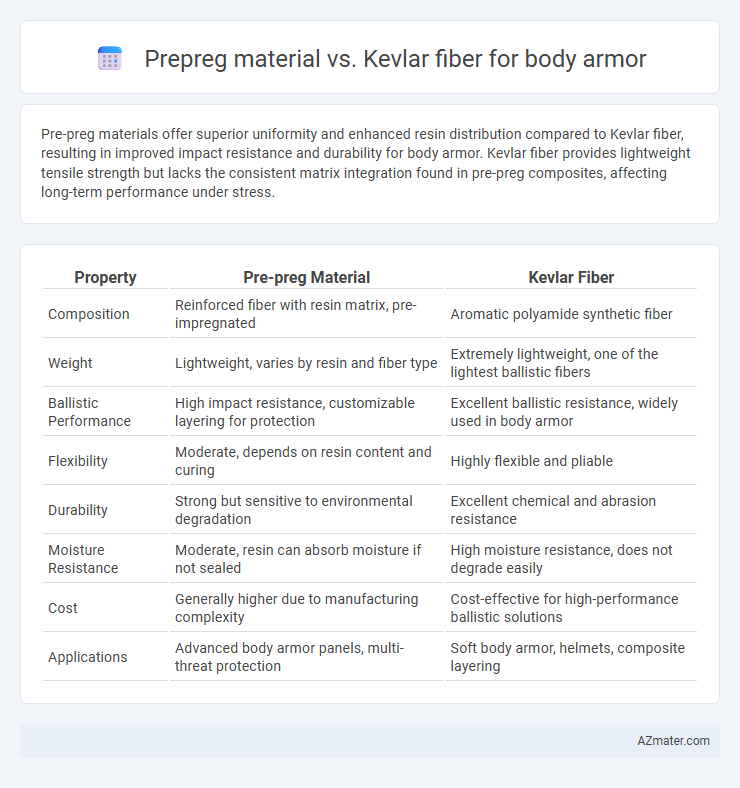
Pre-preg materials offer superior uniformity and enhanced resin distribution compared to Kevlar fiber, resulting in improved impact resistance and durability for body armor. Kevlar fiber provides lightweight tensile strength but lacks the consistent matrix integration found in pre-preg composites, affecting long-term performance under stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Pre-preg Material | Kevlar Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Reinforced fiber with resin matrix, pre-impregnated | Aromatic polyamide synthetic fiber |
| Weight | Lightweight, varies by resin and fiber type | Extremely lightweight, one of the lightest ballistic fibers |
| Ballistic Performance | High impact resistance, customizable layering for protection | Excellent ballistic resistance, widely used in body armor |
| Flexibility | Moderate, depends on resin content and curing | Highly flexible and pliable |
| Durability | Strong but sensitive to environmental degradation | Excellent chemical and abrasion resistance |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, resin can absorb moisture if not sealed | High moisture resistance, does not degrade easily |
| Cost | Generally higher due to manufacturing complexity | Cost-effective for high-performance ballistic solutions |
| Applications | Advanced body armor panels, multi-threat protection | Soft body armor, helmets, composite layering |
Introduction to Body Armor Materials
Pre-preg materials in body armor consist of fibers pre-impregnated with resin, offering enhanced control over fiber-resin ratios and improved consistency in ballistic protection. Kevlar fiber, a synthetic para-aramid, is renowned for its high tensile strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional energy absorption, making it a standard in flexible body armor shells. Comparing the two, pre-preg composites can provide superior structural integrity and durability, while Kevlar fibers deliver lightweight flexibility and proven ballistic resistance.
What is Pre-preg Material?
Pre-preg material is a fabric, typically carbon or aramid fibers, pre-impregnated with a resin system that remains partially cured to enable precise control during manufacturing. In body armor, pre-preg materials offer enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and superior impact resistance due to their uniform resin distribution and optimized fiber alignment. Compared to Kevlar fiber alone, pre-preg composites provide improved durability, consistent performance, and easier integration into multi-layer protective systems.
Understanding Kevlar Fiber
Kevlar fiber is a high-strength synthetic aramid known for its exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, making it a critical component in body armor manufacturing. Unlike pre-preg materials, which combine fibers with resins for enhanced rigidity and ease of fabrication, Kevlar fiber alone provides superior flexibility and impact absorption essential for ballistic protection. Understanding the molecular structure of Kevlar reveals its ability to disperse energy effectively, contributing significantly to the durability and protective qualities of body armor.
Key Properties of Pre-preg Material
Pre-preg material for body armor offers superior uniform resin distribution and enhanced fiber alignment compared to Kevlar fiber, resulting in increased strength-to-weight ratio and improved ballistic resistance. The pre-impregnated fibers provide consistent curing and reduced void content, leading to higher structural integrity and durability under impact. These properties make pre-preg composites highly effective for lightweight, high-performance protective gear.
Key Properties of Kevlar Fiber
Kevlar fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, high impact resistance, and excellent energy absorption, making it a preferred choice for body armor applications. Its lightweight nature combined with superior thermal stability enhances wearer mobility and comfort while providing robust protection against ballistic threats. Kevlar's inherent resistance to abrasion and chemical degradation ensures durability and long-term performance in various combat and law enforcement scenarios.
Comparative Ballistic Performance
Pre-preg materials exhibit superior ballistic performance compared to Kevlar fiber due to their enhanced resin distribution and fiber alignment, resulting in greater impact resistance and energy absorption. Kevlar fibers provide excellent tensile strength and lightweight protection but often require multiple layers to achieve comparable stopping power. Comparative testing shows pre-preg composites deliver higher ballistic limit velocities and improved multi-hit durability in body armor applications.
Weight and Comfort Comparison
Pre-preg materials used in body armor offer a lightweight advantage due to their pre-impregnated resin system that ensures uniform fiber distribution and reduced matrix weight, enhancing wearer comfort by minimizing bulk and stiffness. Kevlar fiber, while renowned for its high tensile strength and ballistic resistance, tends to be heavier and less flexible, potentially increasing fatigue during prolonged use. Evaluating body armor weight and comfort, pre-preg composites generally provide superior ergonomic performance compared to traditional Kevlar fiber assemblies.
Durability and Longevity
Pre-preg materials offer superior consistency and enhanced fiber-matrix bonding, resulting in increased durability and longer service life in body armor applications compared to Kevlar fibers alone. Kevlar fiber, while known for its high tensile strength and impact resistance, may degrade faster under environmental exposure without the protective resin encapsulation found in pre-preg composites. The advanced curing process of pre-preg materials ensures better structural integrity and resistance to wear, extending the armor's effective lifespan under repetitive stress conditions.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Pre-preg materials for body armor offer enhanced consistency and reduced manufacturing time but come at a higher material cost compared to Kevlar fiber, which is more economical and widely available. Manufacturing with pre-preg requires controlled curing processes and specialized equipment, increasing production complexity and initial investment. Kevlar fiber allows for flexible hand lay-up or automated weaving techniques, enabling cost-effective mass production suitable for large-scale body armor manufacturing.
Choosing the Best Material for Body Armor
Pre-preg materials offer enhanced consistency and superior bonding in body armor, providing improved ballistic protection and durability compared to standard Kevlar fibers. Kevlar fiber remains popular due to its lightweight, high tensile strength, and flexibility, which contribute to user comfort and mobility during prolonged wear. Selecting the best material depends on the specific threat level, weight constraints, and required flexibility for operational effectiveness.
Infographic: Pre-preg material vs Kevlar fiber for Body armor
 azmater.com
azmater.com