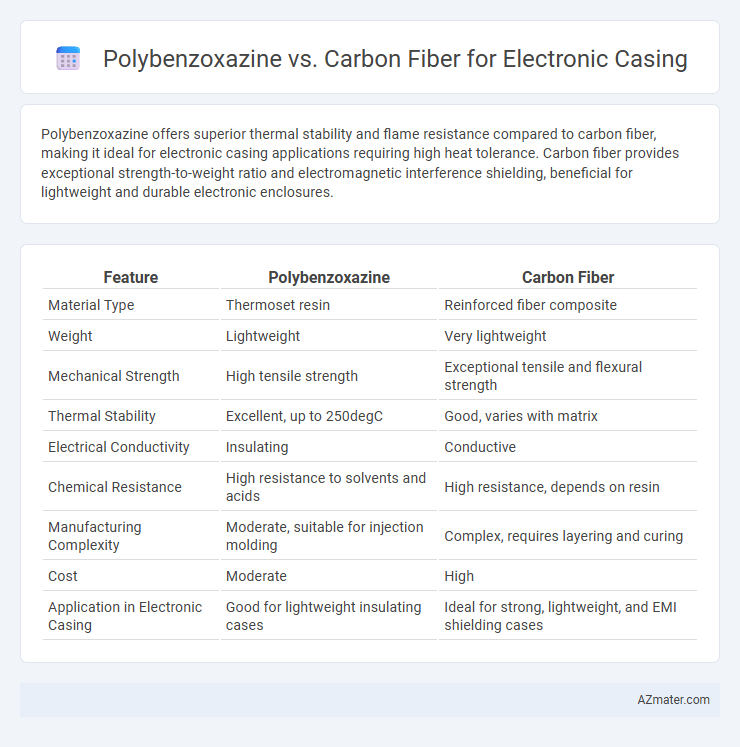
Polybenzoxazine offers superior thermal stability and flame resistance compared to carbon fiber, making it ideal for electronic casing applications requiring high heat tolerance. Carbon fiber provides exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and electromagnetic interference shielding, beneficial for lightweight and durable electronic enclosures.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polybenzoxazine | Carbon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoset resin | Reinforced fiber composite |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength | Exceptional tensile and flexural strength |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent, up to 250degC | Good, varies with matrix |
| Electrical Conductivity | Insulating | Conductive |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to solvents and acids | High resistance, depends on resin |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Moderate, suitable for injection molding | Complex, requires layering and curing |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Application in Electronic Casing | Good for lightweight insulating cases | Ideal for strong, lightweight, and EMI shielding cases |
Introduction to Electronic Casing Materials
Polybenzoxazine offers exceptional thermal stability, flame retardancy, and low moisture absorption, making it an ideal material for electronic casing that demands durability and safety. Carbon fiber provides superior mechanical strength and lightweight properties, enhancing the robustness and portability of electronic enclosures. Choosing between polybenzoxazine and carbon fiber depends on the specific electronic device requirements, balancing thermal performance and structural integrity.
Overview of Polybenzoxazine: Properties and Applications
Polybenzoxazine exhibits excellent thermal stability, low water absorption, and high mechanical strength, making it a superior material for electronic casing compared to carbon fiber's lightweight and high tensile strength characteristics. Its inherent flame retardancy and dimensional stability under heat contribute to enhanced protection for sensitive electronic components. Common applications include advanced electronics, aerospace, and automotive industries where durability and insulation are critical.
Carbon Fiber: Composition and Key Features
Carbon fiber for electronic casing consists primarily of carbon atoms bonded in a crystalline structure, creating fibers that are both lightweight and extremely strong. Its key features include exceptional tensile strength, high stiffness, excellent thermal conductivity, and superior electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding capabilities, making it ideal for protecting sensitive electronic components. Compared to polybenzoxazine, carbon fiber offers enhanced durability and heat resistance, ensuring long-lasting protection in high-performance electronic devices.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polybenzoxazine offers high mechanical strength with excellent impact resistance and thermal stability, making it a strong candidate for electronic casing applications where durability is critical. Carbon fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and stiffness, providing enhanced rigidity and lightweight properties that benefit structural integrity and drop resistance. While carbon fiber outperforms polybenzoxazine in tensile and flexural strength, polybenzoxazine's superior thermal stability and chemical resistance make it advantageous in environments involving heat and exposure to harsh chemicals.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polybenzoxazine exhibits superior thermal stability with a decomposition temperature often exceeding 300degC, making it highly suitable for electronic casing applications requiring enhanced heat resistance. Carbon fiber composites, while providing excellent mechanical strength and thermal conductivity, typically demonstrate lower heat resistance compared to polybenzoxazine resins. The combination of polybenzoxazine's intrinsic flame retardancy and carbon fiber's thermal conductivity enables optimized thermal management in high-performance electronic enclosures.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Polybenzoxazine exhibits superior electrical insulation capabilities compared to carbon fiber, making it ideal for electronic casing applications requiring high dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity. Its inherent molecular structure provides excellent thermal stability and resistance to electrical tracking, ensuring reliable insulation under varying operational conditions. Carbon fiber, while mechanically robust, is electrically conductive, thus necessitating additional insulating layers to prevent short circuits in electronic enclosures.
Weight and Density Analysis
Polybenzoxazine exhibits a lower density of approximately 1.2 g/cm3 compared to carbon fiber composites, which typically range from 1.5 to 1.6 g/cm3, making it a lighter option for electronic casing applications. The reduced weight of polybenzoxazine contributes to improved portability and ergonomic design in handheld and portable devices. Despite its lighter profile, polybenzoxazine maintains excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength, essential for protecting sensitive electronic components.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polybenzoxazine exhibits superior chemical resistance with excellent stability against acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for electronic casings exposed to harsh environments. Carbon fiber offers exceptional mechanical durability and impact resistance but may require protective coatings to enhance chemical resistance in aggressive conditions. The combination of polybenzoxazine's chemical inertness and carbon fiber's structural integrity provides a balanced solution for high-performance electronic enclosure applications.
Manufacturing Process and Cost Efficiency
Polybenzoxazine offers a simpler manufacturing process for electronic casing through straightforward molding techniques, reducing cycle times compared to the more complex layup and curing required for carbon fiber composites. The raw material cost of polybenzoxazine resins is generally lower, enabling cost-effective bulk production without compromising thermal stability and flame resistance essential for electronics. Carbon fiber's high material and processing expenses often lead to increased overall costs, making polybenzoxazine a more economically efficient option for mass-market electronic enclosures.
Suitability for Next-Generation Electronic Devices
Polybenzoxazine offers excellent thermal stability, low water absorption, and superior electrical insulation, making it highly suitable for next-generation electronic casings requiring reliable performance in harsh environments. Carbon fiber excels in mechanical strength and lightweight properties but poses challenges with electrical conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding. For advanced electronics, polybenzoxazine provides a balanced solution with thermal resilience and insulation, while carbon fiber is preferred when structural rigidity and weight reduction are critical.
Infographic: Polybenzoxazine vs Carbon fiber for Electronic casing
 azmater.com
azmater.com