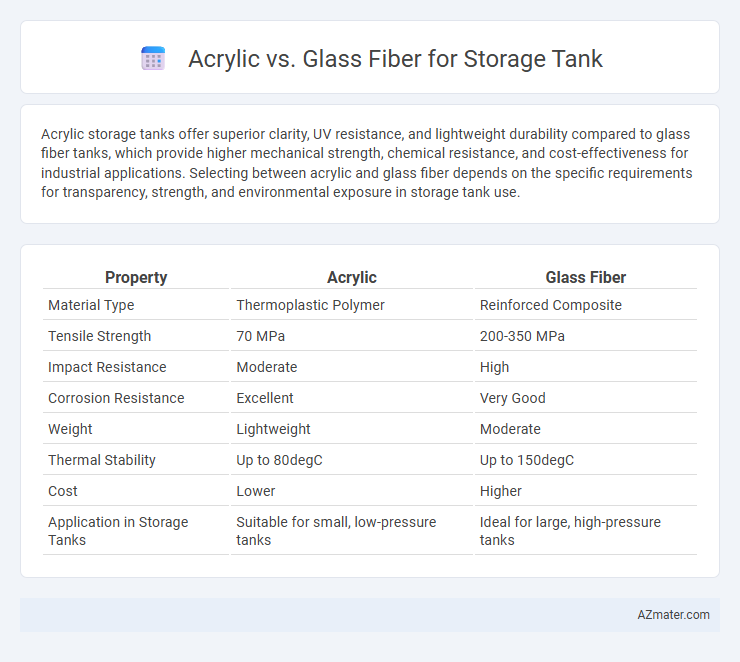
Acrylic storage tanks offer superior clarity, UV resistance, and lightweight durability compared to glass fiber tanks, which provide higher mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness for industrial applications. Selecting between acrylic and glass fiber depends on the specific requirements for transparency, strength, and environmental exposure in storage tank use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylic | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Reinforced Composite |
| Tensile Strength | 70 MPa | 200-350 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Very Good |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 80degC | Up to 150degC |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Application in Storage Tanks | Suitable for small, low-pressure tanks | Ideal for large, high-pressure tanks |
Introduction to Storage Tank Materials
Acrylic and glass fiber are common materials used in the construction of storage tanks due to their distinct properties. Acrylic offers excellent clarity, UV resistance, and impact strength, making it suitable for applications requiring visibility and durability. Glass fiber, reinforced with resin, provides superior tensile strength, chemical resistance, and lightweight characteristics, ideal for large-scale industrial storage tanks exposed to harsh environments.
Overview of Acrylic and Glass Fiber
Acrylic offers excellent clarity, UV resistance, and weather durability, making it suitable for visually accessible storage tanks in mild environments. Glass fiber, reinforced with resin, provides superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and impact durability, ideal for large-scale and industrial storage tanks exposed to harsh conditions. Both materials require proper maintenance, but glass fiber generally ensures longer lifespan and higher structural integrity in demanding storage applications.
Material Properties Comparison
Acrylic offers high transparency, excellent UV resistance, and superior chemical inertness, making it ideal for storage tanks requiring clear visibility and resistance to environmental degradation. Glass fiber, commonly used as fiberglass reinforcement, provides exceptional tensile strength, impact resistance, and durability but lacks transparency, making it suitable for opaque, high-strength storage tank applications. Both materials exhibit corrosion resistance, but glass fiber's mechanical robustness outperforms acrylic in load-bearing and structural integrity.
Durability and Lifespan
Acrylic storage tanks offer moderate durability with resistance to UV light and impact, making them suitable for less demanding environments, while glass fiber reinforced tanks provide superior strength and corrosion resistance, significantly extending their lifespan in harsh chemical and industrial settings. Glass fiber tanks typically last 20-30 years due to their robust composite structure, whereas acrylic tanks may have a shorter lifespan of around 10-15 years under similar conditions. The choice between acrylic and glass fiber for storage tanks hinges on required durability, environmental exposure, and long-term maintenance considerations.
Chemical Resistance
Acrylic storage tanks offer excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and solvents, making them suitable for less aggressive environments. Glass fiber reinforced tanks provide superior chemical resistance against highly corrosive substances and can handle strong acids and alkaline solutions often found in industrial applications. Selecting between acrylic and glass fiber depends on the specific chemical exposure, with glass fiber preferred for aggressive chemicals due to its enhanced durability and resistance.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Acrylic storage tanks offer easier installation due to their lightweight and seamless construction, reducing labor time and costs compared to glass fiber tanks, which require skilled handling and curing processes during setup. Maintenance for acrylic tanks is minimal, involving simple cleaning and UV protection to prevent discoloration, whereas glass fiber tanks demand regular inspections for potential delamination and gel coat repairs to maintain structural integrity. The low porosity of acrylic reduces contamination risks, enhancing longevity and lowering long-term maintenance efforts compared to the more porous and repair-prone glass fiber materials.
Cost Analysis: Acrylic vs Glass Fiber
Acrylic storage tanks generally present a higher initial cost compared to glass fiber tanks, primarily due to material quality and manufacturing processes. Glass fiber tanks offer cost advantages in large-scale applications, with lower maintenance expenses and greater durability under chemical exposure. Life cycle cost analysis reveals that despite acrylic's higher upfront price, its superior clarity and UV resistance can reduce replacement frequency, balancing long-term expenses against glass fiber's economical advantage.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Glass fiber storage tanks offer superior structural integrity and resistance to impact, reducing the risk of leaks and chemical spills compared to acrylic options. Acrylic tanks, while lightweight and visually clear, are more prone to cracking under stress, posing potential safety hazards in containment. Environmentally, glass fiber composites often incorporate recycled materials and exhibit longer lifespans, minimizing waste, whereas acrylic production involves higher emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Common Applications in Industry
Acrylic storage tanks are widely used in industries requiring chemical resistance and clarity, such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and water treatment, due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. Glass fiber reinforced storage tanks are preferred in heavy industrial applications like chemical manufacturing, petrochemical processing, and wastewater treatment because of their high strength, durability, and resistance to corrosive environments. Both materials offer tailored solutions for storage tank fabrication, with acrylic favored for clarity and chemical inertness, while glass fiber excels in structural integrity and long-term durability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Storage Tank Material
Acrylic storage tanks provide excellent clarity, UV resistance, and lightweight properties, making them ideal for applications requiring visibility and ease of handling. Glass fiber tanks offer superior strength, chemical resistance, and durability, suitable for harsh environments and heavy-duty storage needs. Selecting the right material depends on specific requirements such as exposure conditions, load capacity, and budget, with glass fiber favored for robustness and acrylic chosen for aesthetic and lightweight advantages.
Infographic: Acrylic vs Glass fiber for Storage tank
 azmater.com
azmater.com