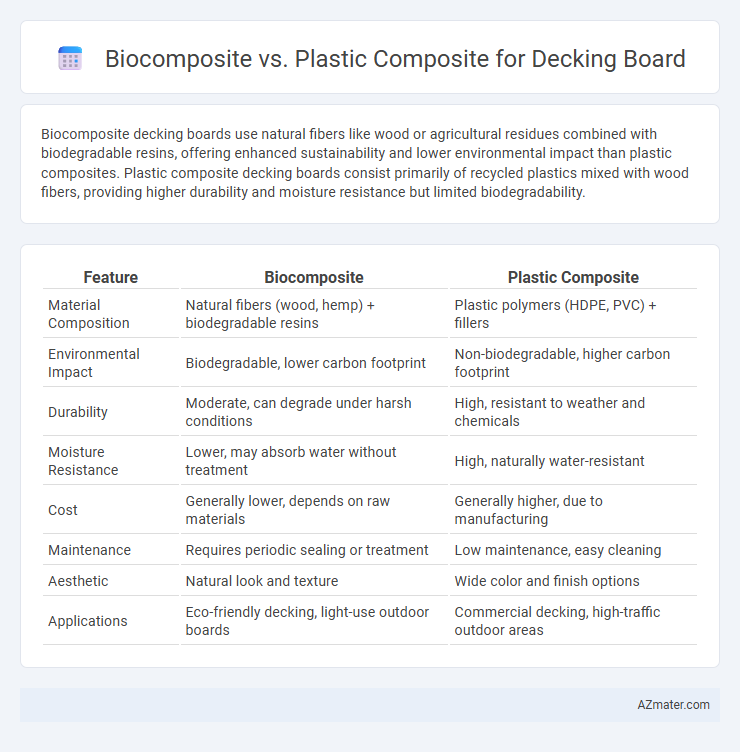
Biocomposite decking boards use natural fibers like wood or agricultural residues combined with biodegradable resins, offering enhanced sustainability and lower environmental impact than plastic composites. Plastic composite decking boards consist primarily of recycled plastics mixed with wood fibers, providing higher durability and moisture resistance but limited biodegradability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biocomposite | Plastic Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers (wood, hemp) + biodegradable resins | Plastic polymers (HDPE, PVC) + fillers |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Durability | Moderate, can degrade under harsh conditions | High, resistant to weather and chemicals |
| Moisture Resistance | Lower, may absorb water without treatment | High, naturally water-resistant |
| Cost | Generally lower, depends on raw materials | Generally higher, due to manufacturing |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic sealing or treatment | Low maintenance, easy cleaning |
| Aesthetic | Natural look and texture | Wide color and finish options |
| Applications | Eco-friendly decking, light-use outdoor boards | Commercial decking, high-traffic outdoor areas |
Introduction to Decking Materials
Decking materials primarily consist of natural wood, plastic composites, and biocomposites, each offering unique benefits for outdoor applications. Plastic composites combine wood fibers with synthetic resins, enhancing durability and resistance to moisture and insects compared to traditional wood. Biocomposites integrate natural fibers and bio-based polymers, providing an eco-friendly alternative with comparable strength and increased biodegradability for sustainable decking solutions.
What Are Biocomposites?
Biocomposites are materials made by combining natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or wood with biodegradable polymers or bio-based resins, creating an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic composites. These composites offer enhanced sustainability, reduced environmental impact, and improved biodegradability compared to conventional plastic composites used in decking boards. Their natural fiber content also provides superior moisture resistance and structural strength, making biocomposites a preferred choice for durable and green decking solutions.
Understanding Plastic Composites
Plastic composites, commonly used in decking boards, consist of a blend of plastic polymers and fillers such as wood fibers or other natural materials, offering enhanced durability and resistance to moisture compared to traditional wood. These composites provide low maintenance and superior weather resistance, making them ideal for outdoor applications where longevity and minimal upkeep are crucial. Understanding the chemical composition and manufacturing process of plastic composites helps to highlight their advantages over biocomposites, such as improved structural integrity and resistance to biological degradation.
Environmental Impact: Biocomposite vs Plastic Composite
Biocomposite decking boards typically have a lower environmental impact than plastic composites due to their use of natural fibers like wood or bamboo combined with biodegradable resins, which reduce reliance on fossil fuels and improve biodegradability. Plastic composites, often composed of high percentages of non-recyclable plastics, contribute to microplastic pollution and have longer degradation periods in landfills. The production of biocomposites also tends to generate fewer greenhouse gas emissions, supporting sustainable building practices and reducing overall carbon footprint compared to conventional plastic composites.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Biocomposite decking boards, composed of natural fibers and biodegradable resins, offer moderate durability with resistance to rot and insect damage but may degrade faster under prolonged moisture exposure compared to plastic composites. Plastic composite boards, made from recycled plastics and wood fibers, provide superior lifespan ranging from 25 to 30 years due to enhanced moisture resistance and UV stability, minimizing warping and cracking. The durability of plastic composites surpasses biocomposites, making them a preferred choice for long-term decking applications where longevity and minimal maintenance are critical.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Biocomposite decking boards offer superior aesthetic appeal with natural wood-like textures and rich color variations that enhance outdoor spaces. Their eco-friendly composition allows for customization in shapes and finishes, providing greater design flexibility compared to plastic composites. Plastic composites, while durable, often lack the authentic visual warmth and intricate detailing achievable with biocomposites.
Installation Process and Maintenance
Biocomposite decking boards offer easier installation due to their uniform density and reduced weight compared to plastic composites, allowing for straightforward cutting and fastening with standard tools. Maintenance for biocomposites typically involves regular cleaning with mild soap and water to prevent mold and mildew, whereas plastic composites may require specialized cleaners to avoid surface damage. Both materials resist rot and insect damage, but biocomposites tend to have better breathability, reducing long-term moisture retention issues.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Biocomposite decking boards generally feature higher upfront costs ranging from $7 to $12 per square foot compared to plastic composite boards, which average $5 to $10 per square foot. Long-term expenses favor biocomposites due to their superior durability, lower maintenance requirements, and enhanced resistance to mold and UV damage, reducing repair and replacement costs over time. Plastic composites may incur higher lifecycle costs caused by frequent maintenance, including staining, sealing, and potential faster degradation in harsh weather conditions.
Performance in Varying Climates
Biocomposite decking boards exhibit superior moisture resistance and dimensional stability compared to plastic composites, making them ideal for varying climates with fluctuating humidity levels. Plastic composites often suffer from thermal expansion and contraction, leading to warping or cracking in extreme temperatures. The natural fibers in biocomposites enhance breathability and reduce heat retention, improving overall performance in hot and cold environments.
Which Decking Material Is Right for You?
Biocomposite decking boards, made from natural fibers and biodegradable resins, offer superior environmental benefits and enhanced resistance to mold and moisture compared to traditional plastic composites. Plastic composites, often crafted from recycled plastics and wood fibers, provide greater durability and low maintenance but may contribute to microplastic pollution over time. Choosing the right decking material depends on prioritizing sustainability and biodegradability with biocomposites or long-lasting, weather-resistant performance with plastic composites.
Infographic: Biocomposite vs Plastic Composite for Decking Board
 azmater.com
azmater.com