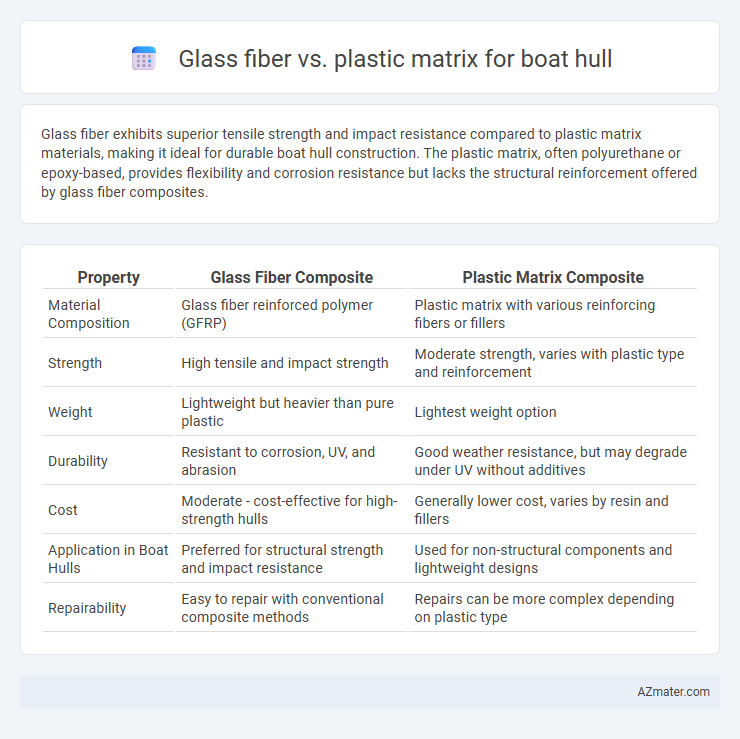
Glass fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to plastic matrix materials, making it ideal for durable boat hull construction. The plastic matrix, often polyurethane or epoxy-based, provides flexibility and corrosion resistance but lacks the structural reinforcement offered by glass fiber composites.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber Composite | Plastic Matrix Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) | Plastic matrix with various reinforcing fibers or fillers |
| Strength | High tensile and impact strength | Moderate strength, varies with plastic type and reinforcement |
| Weight | Lightweight but heavier than pure plastic | Lightest weight option |
| Durability | Resistant to corrosion, UV, and abrasion | Good weather resistance, but may degrade under UV without additives |
| Cost | Moderate - cost-effective for high-strength hulls | Generally lower cost, varies by resin and fillers |
| Application in Boat Hulls | Preferred for structural strength and impact resistance | Used for non-structural components and lightweight designs |
| Repairability | Easy to repair with conventional composite methods | Repairs can be more complex depending on plastic type |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Glass fiber reinforced plastic (GFRP) is a widely used boat hull material due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance compared to traditional plastic matrices. The plastic matrix commonly used in boat hulls includes polyester, vinyl ester, and epoxy resins, which bind the glass fibers and provide structural integrity and impact resistance. Glass fiber composites offer superior durability and stiffness, making them preferable for high-performance marine applications.
Overview of Glass Fiber Composites
Glass fiber composites for boat hulls consist of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, providing high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent durability in marine environments. These composites offer superior resistance to corrosion, impact, and fatigue compared to traditional plastic matrices, enhancing hull performance and longevity. Their ability to be molded into complex shapes allows for optimized hydrodynamics and structural efficiency in boat design.
Understanding Plastic Matrix Materials
Plastic matrix materials in boat hull construction primarily include polyester, vinyl ester, and epoxy resins, each offering distinct mechanical properties and chemical resistance. Polyester resin is widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of handling but has lower strength and water resistance compared to epoxy, which provides superior adhesion and durability but at a higher price. Vinyl ester serves as a middle ground, combining good corrosion resistance and higher strength than polyester, making the choice of plastic matrix crucial for optimizing the performance and longevity of glass fiber reinforced boat hulls.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Glass fiber reinforced composites exhibit superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to plastic matrix materials, making them ideal for boat hulls that require high structural integrity. The durability of glass fiber hulls is enhanced by their excellent resistance to water absorption, UV degradation, and chemical corrosion, ensuring long-term performance in harsh marine environments. Plastic matrix hulls generally offer lower mechanical strength and are more prone to wear and deformation, reducing their lifespan under continuous stress and exposure to elements.
Weight and Performance Considerations
Glass fiber composites offer higher strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional plastic matrix materials, making them ideal for lightweight boat hulls that demand enhanced durability and rigidity. The glass fiber reinforcement improves impact resistance and structural integrity while maintaining lower overall weight, directly contributing to better speed and fuel efficiency. In contrast, plastic matrix hulls tend to be heavier and less stiff, which can compromise performance and increase maintenance due to their lower mechanical properties.
Resistance to Water and Corrosion
Glass fiber reinforced with a plastic matrix offers superior resistance to water absorption and corrosion compared to traditional plastic hulls, as the glass fibers provide a durable barrier against moisture intrusion. The composite structure enhances durability in marine environments, reducing the risk of hull delamination and chemical degradation from saltwater exposure. Advanced epoxy or polyester resin matrices combined with glass fibers ensure long-lasting structural integrity and minimal maintenance in corrosive aquatic conditions.
Cost Analysis: Glass Fiber vs Plastic Matrix
Glass fiber boat hulls generally incur higher initial material costs compared to plastic matrix alternatives due to the extensive manufacturing and raw material expenses. Plastic matrix hulls, often incorporating thermoplastic composites, offer cost advantages through lower production energy requirements and faster molding processes, reducing labor expenses. Over the lifecycle, glass fiber exhibits superior durability and repairability, potentially offsetting upfront costs with lower maintenance, while plastic matrix materials may demand more frequent replacement, impacting the total cost of ownership.
Manufacturing and Repair Processes
Glass fiber reinforced composites offer superior strength and durability for boat hull manufacturing, utilizing processes like hand lay-up and vacuum infusion to ensure optimal fiber-resin bonding and structural integrity. Plastic matrix composites, often thermoplastics like polyethylene or polypropylene, allow faster manufacturing through molding techniques such as injection molding but typically exhibit lower mechanical strength than glass fiber counterparts. Repairing glass fiber hulls involves layering new fiberglass cloth with resin to restore strength, while plastic matrix hull repairs require heat welding or patching, which can be less structurally reliable and more challenging to match in appearance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass fiber boat hulls offer high durability but pose significant environmental challenges due to energy-intensive manufacturing and difficulty in recycling, leading to long-term landfill waste. Plastic matrix composites, particularly those using bio-based or recycled polymers, reduce fossil fuel dependency and lower carbon footprints, enhancing sustainability. However, the environmental benefits depend on the source of the plastic and end-of-life recyclability infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Boat Hull
Glass fiber boat hulls offer superior strength, durability, and resistance to impact compared to plastic matrix alternatives, making them ideal for high-performance and long-lasting marine vessels. Plastic matrix materials, such as polyethylene or polypropylene, provide advantages like lighter weight and improved corrosion resistance but may lack the rigidity and structural integrity required for demanding conditions. Choosing the right material depends on factors like intended use, environmental exposure, maintenance needs, and budget constraints to ensure optimal boat hull performance and longevity.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Plastic matrix for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com