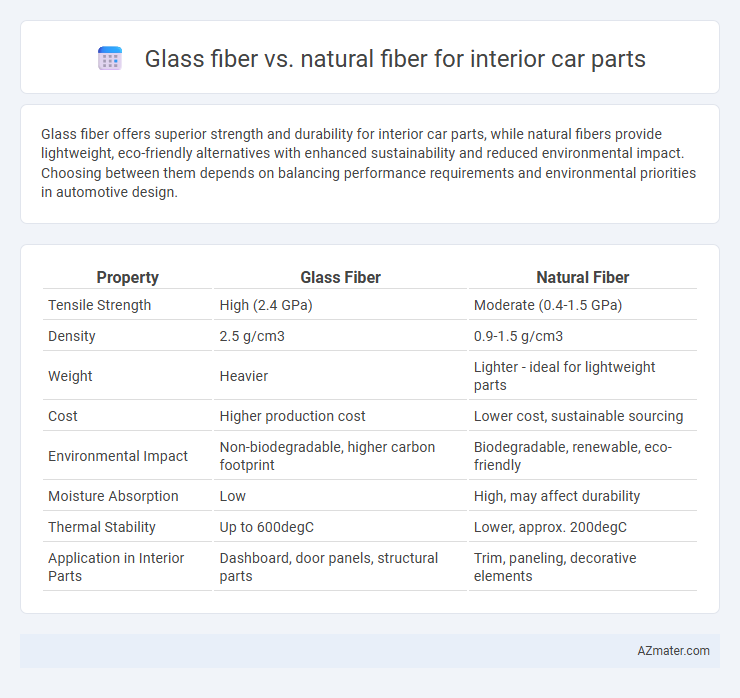
Glass fiber offers superior strength and durability for interior car parts, while natural fibers provide lightweight, eco-friendly alternatives with enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact. Choosing between them depends on balancing performance requirements and environmental priorities in automotive design.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber | Natural Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High (2.4 GPa) | Moderate (0.4-1.5 GPa) |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 0.9-1.5 g/cm3 |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter - ideal for lightweight parts |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower cost, sustainable sourcing |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint | Biodegradable, renewable, eco-friendly |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | High, may affect durability |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 600degC | Lower, approx. 200degC |
| Application in Interior Parts | Dashboard, door panels, structural parts | Trim, paneling, decorative elements |
Introduction to Fiber Materials in Automotive Interiors
Glass fiber offers superior strength, durability, and heat resistance, making it a preferred choice for structural components in automotive interiors. Natural fibers, such as hemp or flax, provide eco-friendly, lightweight alternatives with good acoustic absorption and biodegradable properties, aligning with sustainable manufacturing trends. The integration of these fiber materials enhances vehicle performance, comfort, and environmental impact.
Overview of Glass Fiber and Natural Fiber
Glass fiber offers high tensile strength, excellent durability, and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it a preferred material for interior car parts requiring structural integrity and long-term performance. Natural fibers such as flax, hemp, and jute provide lightweight, renewable, and biodegradable alternatives with good acoustic and thermal insulation properties, promoting sustainability in vehicle manufacturing. The choice between glass fiber and natural fiber depends on balancing performance requirements with environmental impact and weight reduction goals.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Glass fiber offers superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to natural fibers, making it ideal for interior car parts requiring high durability and impact resistance. Natural fibers such as flax or hemp provide lower density and better vibration damping but generally exhibit reduced mechanical strength and lower fatigue resistance. The enhanced mechanical properties of glass fiber composites contribute to improved structural integrity and longevity in automotive interiors versus natural fiber alternatives.
Weight and Density Differences
Glass fiber typically exhibits a density of around 2.5 g/cm3, significantly higher than natural fibers like hemp or flax, which range from 1.3 to 1.5 g/cm3, resulting in heavier components for interior car parts. The lower density of natural fibers contributes to reduced overall weight, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions in automotive design. Weight savings from natural fiber composites can range between 20-40% compared to traditional glass fiber parts, making them advantageous for lightweight vehicle interior applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass fiber, widely used in interior car parts, poses significant environmental concerns due to energy-intensive production and recyclability challenges. Natural fibers such as hemp, flax, and jute offer a sustainable alternative with lower carbon footprints, biodegradable properties, and potential for renewable sourcing. The shift toward natural fiber composites enhances eco-friendly automotive design by reducing plastic use and promoting circular economy principles in vehicle manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: Glass Fiber vs Natural Fiber
Glass fiber offers a lower initial cost and higher durability compared to natural fibers, making it more cost-effective for mass production of interior car parts. Natural fibers, such as hemp or flax, generally incur higher processing expenses due to variability in quality and additional treatments required for moisture resistance. While natural fibers promote sustainability, their fluctuating raw material costs and reduced lifespan often lead to higher total ownership costs over time compared to glass fiber alternatives.
Manufacturing Processes and Compatibility
Glass fiber composites for interior car parts are manufactured through processes like injection molding and compression molding, offering high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent compatibility with thermosetting and thermoplastic resins. Natural fiber composites, often processed via extrusion or injection molding, provide sustainable alternatives with good mechanical properties but require surface treatments for enhanced fiber-matrix adhesion and moisture resistance. Compatibility challenges for natural fibers include sensitivity to humidity and lower thermal stability compared to glass fibers, impacting their long-term performance in automotive interiors.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetics
Glass fiber offers superior design flexibility for interior car parts due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and ease of molding into complex shapes, allowing intricate and customized aesthetic features. Natural fibers provide a unique tactile and visual appeal with eco-friendly credentials, enhancing interior aesthetics through their organic textures and finishes while supporting sustainable design trends. The choice between glass fiber and natural fiber significantly impacts the balance between advanced design capabilities and environmentally conscious, visually warm interiors.
Durability and Aging Performance
Glass fiber offers superior durability and aging performance for interior car parts due to its high resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation, ensuring long-lasting structural integrity. Natural fibers, while environmentally friendly and lightweight, tend to absorb moisture and degrade faster under heat and humidity, leading to reduced mechanical strength over time. The enhanced dimensional stability and resistance to thermal and oxidative degradation make glass fiber a more reliable material for maintaining interior part performance throughout the vehicle's lifespan.
Future Trends in Automotive Interior Materials
Glass fiber offers superior strength, durability, and lightweight properties essential for automotive interior parts, while natural fibers like hemp and flax provide eco-friendly, biodegradable alternatives aligned with sustainability goals. Future trends emphasize hybrid composites combining glass and natural fibers to enhance performance and reduce environmental impact, supported by advancements in resin technology and bio-based polymers. Growing regulatory pressure and consumer demand drive innovation toward renewable materials that maintain high safety standards and improve vehicle fuel efficiency.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Natural fiber for Interior car part
 azmater.com
azmater.com