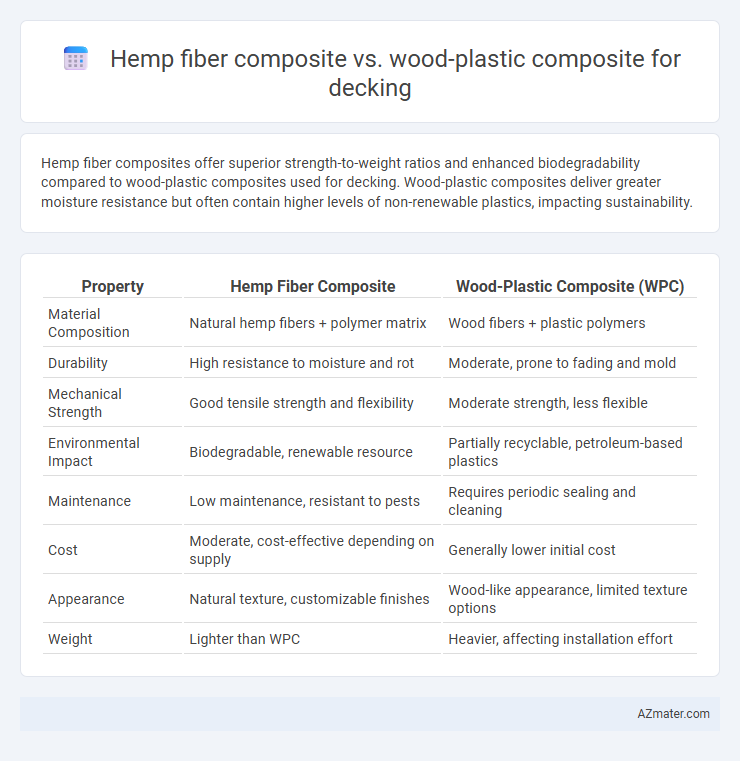
Hemp fiber composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced biodegradability compared to wood-plastic composites used for decking. Wood-plastic composites deliver greater moisture resistance but often contain higher levels of non-renewable plastics, impacting sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber Composite | Wood-Plastic Composite (WPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural hemp fibers + polymer matrix | Wood fibers + plastic polymers |
| Durability | High resistance to moisture and rot | Moderate, prone to fading and mold |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength and flexibility | Moderate strength, less flexible |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable resource | Partially recyclable, petroleum-based plastics |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, resistant to pests | Requires periodic sealing and cleaning |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective depending on supply | Generally lower initial cost |
| Appearance | Natural texture, customizable finishes | Wood-like appearance, limited texture options |
| Weight | Lighter than WPC | Heavier, affecting installation effort |
Introduction: Exploring Sustainable Decking Materials
Hemp fiber composite offers a renewable, biodegradable alternative with superior tensile strength and moisture resistance compared to traditional wood-plastic composites (WPC), which primarily rely on recycled plastics and wood fibers. WPC decking is widely popular for its durability and low maintenance but often involves higher carbon footprints due to plastic content and limited biodegradability. Selecting hemp fiber composites promotes reduced environmental impact and enhances deck longevity through natural fiber reinforcement combined with advanced polymer matrices.
Overview of Hemp Fiber Composite Decking
Hemp fiber composite decking features high tensile strength, natural resistance to moisture, and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional decking materials. It offers superior durability and lighter weight compared to wood-plastic composites (WPC), with improved thermal stability and reduced expansion under temperature fluctuations. The material's enhanced antimicrobial properties and resistance to mold and insect attacks contribute to lower maintenance requirements and longer service life in outdoor applications.
Overview of Wood-Plastic Composite Decking
Wood-plastic composite (WPC) decking combines wood fibers with thermoplastics, offering enhanced durability, resistance to rot, and lower maintenance compared to traditional wood. WPC materials provide improved weather resistance, dimensional stability, and reduced susceptibility to insect damage. This composite decking is widely favored for outdoor applications due to its balance of natural aesthetics and long-lasting performance.
Raw Materials and Sourcing: Hemp vs Wood-Plastic
Hemp fiber composite decking utilizes fast-growing hemp stalks, which are renewable and require less water and pesticides compared to traditional wood fibers, making sourcing more sustainable and eco-friendly. Wood-plastic composite decking relies on wood flour or sawdust often sourced from forestry byproducts combined with recycled plastics, but wood availability can fluctuate due to deforestation concerns. The renewable nature of hemp combined with lower environmental impact during cultivation positions hemp fiber composites as a more sustainable raw material for decking applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Hemp fiber composite decking exhibits superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to traditional wood-plastic composites, making it more resilient under heavy loads and mechanical stresses. The natural cellulose fibers in hemp enhance fiber-matrix adhesion, resulting in improved stiffness and reduced deformation over time. Hemp composites also demonstrate greater resistance to moisture, rot, and UV degradation, contributing to longer-lasting durability and lower maintenance requirements for outdoor decking applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior environmental benefits over wood-plastic composites due to hemp's rapid growth cycle and carbon sequestration capabilities, significantly reducing the overall carbon footprint of decking materials. Unlike wood-plastic composites, which rely on petroleum-based plastics and harvested wood, hemp composites utilize renewable plant fibers and biodegradable resins, minimizing landfill waste and promoting a circular economy. The biodegradability and lower energy consumption in hemp fiber composite production contribute to enhanced sustainability and reduced ecological damage in decking applications.
Moisture Resistance and Weather Performance
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior moisture resistance compared to wood-plastic composites due to the hydrophobic nature of hemp fibers, reducing water absorption and minimizing swelling and warping in decking applications. Weather performance is enhanced in hemp fiber composites by their improved UV stability and resistance to microbial degradation, leading to longer-lasting decks in harsh environmental conditions. Wood-plastic composites often require chemical additives to achieve similar moisture and weather durability but may still fall short in maintaining structural integrity over time.
Maintenance and Lifespan Considerations
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior resistance to moisture absorption and UV degradation, reducing maintenance frequency compared to wood-plastic composites, which often require regular sealing and treatment to prevent rot and warping. The lifespan of hemp fiber decking typically extends beyond 25 years due to its natural durability and resistance to fungal growth, while wood-plastic composites generally last 15 to 20 years before showing signs of wear and structural weakening. Regular cleaning and minimal protective coatings are sufficient for hemp composites, offering a more sustainable and cost-effective solution for long-term decking applications.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Hemp fiber composites for decking typically offer a lower material cost compared to wood-plastic composites (WPC), driven by the renewable nature and faster growth cycle of hemp fibers, leading to competitive pricing in production. Wood-plastic composites dominate market availability with widespread distribution channels and established supply chains, resulting in easier procurement and a broader variety of product options. While hemp fiber composites are emerging with sustainable appeal, they currently have limited market penetration and fewer suppliers, impacting overall accessibility and consumer choice.
Future Trends in Eco-Friendly Decking Solutions
Hemp fiber composites offer superior sustainability and biodegradability compared to traditional wood-plastic composites, which often rely on non-renewable plastics. Innovations in hemp composite technology enhance durability, moisture resistance, and carbon sequestration, positioning them as a leading material in eco-friendly decking solutions. Increasing regulatory support and consumer demand for low-impact materials drive the adoption of hemp fiber composites in the next generation of decking products.
Infographic: Hemp fiber composite vs Wood-plastic composite for Decking
 azmater.com
azmater.com