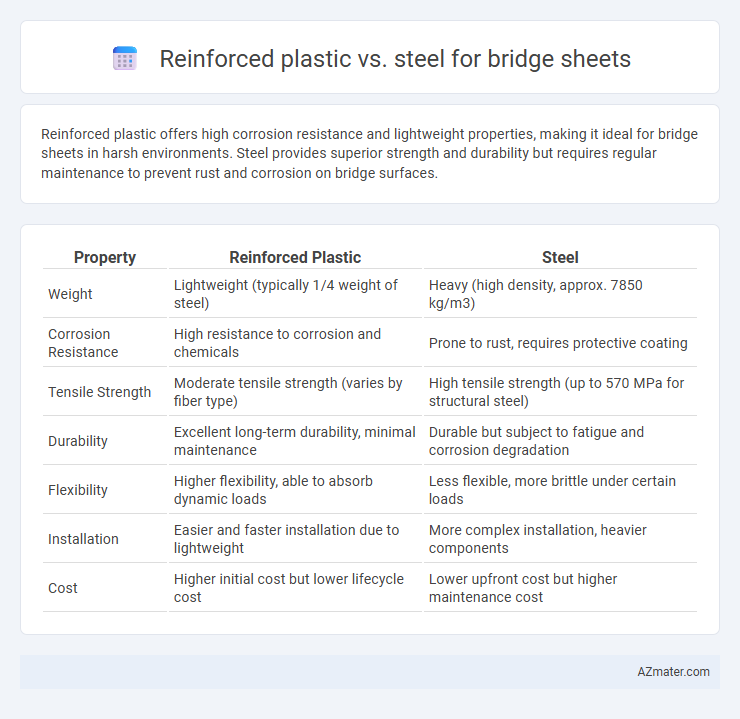
Reinforced plastic offers high corrosion resistance and lightweight properties, making it ideal for bridge sheets in harsh environments. Steel provides superior strength and durability but requires regular maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion on bridge surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Reinforced Plastic | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight (typically 1/4 weight of steel) | Heavy (high density, approx. 7850 kg/m3) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to corrosion and chemicals | Prone to rust, requires protective coating |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate tensile strength (varies by fiber type) | High tensile strength (up to 570 MPa for structural steel) |
| Durability | Excellent long-term durability, minimal maintenance | Durable but subject to fatigue and corrosion degradation |
| Flexibility | Higher flexibility, able to absorb dynamic loads | Less flexible, more brittle under certain loads |
| Installation | Easier and faster installation due to lightweight | More complex installation, heavier components |
| Cost | Higher initial cost but lower lifecycle cost | Lower upfront cost but higher maintenance cost |
Introduction to Bridge Sheet Materials
Bridge sheets serve as critical sealing elements that prevent water and debris from penetrating structural joints, ensuring durability and safety. Reinforced plastic offers lightweight properties, corrosion resistance, and flexibility ideal for modern bridge designs, while steel provides superior strength and load-bearing capacity but is prone to corrosion without protective treatments. Material selection depends on environmental exposure, load requirements, and maintenance considerations for optimal bridge performance.
Overview of Reinforced Plastic Sheets
Reinforced plastic sheets, composed of fiberglass or carbon fiber embedded in a polymer matrix, offer high strength-to-weight ratios ideal for bridge applications where weight reduction is critical. These composites exhibit exceptional corrosion resistance, reducing maintenance costs compared to traditional steel sheets prone to rust and fatigue. Their durability under various environmental conditions enhances longevity, making them increasingly preferred for modern bridge construction and repair projects.
Characteristics of Steel Bridge Sheets
Steel bridge sheets offer exceptional tensile strength and durability, making them ideal for supporting heavy loads and resisting impact forces. Their high corrosion resistance can be enhanced with protective coatings, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environmental conditions. Steel also provides excellent weldability and flexibility in fabrication, allowing for precise construction and maintenance in bridge engineering.
Comparative Strength and Durability
Reinforced plastic offers superior corrosion resistance and lighter weight compared to steel, enhancing longevity and ease of installation for bridge sheets. Steel demonstrates higher tensile strength and better load-bearing capacity, making it suitable for heavy traffic and structural demands. Durability in harsh environments favors reinforced plastic due to its resistance to rust and chemical degradation, while steel requires regular maintenance to prevent corrosion and extend lifespan.
Corrosion Resistance: Steel vs Reinforced Plastic
Reinforced plastic offers superior corrosion resistance compared to steel, making it ideal for bridge sheets exposed to harsh environmental conditions such as saltwater or industrial pollution. Steel, even when coated, is prone to rust and corrosion over time, compromising structural integrity and increasing maintenance costs. Reinforced plastic's resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation ensures long-lasting performance and reduced need for repairs.
Weight and Structural Load Considerations
Reinforced plastic offers significantly lower weight compared to steel, reducing the overall dead load on bridge structures and enabling longer spans with less support. Steel, while heavier, provides higher tensile strength and stiffness, crucial for handling substantial live and dynamic loads in heavy-traffic scenarios. Weight efficiency of reinforced plastic enhances ease of installation and minimizes foundation requirements, whereas steel's superior load-bearing capacity ensures durability and resilience under extreme structural demands.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Reinforced plastic bridge sheets offer easier and faster installation due to their lightweight nature, reducing labor costs and minimizing the need for heavy equipment compared to steel. Maintenance requirements for reinforced plastic are lower since it resists corrosion, rust, and environmental degradation without frequent coatings or repairs, unlike steel which demands regular inspections and protective treatments to prevent deterioration. These factors result in reduced downtime and overall lifecycle costs, making reinforced plastic a cost-effective alternative in bridge sheet applications where durability and ease of upkeep are critical.
Cost Comparison and Lifecycle Analysis
Reinforced plastic bridge sheets typically offer lower initial costs compared to steel due to reduced material and installation expenses, while steel sheets involve higher upfront investment owing to fabrication and heavy equipment requirements. Lifecycle analysis reveals that reinforced plastic provides superior corrosion resistance and lower maintenance costs over time, extending service life and minimizing downtime, whereas steel demands regular inspections and treatments to prevent rust and fatigue. Cost-effectiveness of reinforced plastic increases in highly corrosive environments, but steel may provide greater structural strength and durability under extreme loads and impacts.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reinforced plastic offers significant environmental benefits over steel for bridge sheets due to its lighter weight, which reduces transportation emissions and foundation energy demands. Unlike steel, reinforced plastic does not corrode, minimizing maintenance needs and extending the bridge's lifecycle, thereby reducing resource consumption over time. However, the recyclability and end-of-life disposal of reinforced plastics remain challenges compared to steel, which is highly recyclable and widely reused in infrastructure projects.
Ideal Applications and Use Cases
Reinforced plastic excels in bridge sheet applications requiring corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and ease of installation, making it ideal for pedestrian bridges and temporary structures. Steel offers superior strength and durability, suitable for heavy-load-bearing bridges and long-span applications where structural integrity under dynamic loads is critical. Selecting between reinforced plastic and steel depends on environmental conditions, load requirements, and maintenance considerations to optimize performance and lifespan.
Infographic: Reinforced plastic vs Steel for Bridge Sheet
 azmater.com
azmater.com