Bamboo fiber composites offer a sustainable, lightweight alternative to traditional fiber reinforced polymers (FRP) in boat hull construction, providing comparable strength and improved environmental impact. Bamboo fibers enhance biodegradability and reduce carbon footprint while maintaining resistance to fatigue and water absorption typical in FRP materials.
Table of Comparison
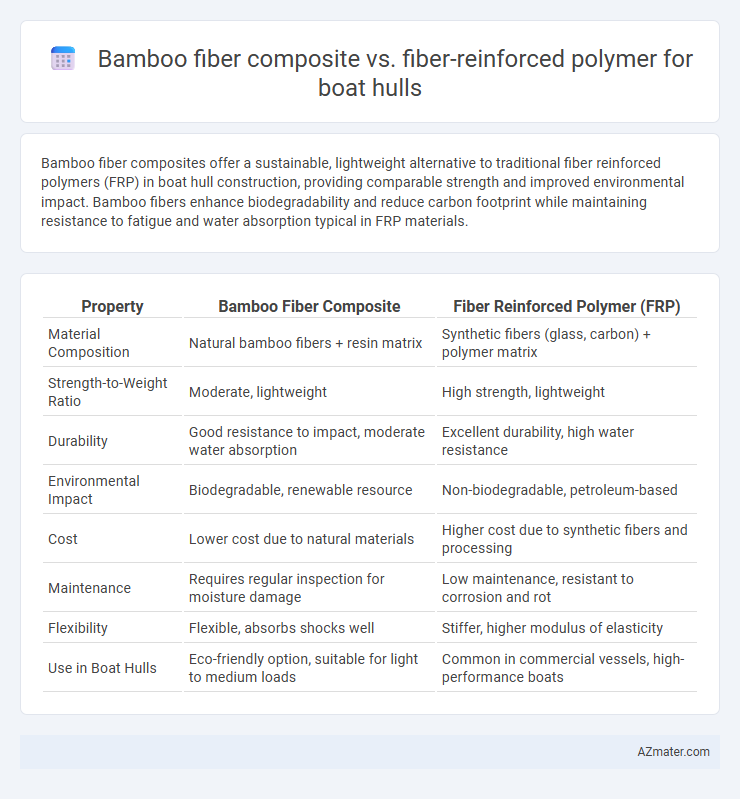
| Property | Bamboo Fiber Composite | Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural bamboo fibers + resin matrix | Synthetic fibers (glass, carbon) + polymer matrix |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Moderate, lightweight | High strength, lightweight |
| Durability | Good resistance to impact, moderate water absorption | Excellent durability, high water resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable resource | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Cost | Lower cost due to natural materials | Higher cost due to synthetic fibers and processing |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspection for moisture damage | Low maintenance, resistant to corrosion and rot |
| Flexibility | Flexible, absorbs shocks well | Stiffer, higher modulus of elasticity |
| Use in Boat Hulls | Eco-friendly option, suitable for light to medium loads | Common in commercial vessels, high-performance boats |
Introduction to Sustainable Boat Hull Materials
Bamboo fiber composite offers a renewable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional fiber-reinforced polymers (FRP) commonly used in boat hull construction. Bamboo's rapid growth cycle and natural strength provide improved biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint compared to synthetic fibers like glass or carbon in FRP. Sustainable boat hull materials incorporating bamboo fiber composites enhance environmental performance without compromising structural integrity or durability.
Overview of Bamboo Fiber Composites
Bamboo fiber composites for boat hulls offer a sustainable alternative to traditional fiber reinforced polymers (FRP) by utilizing natural bamboo fibers combined with bio-based or synthetic resins, resulting in lightweight yet strong materials. These composites exhibit impressive mechanical properties such as high tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility due to bamboo's unique fibrous structure, making them suitable for marine applications. Moreover, bamboo fiber composites enhance environmental benefits through biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint while maintaining durability and resistance to water absorption compared to conventional FRP materials.
