integrity over time without significant degradation. Maintenance costs for hemp fiber composites are lower, as they do not need frequent treatments or inspections typical for metal matrices exposed to corrosive environments.
Future Trends and Industry Adoption
Hemp fiber composites exhibit growing potential in automotive body panels due to their biodegradability, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness, contributing to reduced vehicle emissions and enhanced sustainability. Metal matrix composites continue to dominate high-performance applications offering superior strength, thermal stability, and wear resistance, particularly in electric vehicle manufacturing. Industry adoption trends indicate increasing integration of hemp fiber composites driven by regulatory pressure for eco-friendly materials, while metal matrix composites maintain a critical role in performance-intensive components, suggesting a complementary future in automotive design.
Infographic: Hemp fiber composite vs Metal matrix composite for Automotive body panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com