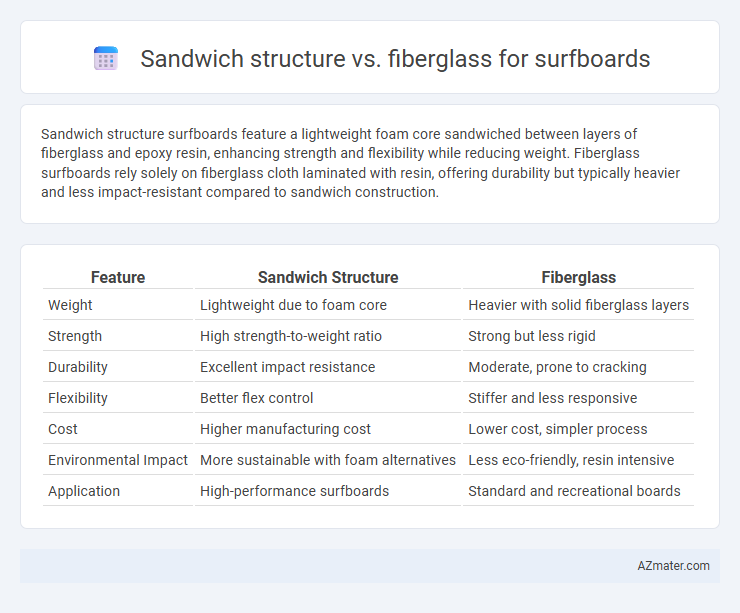
Sandwich structure surfboards feature a lightweight foam core sandwiched between layers of fiberglass and epoxy resin, enhancing strength and flexibility while reducing weight. Fiberglass surfboards rely solely on fiberglass cloth laminated with resin, offering durability but typically heavier and less impact-resistant compared to sandwich construction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sandwich Structure | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight due to foam core | Heavier with solid fiberglass layers |
| Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio | Strong but less rigid |
| Durability | Excellent impact resistance | Moderate, prone to cracking |
| Flexibility | Better flex control | Stiffer and less responsive |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, simpler process |
| Environmental Impact | More sustainable with foam alternatives | Less eco-friendly, resin intensive |
| Application | High-performance surfboards | Standard and recreational boards |
Introduction: Evolution of Surfboard Materials
The evolution of surfboard materials has shifted from traditional fiberglass to advanced sandwich structures, enhancing performance and durability. Sandwich construction combines lightweight cores with fiberglass skins, providing superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to conventional fiberglass boards. This innovation has revolutionized surfboard design, offering surfers increased responsiveness and longevity in various wave conditions.
Understanding Sandwich Structure Surfboards
Sandwich structure surfboards feature multiple layers including a rigid foam core and outer fiberglass skins, providing enhanced strength-to-weight ratio and increased durability compared to traditional fiberglass boards. This construction method improves impact resistance and flex control, resulting in better performance and longevity for surfers. Understanding the fiberglass layers' role in the sandwich design highlights how these boards optimize stiffness while maintaining lightweight characteristics essential for maneuverability.
What is Fiberglass in Surfboard Construction?
Fiberglass in surfboard construction refers to a woven fabric made from fine glass fibers that is laminated over the foam core to provide strength and durability. This material enhances the board's rigidity and resistance to water damage, making it essential for maintaining shape and performance. Compared to sandwich structures, fiberglass is lighter but may require additional reinforcement to achieve similar impact resistance and longevity.
Key Differences: Sandwich Structure vs. Fiberglass
Sandwich structure surfboards feature a core material, often EPS foam, encased between fiberglass layers and an outer protective skin, resulting in enhanced strength-to-weight ratio and increased durability compared to traditional fiberglass boards. Fiberglass surfboards rely heavily on fiberglass cloth and resin over a foam core, offering good flex and repairability but generally being heavier and less impact resistant than sandwich constructions. The sandwich structure's multilayer design improves impact resistance and stiffness, making it preferable for performance and long-term use, whereas fiberglass boards are favored for their cost-effectiveness and classic feel.
Weight and Performance Comparison
Sandwich structure surfboards feature a lightweight foam core encapsulated by fiberglass layers, resulting in reduced overall weight without compromising strength. Fiberglass-only boards tend to be heavier due to solid lamination but offer excellent durability and stiffness. The sandwich design enhances performance by providing superior flex and responsiveness, making it ideal for agile maneuvers, while fiberglass boards deliver more stability and impact resistance in rough conditions.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Sandwich structure surfboards feature a foam core encased in layers of fiberglass and epoxy resin, offering enhanced impact resistance and reduced weight compared to traditional fiberglass boards. Fiberglass surfboards, constructed with polyurethane foam and polyester resin, tend to be heavier and more prone to dings and delamination, requiring frequent repairs and maintenance. In terms of durability, sandwich construction provides superior strength and long-term resilience, while fiberglass boards demand more careful handling and routine upkeep to maintain performance.
Flexibility and Ride Feel Analysis
Sandwich structure surfboards feature a core material encapsulated by composite skins, offering enhanced flexibility and responsive flex patterns that adapt dynamically to wave pressure. Fiberglass boards, constructed with woven glass fibers and resin, provide a stiffer ride with less flex, delivering more control but reduced vibration absorption. In ride feel analysis, sandwich structures yield smoother, more forgiving rides ideal for performance surfing, while fiberglass boards excel in durability and precision in high-impact conditions.
Cost Implications for Surfers
Sandwich structure surfboards typically involve a higher initial investment due to advanced materials and manufacturing techniques, but they offer superior durability and longevity, reducing replacement costs for surfers over time. Fiberglass boards are generally more affordable upfront, making them accessible for beginners or budget-conscious surfers, though they may require more frequent repairs or replacements because of lower impact resistance. Balancing cost implications, surfers looking for long-term value often prefer sandwich structures, while those prioritizing short-term savings might choose fiberglass options.
Environmental Impact: Sandwich Structure vs. Fiberglass
Sandwich structure surfboards typically use EPS foam cores wrapped in epoxy resin and fiberglass, offering improved durability and reduced weight while being more energy-efficient to produce compared to traditional polyurethane foam boards. Fiberglass surfboards, made with polyester resin and polyurethane foam, contribute higher volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and generate non-biodegradable waste, raising environmental concerns. Selecting sandwich structures can lower carbon footprint and promote sustainability due to their recyclable materials and longer lifespan.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Surf Style
Sandwich structure surfboards offer enhanced durability and lightweight performance, making them ideal for aggressive surfers seeking responsiveness and strength in diverse wave conditions. Fiberglass boards provide a classic feel with superior flex and repairability, favored by traditionalists who prioritize smooth carving and a more forgiving ride. Selecting between sandwich structure and fiberglass depends on your surfing style--opt for sandwich if you need robustness and agility, or fiberglass for a more classic, flexible experience.
Infographic: Sandwich structure vs Fiberglass for Surfboard
 azmater.com
azmater.com