Pre-preg glass fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability compared to polyester, making it ideal for high-performance boat hulls. Its controlled resin content reduces voids and improves structural integrity, resulting in better impact resistance and longevity.
Table of Comparison
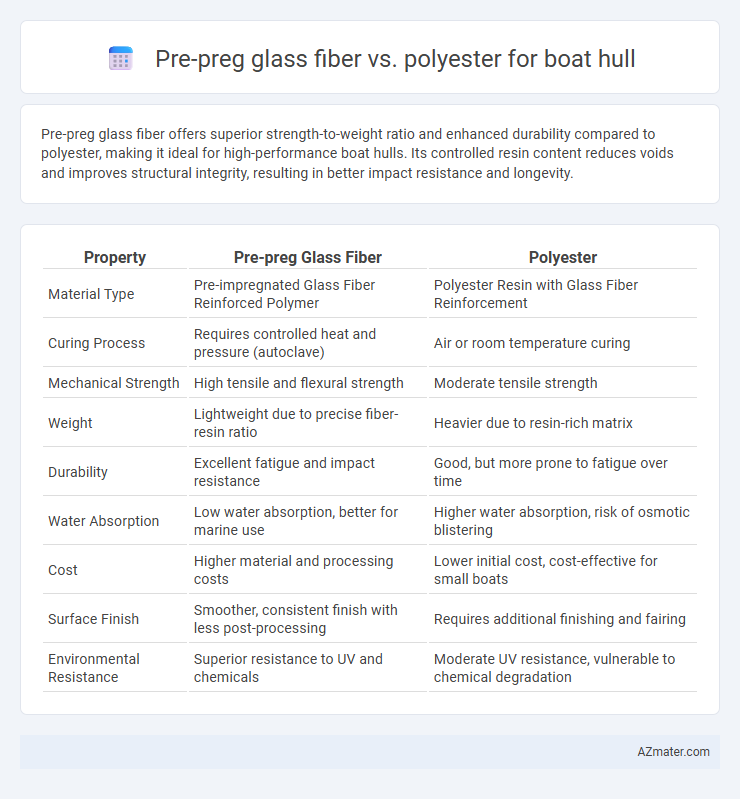
| Property | Pre-preg Glass Fiber | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Pre-impregnated Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer | Polyester Resin with Glass Fiber Reinforcement |
| Curing Process | Requires controlled heat and pressure (autoclave) | Air or room temperature curing |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile and flexural strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Weight | Lightweight due to precise fiber-resin ratio | Heavier due to resin-rich matrix |
| Durability | Excellent fatigue and impact resistance | Good, but more prone to fatigue over time |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption, better for marine use | Higher water absorption, risk of osmotic blistering |
| Cost | Higher material and processing costs | Lower initial cost, cost-effective for small boats |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, consistent finish with less post-processing | Requires additional finishing and fairing |
| Environmental Resistance | Superior resistance to UV and chemicals | Moderate UV resistance, vulnerable to chemical degradation |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Pre-preg glass fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced resin control compared to traditional polyester, making it an advanced choice for boat hull construction. Polyester resin, while cost-effective and widely used, generally provides lower mechanical properties and increased weight, affecting overall performance and durability. Selecting pre-preg glass fiber improves hull stiffness, impact resistance, and longevity, crucial factors in high-performance and commercial marine applications.
Overview of Pre-preg Glass Fiber
Pre-preg glass fiber consists of glass fibers pre-impregnated with a precisely measured resin system, ensuring consistent fiber-to-resin ratios for enhanced structural integrity and reduced void content. This material offers superior mechanical properties, improved strength-to-weight ratios, and excellent resistance to fatigue and environmental degradation compared to traditional hand-laid polyester. Ideal for high-performance boat hulls, pre-preg glass fiber delivers precision, durability, and improved manufacturing efficiency in marine composite construction.
Overview of Polyester Resin
Polyester resin is a widely used matrix material in boat hull construction due to its affordability, ease of use, and compatibility with glass fibers, offering good mechanical strength and water resistance. Compared to pre-preg glass fiber composites, polyester resin systems cure through a catalytic reaction, allowing for faster production cycles but typically resulting in lower strength-to-weight ratios. Its moderate cost and adequate durability make polyester resin a popular choice for recreational and small commercial boat hulls where budget constraints outweigh the need for advanced performance characteristics.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Pre-preg glass fiber offers superior strength and enhanced durability compared to polyester resin for boat hull construction due to its controlled resin-to-fiber ratio and consistent curing process. This results in higher tensile strength, better fatigue resistance, and reduced void content, which significantly improves the hull's impact resistance and lifespan. In contrast, polyester resin composites often exhibit higher porosity and lower mechanical performance, making pre-preg glass fiber the preferred choice for high-performance marine applications.
Weight and Performance Considerations
Pre-preg glass fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to polyester, resulting in lighter boat hulls with enhanced structural integrity and better fuel efficiency. The precision in resin content control within pre-preg materials reduces excess weight without compromising durability, leading to improved performance and faster speeds on the water. Polyester, while more cost-effective, generally results in heavier hulls with lower mechanical properties, affecting overall agility and long-term resilience in marine environments.
Resistance to Water and Corrosion
Pre-preg glass fiber offers superior resistance to water absorption and corrosion compared to polyester resin, making it ideal for boat hull construction. The epoxy matrix in pre-preg materials provides a denser, less permeable barrier, preventing water ingress and reducing osmotic blistering. Polyester resin, while cost-effective, is more prone to hydrolytic degradation and requires additional coatings for adequate protection against marine environments.
Cost Analysis: Pre-preg Glass Fiber vs Polyester
Pre-preg glass fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability but comes with a significantly higher initial material cost compared to polyester resin, making it less economical for budget-conscious boat hull projects. Polyester resin is more cost-effective due to its lower raw material price and easier application process, reducing labor expenses but sacrificing some performance characteristics and lifespan. When evaluating total lifecycle costs, pre-preg glass fiber may present long-term savings through reduced maintenance and repair needs despite the upfront investment.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Pre-preg glass fiber involves fibers pre-impregnated with a precise amount of resin, ensuring uniform resin distribution and reduced void content during curing, which enhances strength and consistency in boat hull manufacturing. Polyester fiberglass utilizes a wet lay-up process where fiberglass is manually saturated with polyester resin, offering a more flexible but less controlled cure and potentially higher voids, impacting the hull's durability. The pre-preg method requires cold storage and controlled curing ovens, increasing manufacturing complexity and cost, while polyester fiberglass can cure at room temperature, allowing for simpler and more cost-effective production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Pre-preg glass fiber boat hulls exhibit a lower environmental impact than traditional polyester composites due to their reduced resin content and improved curing efficiency, which minimize volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. The closed mold process used with pre-preg materials enhances waste reduction and promotes better resource utilization, supporting sustainability in boat manufacturing. Polyester resins, often derived from petrochemicals, contribute to higher carbon footprints and greater environmental toxicity during production and disposal compared to the more advanced pre-preg glass fiber options.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Boat Hull
Pre-preg glass fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced resin control compared to traditional polyester, making it ideal for high-performance boat hulls requiring durability and precision. Polyester resin is more cost-effective and easier to work with, suitable for smaller or less complex hulls where budget constraints are a priority. Selecting the right material depends on balancing performance demands, budget, and manufacturing capabilities to achieve optimal longevity and structural integrity in the boat hull.
Infographic: Pre-preg Glass Fiber vs Polyester for Boat Hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com