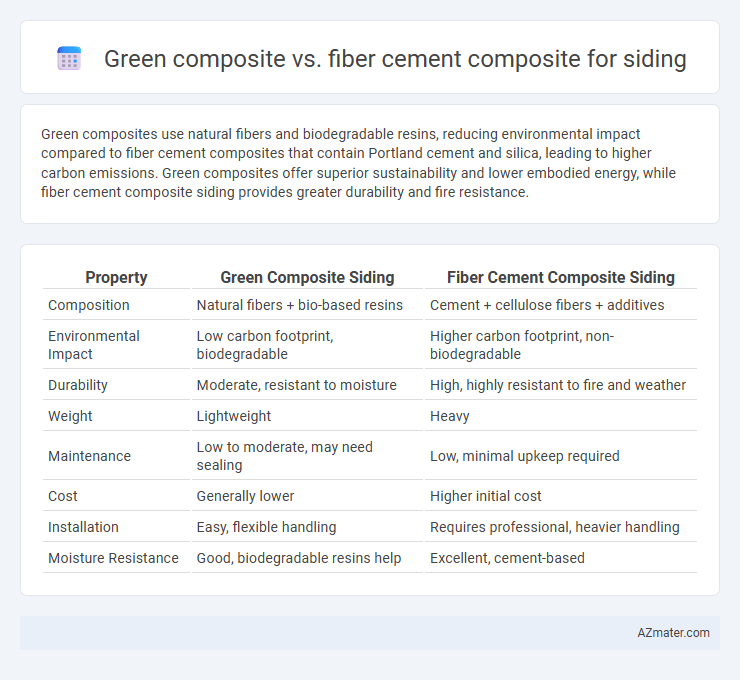
Green composites use natural fibers and biodegradable resins, reducing environmental impact compared to fiber cement composites that contain Portland cement and silica, leading to higher carbon emissions. Green composites offer superior sustainability and lower embodied energy, while fiber cement composite siding provides greater durability and fire resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Green Composite Siding | Fiber Cement Composite Siding |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Natural fibers + bio-based resins | Cement + cellulose fibers + additives |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | Higher carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Durability | Moderate, resistant to moisture | High, highly resistant to fire and weather |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate, may need sealing | Low, minimal upkeep required |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher initial cost |
| Installation | Easy, flexible handling | Requires professional, heavier handling |
| Moisture Resistance | Good, biodegradable resins help | Excellent, cement-based |
Introduction to Siding Materials
Green composites for siding are eco-friendly materials made from natural fibers combined with bio-based resins, offering sustainability and thermal insulation advantages. Fiber cement composites consist of cement mixed with cellulose fibers, providing durability, fire resistance, and low maintenance for exterior cladding. Both materials serve as effective siding options but differ in environmental impact, performance properties, and installation requirements.
Overview of Green Composites
Green composites for siding are environmentally friendly materials primarily composed of natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute combined with bio-based or biodegradable resins. These composites offer enhanced sustainability by reducing reliance on synthetic fibers and petrochemical resins, leading to lower carbon footprints and improved recyclability compared to traditional fiber cement composites made with cement, sand, and synthetic fibers. Green composites also provide benefits such as lightweight construction, superior insulation properties, and resistance to moisture and fungal growth, making them a compelling alternative for eco-conscious building projects.
Overview of Fiber Cement Composites
Fiber cement composites are engineered building materials composed of cement reinforced with cellulose fibers, offering high durability, fire resistance, and low maintenance for siding applications. These composites provide excellent moisture resistance and dimensional stability, making them suitable for various climate conditions. Fiber cement siding also boasts superior strength and longevity compared to traditional wood or vinyl options, contributing to increased property value and sustainability.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green composites for siding, made from natural fibers like hemp or flax combined with biodegradable resins, offer significantly lower carbon footprints and reduced landfill waste compared to fiber cement composites. Fiber cement siding involves cement production, which is energy-intensive and emits high CO2 levels, contributing to environmental degradation. Life cycle assessments reveal green composites outperform fiber cement in terms of recyclability, renewable resource usage, and overall environmental sustainability.
Durability and Longevity
Green composites, made from natural fibers and biodegradable resins, offer moderate durability but may degrade faster in high-moisture or UV-exposed environments compared to fiber cement composites. Fiber cement composites, composed of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, provide superior resistance to weathering, rot, insects, and fire, ensuring longevity often exceeding 50 years with minimal maintenance. The enhanced strength and water resistance of fiber cement siding make it a more durable and long-lasting option for exterior cladding in diverse climates.
Installation Process Differences
Green composites for siding typically feature lightweight materials like natural fibers combined with bio-based resins, allowing easier cutting and faster installation with standard woodworking tools. Fiber cement composites require specialized cutting tools and safety measures due to dust generation from silica content, which prolongs installation time and increases labor requirements. The simpler handling and reduced tool wear make green composites more efficient for installers seeking eco-friendly, less labor-intensive siding solutions.
Cost Analysis
Green composite siding typically offers a higher upfront cost compared to fiber cement due to the use of sustainable materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes, though it often results in lower long-term maintenance expenses. Fiber cement composite siding generally costs less initially, averaging around $5 to $10 per square foot, and provides durability with moderate maintenance requirements. When factoring in installation, lifecycle, and environmental impact, green composites present a competitive investment despite their premium price, especially for eco-conscious projects emphasizing sustainable building practices.
Aesthetic Options and Design Flexibility
Green composites for siding offer a wide range of aesthetic options, including natural textures and customizable color palettes that mimic wood and stone, enhancing curb appeal. Fiber cement composites provide design flexibility with their ability to be molded into various shapes and styles, such as shingles, planks, and panels, while maintaining durability and resistance to weather. Both materials support modern architectural trends through versatile finishes, but green composites excel in eco-friendly, natural appearances, whereas fiber cement composites prioritize structural adaptability and traditional aesthetics.
Maintenance Requirements
Green composite siding requires minimal maintenance due to its resistance to rot, insects, and moisture, often needing only occasional cleaning with soap and water. Fiber cement composite siding demands periodic repainting and sealing to prevent moisture infiltration and potential cracking over time. Both materials offer durability, but green composites generally provide lower long-term maintenance costs and efforts compared to fiber cement composites.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Siding Material
Green composites offer superior environmental benefits due to their use of natural fibers and biodegradable resins, making them a sustainable choice for siding. Fiber cement composites provide durability, fire resistance, and low maintenance, often outperforming green composites in longevity and structural integrity. Choosing the best siding material depends on prioritizing sustainability or durability, with green composites ideal for eco-conscious projects and fiber cement composites suited for long-lasting, low-maintenance applications.
Infographic: Green composite vs Fiber cement composite for Siding
 azmater.com
azmater.com