Fundamentals of Fiber Reinforced Polymers (FRPs)
Bamboo fiber composite offers a renewable and lightweight alternative to traditional fiber reinforced polymers (FRPs), utilizing natural fibers that provide high tensile strength and excellent energy absorption in boat hull applications. Fiber reinforced polymers combine synthetic fibers such as glass or carbon with polymer matrices, resulting in exceptional corrosion resistance, durability, and enhanced mechanical properties critical for marine environments. Understanding the fundamentals of FRPs, including fiber-matrix interaction, fiber orientation, and resin selection, is essential for optimizing the structural performance and longevity of boat hulls fabricated with either bamboo fiber composites or conventional FRPs.
Mechanical Properties: Bamboo Fiber vs FRP
Bamboo fiber composites exhibit high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance compared to conventional fiber reinforced polymers (FRP), making them a sustainable alternative for boat hulls. The natural fibers in bamboo provide superior flexibility and energy absorption, enhancing hull durability under dynamic marine conditions. While FRPs offer consistent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, bamboo composites deliver comparable stiffness with reduced weight, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Analysis
Bamboo fiber composite boat hulls offer a renewable, biodegradable alternative to traditional fiber reinforced polymers (FRPs), significantly reducing carbon footprints and end-of-life environmental hazards. Bamboo's rapid growth cycle and carbon sequestration capacity enhance sustainability compared to petrochemical-based FRPs, which rely on non-renewable resources and emit volatile organic compounds during manufacturing. Lifecycle assessments highlight bamboo composites' lower energy consumption and waste generation, making them a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable marine applications.
Cost Comparison and Economic Feasibility
Bamboo fiber composites offer a lower material cost compared to traditional fiber reinforced polymers (FRPs) due to the renewability and abundance of bamboo, making them economically feasible for small to medium-sized boat hulls. While FRPs typically provide higher strength-to-weight ratios and durability, their production involves expensive synthetic fibers and resins, increasing overall costs for large-scale manufacturing. Lifecycle cost analysis often favors bamboo composites in regions with abundant bamboo cultivation, as reduced raw material and processing expenses contribute to more cost-effective boat hull solutions.
Durability and Maintenance in Marine Environments
Bamboo fiber composites exhibit competitive durability in marine environments due to their natural resistance to moisture and saltwater degradation, reducing the risk of rot and corrosion compared to some synthetic fibers. Fiber reinforced polymers (FRPs), particularly those using glass or carbon fibers, offer superior mechanical strength and long-term durability but may require more frequent inspections and maintenance to prevent microcracking and osmotic blistering. Maintenance demands for bamboo composites are generally lower as they resist fungal growth and UV damage naturally, whereas FRPs often necessitate protective coatings and specialized repair techniques to sustain hull integrity over time.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Bamboo fiber composite boat hulls utilize a sustainable manufacturing process involving natural fiber extraction, resin impregnation, and compression molding, which offers a lower environmental footprint and potential cost savings. Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) hulls are produced through well-established methods such as hand lay-up, vacuum infusion, or resin transfer molding, ensuring high consistency and scalability for mass production. While FRP manufacturing benefits from mature industrial infrastructure and broad supplier networks, bamboo composites require advancing processing techniques to achieve similar scalability and mechanical reliability.
Performance Case Studies in Boat Building
Bamboo fiber composite in boat hull construction demonstrates comparable tensile strength and improved vibration damping compared to traditional fiber reinforced polymers (FRP), as evidenced by case studies in small to medium-sized vessels. Performance evaluations reveal bamboo composites offer enhanced sustainability with reduced environmental impact while maintaining corrosion resistance and durability in marine environments. Field tests on prototype hulls confirm bamboo fiber composites provide cost-effective alternatives without compromising structural integrity or hydrodynamic efficiency.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Hull Materials
Bamboo fiber composites offer promising sustainability advantages, featuring high strength-to-weight ratios and biodegradability, making them a potential eco-friendly alternative to traditional fiber reinforced polymers (FRPs) in boat hull construction. Innovations in hybrid composites combining bamboo fibers with epoxy or bio-based resins are enhancing durability and impact resistance while reducing environmental impact. Future research centers on optimizing processing techniques and nano-enhancements to improve mechanical properties and water resistance, positioning bamboo composites as viable, greener replacements for conventional FRPs in marine applications.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber composite vs Fiber reinforced polymer for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com