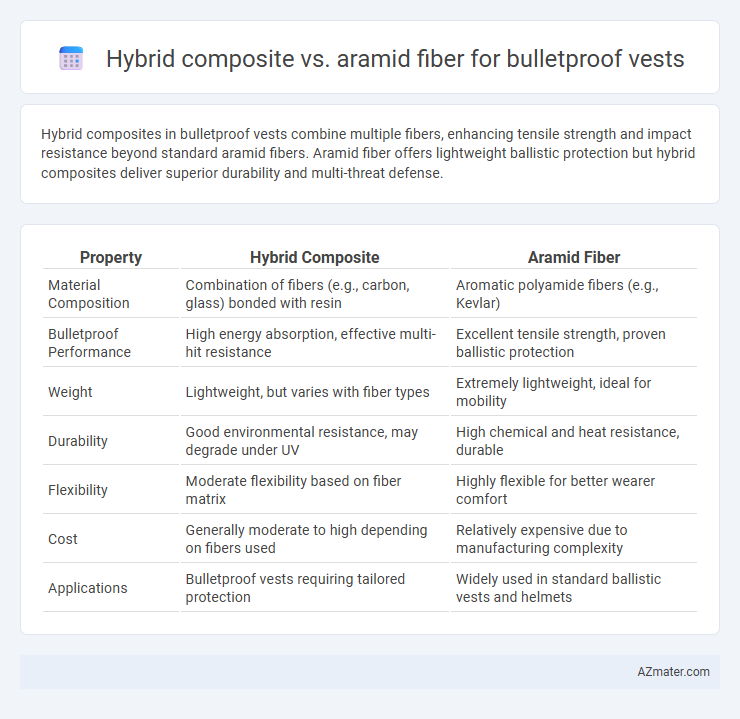
Hybrid composites in bulletproof vests combine multiple fibers, enhancing tensile strength and impact resistance beyond standard aramid fibers. Aramid fiber offers lightweight ballistic protection but hybrid composites deliver superior durability and multi-threat defense.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hybrid Composite | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Combination of fibers (e.g., carbon, glass) bonded with resin | Aromatic polyamide fibers (e.g., Kevlar) |
| Bulletproof Performance | High energy absorption, effective multi-hit resistance | Excellent tensile strength, proven ballistic protection |
| Weight | Lightweight, but varies with fiber types | Extremely lightweight, ideal for mobility |
| Durability | Good environmental resistance, may degrade under UV | High chemical and heat resistance, durable |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility based on fiber matrix | Highly flexible for better wearer comfort |
| Cost | Generally moderate to high depending on fibers used | Relatively expensive due to manufacturing complexity |
| Applications | Bulletproof vests requiring tailored protection | Widely used in standard ballistic vests and helmets |
Introduction to Bulletproof Vest Materials
Bulletproof vest materials primarily include hybrid composites and aramid fibers, each offering distinct protective properties. Hybrid composites combine multiple fibers such as carbon, glass, or aramid to optimize strength, flexibility, and impact resistance in ballistic protection. Aramid fibers, including Kevlar, are renowned for their high tensile strength-to-weight ratio, superior durability, and resistance to heat, making them a standard choice in soft body armor applications.
Understanding Hybrid Composites
Hybrid composites in bulletproof vests combine aramid fibers with other high-performance materials such as ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) or carbon fibers to optimize ballistic resistance and weight. These composites enhance energy absorption and distribution more effectively than aramid fiber alone, providing improved multi-hit capability and durability. The integration of hybrid composites significantly advances protection by balancing flexibility, strength, and reduced vest bulk.
Overview of Aramid Fiber Technology
Aramid fiber technology, primarily represented by Kevlar and Twaron, offers high tensile strength and exceptional impact resistance, making it a preferred material for bulletproof vests. These fibers are lightweight, heat-resistant, and capable of dissipating ballistic energy efficiently through molecular chain alignment. While hybrid composites combine multiple materials to enhance protective performance, aramid fibers remain a benchmark for durability, flexibility, and proven ballistic protection in personal armor applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Hybrid composite materials in bulletproof vests offer superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to pure Aramid fiber, enhancing overall ballistic performance. While Aramid fibers provide excellent energy absorption and flexibility, hybrid composites combine multiple fiber types and resins to achieve improved stiffness, durability, and weight reduction. The mechanical properties such as higher modulus of elasticity and increased fracture toughness in hybrid composites result in better multi-hit capability and longer service life for protective gear.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Hybrid composites in bulletproof vests combine materials like polyethylene and aramid fibers, resulting in significantly lighter weight compared to pure aramid fiber vests, enhancing wearer comfort and mobility. Aramid fiber, known for its high tensile strength and heat resistance, offers excellent ballistic protection but tends to be heavier and less flexible. The flexibility of hybrid composites allows better contouring to body shapes, improving overall wearability without compromising protection levels.
Ballistic Performance Analysis
Hybrid composite materials for bulletproof vests offer enhanced ballistic performance by combining high-strength fibers such as carbon and aramid, resulting in improved energy absorption and multi-hit resistance. Aramid fibers like Kevlar provide excellent tensile strength and impact resistance but may fall short in weight efficiency and flexibility compared to hybrid composites. Ballistic performance analysis indicates that hybrid composites achieve superior penetration resistance and durability under repeated ballistic impacts, making them a preferred choice for advanced body armor solutions.
Durability and Longevity
Hybrid composites in bulletproof vests combine materials like carbon fiber and Kevlar, offering enhanced durability and resistance to impact compared to traditional Aramid fibers alone. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide excellent tensile strength and flexibility but may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and moisture conditions. Hybrid composites exhibit superior longevity by resisting environmental wear and maintaining structural integrity over extended periods, making them ideal for high-performance ballistic protection.
Cost and Availability Factors
Hybrid composite bulletproof vests often offer a cost-effective alternative compared to pure Aramid fiber vests, as they combine materials to optimize performance while reducing expenses. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are widely available and provide excellent ballistic resistance but can be more expensive due to high production costs and specialized manufacturing processes. Availability of hybrid composites may vary depending on regional manufacturing capabilities, while Aramid fibers benefit from established global supply chains ensuring steadier market presence.
Applications in Modern Body Armor
Hybrid composites in bulletproof vests combine multiple fiber types, such as aramid and UHMWPE, enhancing ballistic performance and durability while maintaining lightweight properties crucial for modern body armor. Aramid fibers, known for high tensile strength and impact resistance, remain a staple in ballistic protection but may lack the flexibility and multi-threat resistance offered by hybrid composites. These advanced materials enable body armor to provide superior trauma absorption, multi-hit capability, and adaptability for law enforcement and military applications.
Future Trends in Bulletproof Vest Materials
Future trends in bulletproof vest materials emphasize the integration of hybrid composites combining ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) and aramid fibers such as Kevlar to enhance ballistic resistance and flexibility. Advances in nanotechnology and fiber weaving techniques aim to improve multi-threat protection while reducing vest weight and bulk. Research continues to explore bio-based resins and graphene-enhanced composites to optimize durability and environmental sustainability in next-generation body armor.
Infographic: Hybrid composite vs Aramid fiber for Bulletproof vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com