Nanocomposite materials offer superior strength, durability, and resistance to moisture compared to traditional plywood, making them ideal for high-performance furniture applications. Plywood remains cost-effective and widely used but lacks the enhanced mechanical properties and longevity that nanocomposites provide in modern furniture design.
Table of Comparison
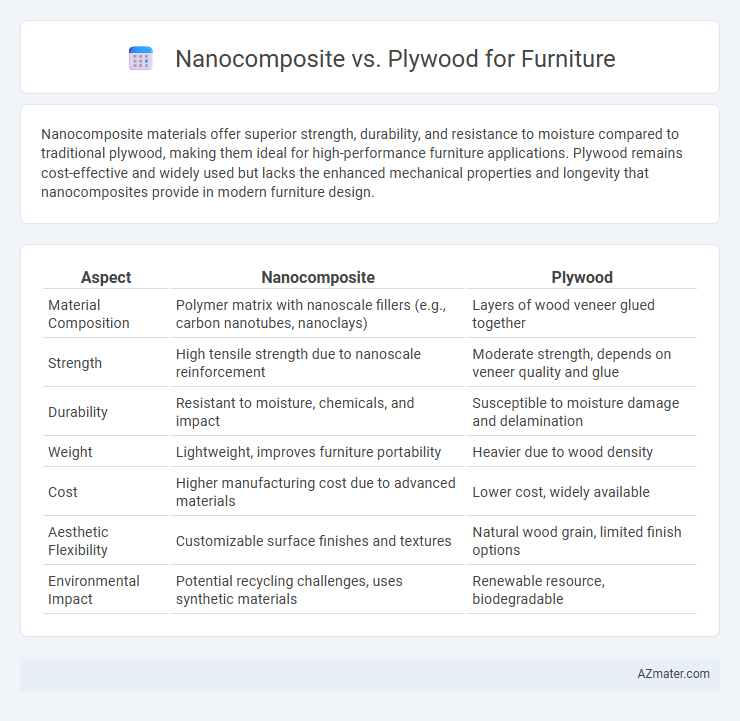
| Aspect | Nanocomposite | Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymer matrix with nanoscale fillers (e.g., carbon nanotubes, nanoclays) | Layers of wood veneer glued together |
| Strength | High tensile strength due to nanoscale reinforcement | Moderate strength, depends on veneer quality and glue |
| Durability | Resistant to moisture, chemicals, and impact | Susceptible to moisture damage and delamination |
| Weight | Lightweight, improves furniture portability | Heavier due to wood density |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost due to advanced materials | Lower cost, widely available |
| Aesthetic Flexibility | Customizable surface finishes and textures | Natural wood grain, limited finish options |
| Environmental Impact | Potential recycling challenges, uses synthetic materials | Renewable resource, biodegradable |
Introduction to Nanocomposite and Plywood Materials
Nanocomposite materials combine nanoparticles with a matrix like polymers or resins, enhancing mechanical strength, durability, and resistance to moisture compared to traditional materials. Plywood consists of multiple layers of wood veneer bonded together with adhesives, offering stability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness for furniture applications. Both materials provide unique structural benefits, with nanocomposites excelling in innovation and plywood favoring classic, reliable performance.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Nanocomposite furniture combines polymer matrices with nanoparticles like clay, carbon nanotubes, or silica to enhance mechanical strength and durability, using advanced processes such as melt blending or in situ polymerization. Plywood consists of multiple thin wood veneers glued together with adhesives, relying on a traditional hot press method to ensure strong bonding and dimensional stability. The nanocomposite manufacturing process offers more precise control over material properties, while plywood manufacturing focuses on layering natural wood fibers for structural integrity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Nanocomposite materials exhibit superior strength and durability compared to traditional plywood due to their enhanced molecular bonding and resistance to moisture, impact, and wear. Plywood, while affordable and widely used, tends to weaken over time when exposed to humidity and heavy loads, leading to potential warping and delamination. Nanocomposites offer higher tensile strength, improved stiffness, and longer lifespan, making them a more reliable choice for high-performance and long-lasting furniture applications.
Weight and Structural Performance
Nanocomposite materials offer significantly lower weight compared to traditional plywood, enhancing furniture mobility and ease of installation. Their superior structural performance arises from advanced matrix-filler interactions, providing higher strength-to-weight ratios and increased durability under stress. Plywood, while cost-effective, typically exhibits greater weight and lower mechanical strength, limiting its suitability for lightweight, high-performance furniture applications.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Flexibility
Nanocomposite materials offer superior aesthetic qualities for furniture with customizable finishes that mimic natural wood grains or metallic textures, providing sleek, modern looks unattainable with traditional plywood. Their enhanced surface smoothness and resistance to wear enable intricate design detailing and vibrant color applications, expanding creative possibilities beyond plywood's grain-dependent appearance. Plywood, while valued for its natural wood patterns and warm tones, limits design flexibility due to consistent layering orientation and susceptibility to surface imperfections, making nanocomposites the preferred choice for innovative, high-end furniture design.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocomposites offer enhanced durability and reduced resource consumption compared to traditional plywood, contributing to lower environmental impact in furniture production. Plywood, derived from multiple layers of wood veneer, often involves significant deforestation and chemical adhesives that can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Sustainable nanocomposite materials, incorporating biodegradable polymers and recycled nanoparticles, present a more eco-friendly alternative by minimizing waste and improving the lifecycle footprint of furniture products.
Moisture and Pest Resistance
Nanocomposite materials offer superior moisture resistance compared to plywood, as their matrix often incorporates hydrophobic polymers that prevent water absorption and swelling. In contrast, plywood, composed of layered wood veneers, is more susceptible to moisture-induced warping and fungal growth, diminishing its durability in humid environments. Pest resistance is also enhanced in nanocomposites due to embedded antimicrobial agents, whereas plywood is prone to termite and insect damage without additional chemical treatments.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Nanocomposites offer a cost advantage over plywood in high-performance furniture applications due to their enhanced durability, lightweight properties, and resistance to moisture and pests, which reduce long-term maintenance expenses. While plywood remains widely available and cost-effective in traditional furniture markets, the increasing demand for sustainable and innovative materials is driving growth in the nanocomposite market segment. Market availability of nanocomposite furniture components is expanding rapidly in advanced manufacturing hubs, yet plywood continues to dominate due to established supply chains and lower upfront costs.
Applications in Modern Furniture Design
Nanocomposites offer superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability compared to traditional plywood, making them ideal for high-performance modern furniture applications. Their resistance to moisture, abrasion, and UV degradation enables designers to create sleek, innovative pieces suitable for both indoor and outdoor environments. Plywood remains popular for its cost-effectiveness and versatility but is gradually being supplemented by nanocomposites in cutting-edge furniture designs that demand longevity and advanced material properties.
Future Trends in Furniture Materials
Nanocomposites in furniture materials are gaining traction due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio, enhanced durability, and resistance to moisture compared to traditional plywood. Future trends highlight the integration of nanotechnology to produce lightweight, eco-friendly furniture with improved mechanical properties and longer lifespans. The shift towards sustainable materials positions nanocomposites as a key innovation in modern furniture manufacturing, potentially replacing plywood in various applications.
Infographic: Nanocomposite vs Plywood for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com