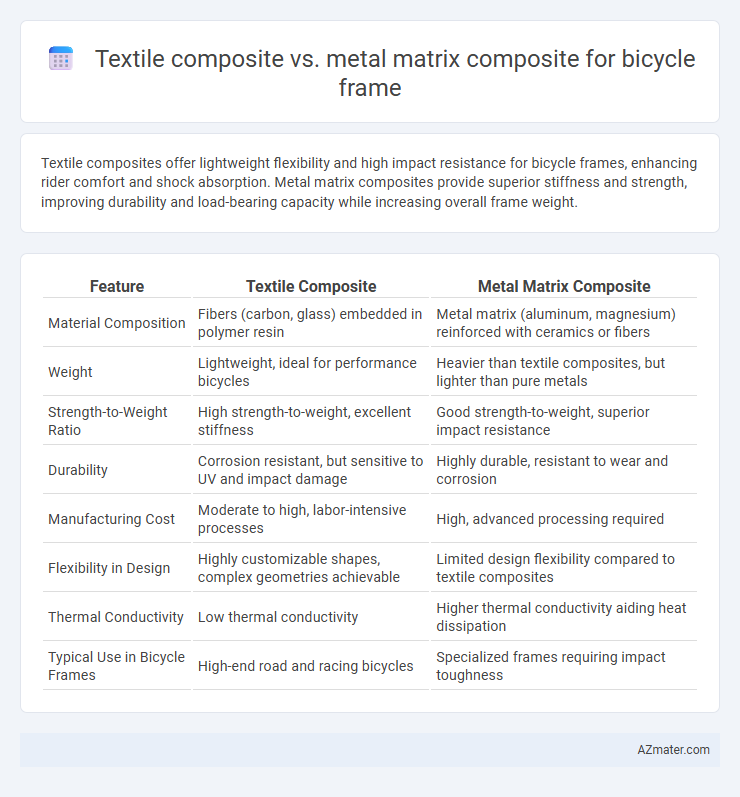
Textile composites offer lightweight flexibility and high impact resistance for bicycle frames, enhancing rider comfort and shock absorption. Metal matrix composites provide superior stiffness and strength, improving durability and load-bearing capacity while increasing overall frame weight.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Textile Composite | Metal Matrix Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Fibers (carbon, glass) embedded in polymer resin | Metal matrix (aluminum, magnesium) reinforced with ceramics or fibers |
| Weight | Lightweight, ideal for performance bicycles | Heavier than textile composites, but lighter than pure metals |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High strength-to-weight, excellent stiffness | Good strength-to-weight, superior impact resistance |
| Durability | Corrosion resistant, but sensitive to UV and impact damage | Highly durable, resistant to wear and corrosion |
| Manufacturing Cost | Moderate to high, labor-intensive processes | High, advanced processing required |
| Flexibility in Design | Highly customizable shapes, complex geometries achievable | Limited design flexibility compared to textile composites |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low thermal conductivity | Higher thermal conductivity aiding heat dissipation |
| Typical Use in Bicycle Frames | High-end road and racing bicycles | Specialized frames requiring impact toughness |
Introduction to Bicycle Frame Materials
Textile composites in bicycle frames offer high strength-to-weight ratios due to advanced fiber reinforcements like carbon and aramid fibers embedded in polymer matrices, enhancing flexibility and vibration dampening. Metal matrix composites incorporate ceramic or other reinforcements within metals such as aluminum or magnesium, providing superior stiffness and impact resistance while maintaining lightweight properties. Selection between textile and metal matrix composites depends on performance priorities such as fatigue resistance, weight savings, and ride comfort specific to cycling applications.
Overview of Textile Composite Materials
Textile composite materials for bicycle frames incorporate high-strength fibers such as carbon, aramid, or glass embedded in polymer matrices, offering an excellent strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced vibration damping compared to metal matrix composites. These composites provide superior design flexibility and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for lightweight, high-performance bicycles with complex geometries. The layered fiber architecture enables tailored mechanical properties to optimize stiffness and impact resistance, distinguishing textile composites from the typically denser and stiffer metal matrix counterparts.
