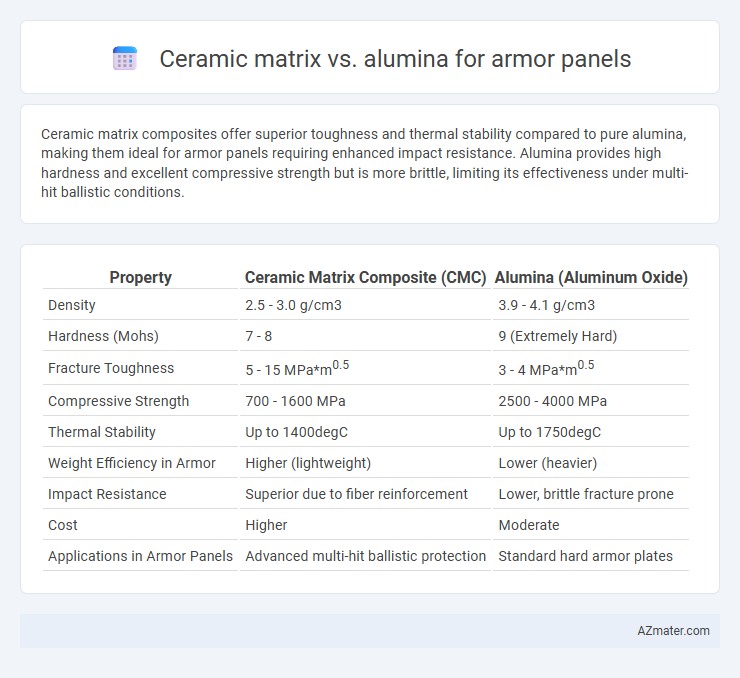
Ceramic matrix composites offer superior toughness and thermal stability compared to pure alumina, making them ideal for armor panels requiring enhanced impact resistance. Alumina provides high hardness and excellent compressive strength but is more brittle, limiting its effectiveness under multi-hit ballistic conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Matrix Composite (CMC) | Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2.5 - 3.0 g/cm3 | 3.9 - 4.1 g/cm3 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 7 - 8 | 9 (Extremely Hard) |
| Fracture Toughness | 5 - 15 MPa*m0.5 | 3 - 4 MPa*m0.5 |
| Compressive Strength | 700 - 1600 MPa | 2500 - 4000 MPa |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1400degC | Up to 1750degC |
| Weight Efficiency in Armor | Higher (lightweight) | Lower (heavier) |
| Impact Resistance | Superior due to fiber reinforcement | Lower, brittle fracture prone |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
| Applications in Armor Panels | Advanced multi-hit ballistic protection | Standard hard armor plates |
Introduction to Advanced Armor Materials
Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) and alumina ceramics serve as critical materials in advanced armor panels due to their exceptional hardness and lightweight properties. CMCs offer enhanced toughness and damage tolerance by combining ceramic fibers with matrices, improving impact resistance compared to monolithic alumina, which excels in hardness but tends to be brittle. The integration of these materials advances ballistic protection by balancing strength, weight, and durability in modern armor systems.
Overview of Ceramic Matrix Composites
Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) offer enhanced fracture toughness and thermal stability compared to monolithic ceramics like alumina, making them highly effective for armor panels. Unlike alumina, CMCs incorporate reinforcing fibers such as silicon carbide or carbon, which improve impact resistance and reduce brittleness under high-stress conditions. These qualities enable ceramic matrix composites to provide superior protection against ballistic threats while maintaining lightweight and durable armor solutions.
Properties and Composition of Alumina Armor
Alumina armor panels are composed primarily of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), offering high hardness and excellent wear resistance, which contribute to their superior ballistic protection against armor-piercing projectiles. Compared to ceramic matrix composites, alumina exhibits a higher density but provides better hardness and compressive strength, making it effective in dissipating energy upon impact. The intrinsic brittleness of alumina is mitigated in armor applications through engineered composite backing layers that enhance toughness and reduce fragmentation risk during ballistic events.
Comparative Ballistic Performance: Ceramic Matrix vs Alumina
Ceramic matrix composites exhibit superior ballistic performance compared to pure alumina by offering enhanced fracture toughness and energy absorption, resulting in improved multi-hit resistance. Alumina provides high hardness and effective projectile fragmentation but is more brittle, leading to lower crack propagation resistance under impact. The composite's ability to mitigate damage while maintaining structural integrity makes ceramic matrix armor panels more reliable in high-velocity ballistic protection scenarios.
Weight and Thickness Considerations
Ceramic matrix composites typically offer a better strength-to-weight ratio compared to alumina, resulting in lighter armor panels without sacrificing protective capabilities. Alumina armor panels often require greater thickness to achieve similar ballistic resistance, increasing overall weight and bulk. Weight and thickness considerations favor ceramic matrix composites in applications demanding enhanced mobility and lower burden for the wearer.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Ceramic matrix composites for armor panels generally offer improved toughness and impact resistance but come at a significantly higher cost due to complex manufacturing processes and limited suppliers. Alumina ceramics remain more cost-effective and widely available, benefiting from established production methods and a robust supply chain. The balance between superior protective performance and budget constraints often dictates material selection, with alumina favored in cost-sensitive applications while ceramic matrix composites are chosen for premium protection despite their higher price point.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Ceramic matrix composites exhibit superior impact resistance due to their ability to absorb and dissipate energy more effectively than pure alumina, which is inherently brittle. Alumina offers high hardness and excellent wear resistance, enhancing panel durability but can suffer from catastrophic failure under high-impact conditions. Combining alumina with a ceramic matrix optimizes armor panels by balancing toughness and structural integrity for enhanced protection performance.
Integration with Backing Materials
Ceramic matrix composites offer superior toughness and better stress distribution when integrated with backing materials, enhancing overall armor panel durability. Alumina ceramics provide excellent hardness and ballistic resistance but exhibit brittleness that requires careful bonding techniques to prevent delamination under impact. Optimizing the interface between ceramics and backing layers significantly improves energy absorption and reduces spallation in armor systems.
Common Applications in Military and Law Enforcement
Ceramic matrix composites and alumina ceramics are widely used materials in armor panels for military and law enforcement applications due to their exceptional hardness and lightweight properties. Ceramic matrix composites offer enhanced impact resistance and structural integrity, making them ideal for vehicle armor and ballistic helmets that require high durability under extreme conditions. Alumina ceramics deliver superior hardness and cost-effectiveness, commonly utilized in personal body armor plates and ballistic shields to provide reliable protection against high-velocity projectiles.
Future Trends in Armor Panel Materials
Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) are gaining traction in armor panels due to their superior toughness and damage tolerance compared to traditional alumina ceramics. Advancements in nano-engineering and hybrid composite structures are driving the evolution of lightweight, high-strength armor solutions with enhanced multi-hit resistance. Researchers are focusing on integrating CMCs with novel binders and fiber reinforcements to optimize ballistic performance and reduce manufacturing costs.
Infographic: Ceramic matrix vs Alumina for Armor panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com