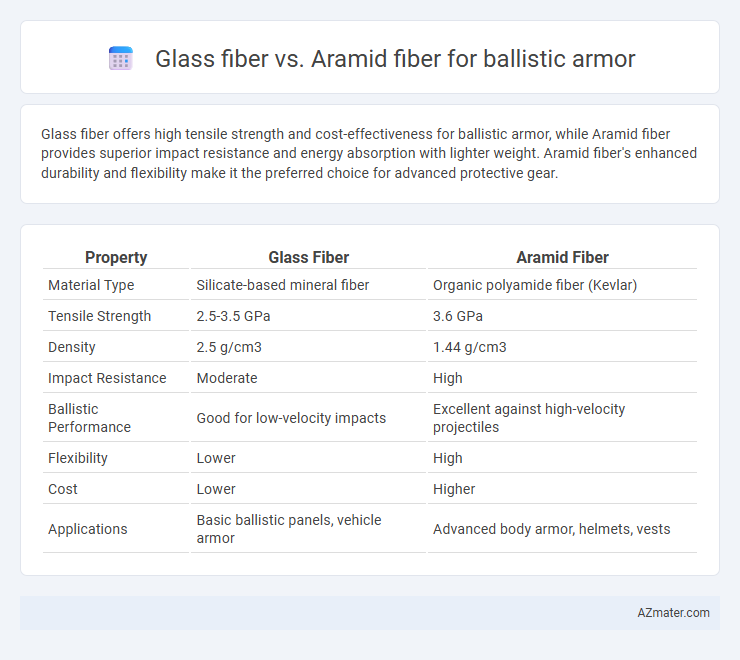
Glass fiber offers high tensile strength and cost-effectiveness for ballistic armor, while Aramid fiber provides superior impact resistance and energy absorption with lighter weight. Aramid fiber's enhanced durability and flexibility make it the preferred choice for advanced protective gear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Silicate-based mineral fiber | Organic polyamide fiber (Kevlar) |
| Tensile Strength | 2.5-3.5 GPa | 3.6 GPa |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Ballistic Performance | Good for low-velocity impacts | Excellent against high-velocity projectiles |
| Flexibility | Lower | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Basic ballistic panels, vehicle armor | Advanced body armor, helmets, vests |
Introduction to Ballistic Armor Materials
Ballistic armor materials primarily utilize glass fiber and aramid fiber due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and energy absorption capabilities. Glass fiber offers high tensile strength and cost efficiency, making it suitable for multi-hit resistance in armor applications. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides superior impact resistance and flexibility, enhancing protection against ballistic threats while maintaining lighter armor weight.
Overview of Glass Fiber
Glass fiber is a widely used reinforcement material in ballistic armor due to its high tensile strength, low cost, and excellent resistance to impact and abrasion. It offers superior energy absorption capabilities and dimensional stability under extreme conditions, making it effective in reducing projectile penetration. While lighter than metals, glass fiber composites provide a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, enhancing mobility for armor applications.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber, a synthetic polymer known for its exceptional tensile strength-to-weight ratio, is widely used in ballistic armor due to its high impact resistance and ability to absorb and dissipate energy effectively. Unlike glass fiber, aramid fibers like Kevlar offer superior flexibility and lighter weight, enhancing wearer mobility and comfort in protective gear. Their molecular structure provides inherent resistance to heat and abrasion, making aramid fibers a preferred choice for advanced body armor applications.
Ballistic Protection Capabilities
Glass fiber offers high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, making it effective against low to medium-velocity projectiles in ballistic armor applications. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides superior ballistic protection due to its high energy absorption, exceptional tensile strength, and resistance to penetration by high-velocity projectiles. The combination of lightweight properties and enhanced durability makes aramid fiber the preferred choice for advanced ballistic armor systems requiring maximum protection.
Weight and Flexibility Comparison
Glass fiber offers heavier ballistic armor compared to aramid fiber, with densities around 2.5 g/cm3 versus 1.44 g/cm3 for aramid, making aramid fiber significantly lighter. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior flexibility due to their polymeric chain structure, enhancing wearer mobility and comfort in protective gear. The combination of lower weight and higher flexibility makes aramid fiber the preferred choice for lightweight, ergonomic ballistic armor applications.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Glass fiber exhibits high tensile strength and excellent resistance to moisture, making it durable against environmental factors such as humidity and chemicals in ballistic armor applications. Aramid fiber offers superior impact resistance and retains structural integrity under extreme temperatures but is more susceptible to UV degradation and moisture absorption over time. Combining both fibers can optimize ballistic armor durability and environmental resistance by leveraging glass fiber's moisture resistance and aramid fiber's impact performance.
Cost Analysis: Glass Fiber vs Aramid Fiber
Glass fiber offers a cost-effective alternative for ballistic armor due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses compared to aramid fiber, which is significantly more expensive because of its complex production process. Despite the higher initial investment, aramid fiber provides superior ballistic performance and durability, often justifying the cost premium in high-threat environments. Budget constraints and performance requirements largely dictate material choice, with glass fiber favored for cost-sensitive applications and aramid fiber selected for maximum protection.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
Glass fiber used in ballistic armor involves a manufacturing process centered on melting silica-based raw materials and extruding fine filaments, which are then woven into fabrics with high tensile strength and rigidity. Aramid fiber, derived from aromatic polyamides, requires complex chemical synthesis and spinning processes that yield fibers with exceptional toughness and energy absorption, essential for impact resistance. Processing glass fiber typically demands higher temperatures during curing, while aramid fiber benefits from lower thermal processing but necessitates careful handling due to sensitivity to UV light and moisture.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Glass fiber and aramid fiber are prominently used in ballistic armor due to their distinct mechanical properties and real-world performance. Glass fiber offers excellent tensile strength and cost-efficiency, making it suitable for applications like vehicle armor and protective panels in military and law enforcement vehicles. Aramid fiber, known for superior impact resistance and energy absorption, is preferred in body armor and helmets, demonstrated by its extensive use in NATO-standard personal protective equipment and studied extensively in case studies highlighting enhanced ballistic resistance against rifle and handgun rounds.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Ballistic Armor
Glass fiber offers cost-effective ballistic protection with high tensile strength and good resistance to impact, making it suitable for lightweight armor applications. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides superior energy absorption, exceptional flexibility, and higher ballistic resistance against high-velocity threats, often preferred in military-grade ballistic vests. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing performance requirements, budget constraints, and intended use, with aramid fibers favored for maximum protection and glass fibers used where cost-efficiency and moderate protection suffice.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Aramid fiber for Ballistic armor
 azmater.com
azmater.com