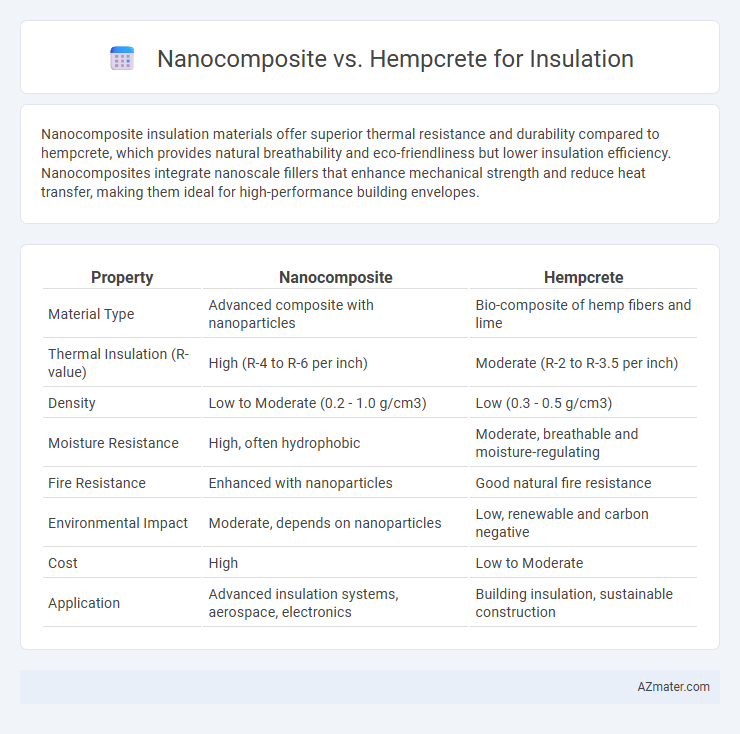
Nanocomposite insulation materials offer superior thermal resistance and durability compared to hempcrete, which provides natural breathability and eco-friendliness but lower insulation efficiency. Nanocomposites integrate nanoscale fillers that enhance mechanical strength and reduce heat transfer, making them ideal for high-performance building envelopes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocomposite | Hempcrete |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced composite with nanoparticles | Bio-composite of hemp fibers and lime |
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | High (R-4 to R-6 per inch) | Moderate (R-2 to R-3.5 per inch) |
| Density | Low to Moderate (0.2 - 1.0 g/cm3) | Low (0.3 - 0.5 g/cm3) |
| Moisture Resistance | High, often hydrophobic | Moderate, breathable and moisture-regulating |
| Fire Resistance | Enhanced with nanoparticles | Good natural fire resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate, depends on nanoparticles | Low, renewable and carbon negative |
| Cost | High | Low to Moderate |
| Application | Advanced insulation systems, aerospace, electronics | Building insulation, sustainable construction |
Introduction: The Need for Sustainable Insulation
Nanocomposite insulation offers advanced thermal performance through engineered materials at the nanoscale, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Hempcrete, a bio-based composite made from hemp fibers and lime, provides natural insulation with excellent thermal mass and moisture regulation properties. Both materials address the growing demand for sustainable insulation solutions that reduce carbon footprints and promote eco-friendly construction.
What are Nanocomposites?
Nanocomposites are advanced materials composed of a matrix embedded with nanoparticles, which significantly enhance thermal insulation, mechanical strength, and durability compared to traditional composites. These nanostructured materials can improve heat resistance and reduce thermal conductivity, making them highly efficient for insulation applications. Their nanoscale additives enable superior performance in energy efficiency and material sustainability when compared to bio-based options like hempcrete.
Understanding Hempcrete as an Insulation Material
Hempcrete is a bio-based insulation material composed of hemp hurds, lime, and water, offering excellent thermal performance with a low thermal conductivity typically around 0.1 to 0.15 W/m*K. Its natural hygroscopic properties regulate indoor humidity by absorbing and releasing moisture, contributing to a healthier indoor environment and enhanced energy efficiency. Unlike traditional nanocomposites, hempcrete provides sustainable insulation with superior breathability and carbon sequestration benefits, making it an eco-friendly alternative in modern construction.
Thermal Performance: Nanocomposite vs Hempcrete
Nanocomposite insulation materials exhibit superior thermal performance due to their enhanced nanoscale structure, providing significantly lower thermal conductivity compared to hempcrete. Hempcrete, while environmentally friendly and offering good thermal mass, has higher thermal conductivity values, typically ranging between 0.1 to 0.14 W/mK, resulting in moderate insulation effectiveness. Nanocomposites achieve thermal conductivities as low as 0.03 W/mK, making them more efficient at reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency in building applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocomposite insulation materials often leverage advanced polymers and nanoparticles, offering superior thermal performance but can involve energy-intensive manufacturing and limited recyclability, raising concerns about long-term environmental impact. Hempcrete, composed of hemp hurds and lime binder, provides a carbon-negative alternative due to hemp's rapid growth and carbon sequestration capabilities while ensuring biodegradability and minimal waste during production. Sustainable insulation choices prioritize renewable resources and lifecycle emissions, where hempcrete outperforms nanocomposites by combining natural material benefits with effective insulation properties.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Nanocomposite insulation materials exhibit superior durability due to their enhanced resistance to moisture, UV degradation, and mechanical wear, significantly extending their lifespan beyond traditional alternatives. Hempcrete, while offering excellent thermal insulation and natural breathability, typically faces challenges with longevity related to its susceptibility to moisture absorption and biological decay without proper treatment. The advanced formulation of nanocomposites provides a more stable and long-lasting insulation solution compared to the organic composition of hempcrete, making them preferable for applications demanding extended durability.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term Investment
Nanocomposite insulation typically demands a higher initial investment due to advanced materials and manufacturing processes, though it offers superior thermal performance and longevity that can reduce energy costs over time. Hempcrete, made from natural hemp fibers and lime, presents a more affordable upfront cost and provides excellent breathability and carbon sequestration benefits, but may require more frequent maintenance or thicker walls to achieve similar insulation values. Evaluating long-term investment involves balancing the upfront expenses of nanocomposites against hempcrete's lower initial price and potential supplementary costs for upkeep and structural support.
Ease of Installation and Construction Methods
Nanocomposite insulation panels offer superior ease of installation due to their lightweight structure and prefabricated form, allowing for quick fitting without specialized tools. Hempcrete requires more manual mixing and on-site application, which can extend construction time and demand skilled labor for proper curing and layering. The modularity of nanocomposites simplifies precise thermal insulation integration compared to the plastering and casting approaches necessary with hempcrete.
Health and Indoor Air Quality Considerations
Nanocomposite insulation materials offer superior air purification properties by incorporating nanoparticles that actively reduce airborne pollutants and allergens, promoting healthier indoor air quality. Hempcrete, a bio-based material, naturally regulates humidity and resists mold and mildew growth, resulting in improved respiratory comfort and reduced risk of harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Both materials contribute to non-toxic, sustainable indoor environments, but nanocomposites may provide advanced filtration benefits beyond the passive qualities of hempcrete.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Eco-Insulation
Nanocomposites exhibit superior thermal insulation properties and mechanical strength, positioning them as a cutting-edge solution in eco-insulation technologies. Hempcrete offers renewable, sustainable insulation with excellent breathability but faces challenges in scalability and uniform performance. Advances in nanomaterial integration and bio-based composites are driving future innovations, enhancing the efficiency and eco-friendliness of both nanocomposites and hempcrete for sustainable building applications.
Infographic: Nanocomposite vs Hempcrete for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com