Overview of Metal Matrix Composites
Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs) consist of metal matrices reinforced with ceramic or metallic fibers, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced wear resistance compared to conventional metals. MMCs provide excellent thermal stability and stiffness, making them suitable for high-performance bicycle frames that demand durability and lightweight properties. Their manufacturing complexity and higher cost often limit extensive use, but they outperform textile composites in mechanical robustness and fatigue resistance.
Weight Comparison: Textile vs Metal Matrix
Textile composites used in bicycle frames typically offer significant weight savings compared to metal matrix composites, with densities often below 1.6 g/cm3 versus metal matrices ranging from 2.5 to 3.0 g/cm3. The reduced weight of textile composites contributes to improved ride agility and acceleration, making them ideal for performance-focused bicycles. Despite metal matrix composites providing superior stiffness and impact resistance, their higher density results in heavier frames that may compromise overall weight efficiency.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Textile composites offer high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, providing lightweight durability ideal for absorbing shocks during cycling. Metal matrix composites demonstrate superior stiffness and wear resistance with enhanced fatigue life, making them suitable for heavy-duty and long-term applications. Strength analysis reveals textile composites excel in flexibility and energy absorption, while metal matrix composites provide greater load-bearing capacity and structural integrity under stress.
Impact on Ride Comfort and Performance
Textile composites in bicycle frames offer superior vibration damping and flexibility, enhancing ride comfort by absorbing road shocks more effectively than metal matrix composites. Metal matrix composites provide higher stiffness and strength-to-weight ratios, improving overall performance through better power transfer and durability. Balancing textile and metal composite properties can optimize both comfort and efficiency in advanced bicycle frame designs.
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Textile composites for bicycle frames offer lower manufacturing complexity due to their flexible weaving processes and compatibility with standard resin infusion techniques, resulting in reduced labor costs and shorter production cycles. Metal matrix composites, however, involve intricate casting or powder metallurgy methods combined with high-temperature processing, significantly increasing manufacturing complexity and expenses. Consequently, textile composites generally present a more cost-effective solution for lightweight, high-strength bicycle frames compared to the resource-intensive production of metal matrix composites.
Corrosion Resistance and Environmental Impact
Textile composites exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to metal matrix composites, as they do not oxidize or degrade when exposed to moisture and chemicals, enhancing bicycle frame longevity. Metal matrix composites require protective coatings to prevent corrosion, which can add weight and maintenance complexity. Environmentally, textile composites often use renewable fibers and lower energy manufacturing processes, reducing carbon footprint, while metal matrix composites involve energy-intensive metal extraction and processing, increasing environmental impact.
Repairability and Longevity
Textile composites in bicycle frames offer superior repairability due to their weave structure, enabling localized fixes without compromising the entire frame, while metal matrix composites (MMCs) often require specialized equipment and expertise for effective repairs. Longevity of textile composites is enhanced by resistance to corrosion and fatigue, whereas MMCs may experience microstructural degradation under cyclic stress despite higher stiffness. Choosing between these materials depends on balancing ease of maintenance and long-term durability tailored to riding conditions and user needs.
Future Trends in Bicycle Frame Materials
Textile composites in bicycle frames offer enhanced flexibility, reduced weight, and superior vibration damping, driving innovation toward more comfortable and ergonomic designs. Metal matrix composites (MMCs) provide exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and improved fatigue resistance, making them suitable for high-performance and racing bicycles. Future trends indicate a growing integration of hybrid materials combining textile composites with MMCs to optimize durability, weight, and ride quality, supported by advancements in nanotechnology and additive manufacturing for customized frame production.
Infographic: Textile composite vs Metal matrix composite for Bicycle frame
 azmater.com
azmater.com