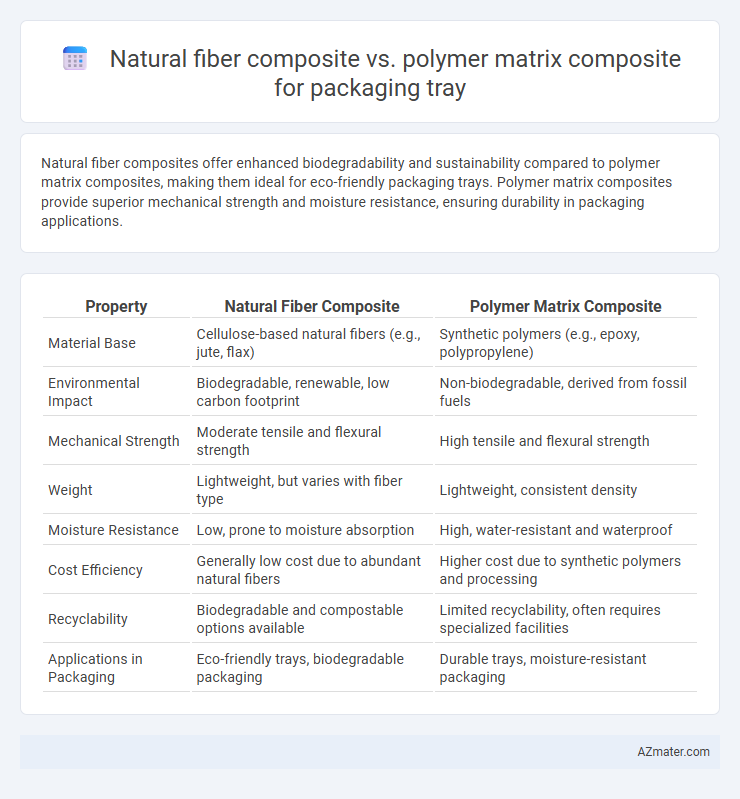
Natural fiber composites offer enhanced biodegradability and sustainability compared to polymer matrix composites, making them ideal for eco-friendly packaging trays. Polymer matrix composites provide superior mechanical strength and moisture resistance, ensuring durability in packaging applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Fiber Composite | Polymer Matrix Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Base | Cellulose-based natural fibers (e.g., jute, flax) | Synthetic polymers (e.g., epoxy, polypropylene) |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, derived from fossil fuels |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile and flexural strength | High tensile and flexural strength |
| Weight | Lightweight, but varies with fiber type | Lightweight, consistent density |
| Moisture Resistance | Low, prone to moisture absorption | High, water-resistant and waterproof |
| Cost Efficiency | Generally low cost due to abundant natural fibers | Higher cost due to synthetic polymers and processing |
| Recyclability | Biodegradable and compostable options available | Limited recyclability, often requires specialized facilities |
| Applications in Packaging | Eco-friendly trays, biodegradable packaging | Durable trays, moisture-resistant packaging |
Introduction to Packaging Tray Materials
Packaging trays made from natural fiber composites offer enhanced environmental sustainability by utilizing renewable plant-based fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute, which improve biodegradability and reduce carbon footprint. Polymer matrix composites, typically composed of synthetic resins reinforced with glass or carbon fibers, provide superior mechanical strength, moisture resistance, and durability essential for protecting heavy or sensitive products. Material selection for packaging trays depends on balancing sustainability goals with performance requirements, making natural fiber composites ideal for eco-friendly applications and polymer matrix composites suited for high-strength, moisture-exposed conditions.
Overview of Natural Fiber Composites
Natural fiber composites for packaging trays utilize renewable fibers like jute, hemp, or flax embedded in bio-based or synthetic matrices, offering an eco-friendly alternative to conventional polymer matrix composites. These composites provide benefits such as biodegradability, lower density, and reduced carbon footprint while maintaining adequate mechanical strength and impact resistance for packaging applications. Innovations in fiber treatment and composite processing enhance moisture resistance and durability, making natural fiber composites increasingly viable for sustainable packaging trays.
Understanding Polymer Matrix Composites
Polymer matrix composites (PMCs) are widely used in packaging trays due to their lightweight, high strength, and customizable properties, offering superior impact resistance and moisture barrier compared to natural fiber composites. PMCs consist of a synthetic polymer resin matrix reinforced with fibers like glass or carbon, enhancing durability and structural integrity under load. Their versatility in processing methods, such as injection molding and thermoforming, enables precise shaping and sourcing of eco-friendly additives to improve sustainability performance in packaging applications.
Material Properties Comparison
Natural fiber composites offer biodegradability, lightweight structure, and enhanced impact resistance compared to polymer matrix composites, which excel in moisture resistance and higher tensile strength. The cellulose content in natural fibers provides improved thermal insulation and lower carbon footprint, while polymer matrices deliver superior chemical resistance and durability under varied environmental conditions. Selection depends on packaging tray requirements prioritizing eco-friendliness versus mechanical performance and longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Natural fiber composites for packaging trays offer significant environmental benefits due to their biodegradability, renewable sourcing, and lower carbon footprint compared to polymer matrix composites made from non-renewable petroleum-based materials. The natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute reduce dependence on fossil fuels and enhance compostability, minimizing landfill waste and pollution. Polymer matrix composites, while offering superior durability and moisture resistance, typically pose challenges in recycling and contribute to long-term environmental persistence, making natural fiber composites a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious packaging solutions.
Mechanical Strength and Performance
Natural fiber composites exhibit lower tensile strength and stiffness compared to polymer matrix composites, which typically provide superior mechanical strength and durability for packaging trays. Polymer matrix composites offer enhanced impact resistance and better load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for heavy-duty and high-performance packaging applications. Despite their lower mechanical properties, natural fiber composites provide sustainable alternatives with adequate performance for lightweight and eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Natural fiber composites for packaging trays typically offer lower material and processing costs due to renewable feedstocks and reduced energy consumption compared to polymer matrix composites, which rely on expensive petroleum-based resins. Economic considerations also include the potential for reduced disposal fees and enhanced biodegradability with natural fibers, translating to long-term savings in waste management. However, polymer matrix composites may deliver superior durability and lifespan, affecting lifecycle cost analyses despite their higher initial material costs.
Applications in Packaging Industry
Natural fiber composites offer lightweight, biodegradable alternatives for packaging trays, improving sustainability and reducing carbon footprint in the packaging industry. Polymer matrix composites provide superior strength, moisture resistance, and durability, making them suitable for protective packaging and heavy-duty applications. Combining natural fibers with polymer matrices can optimize mechanical performance while enhancing eco-friendliness in packaging tray production.
Challenges and Limitations
Natural fiber composites for packaging trays face challenges such as limited moisture resistance, lower mechanical strength, and variable fiber quality affecting consistency and durability. Polymer matrix composites offer superior barrier properties and mechanical performance but involve higher environmental costs and recyclability concerns. Both materials must address processing difficulties and cost-effectiveness to meet industrial packaging requirements.
Future Trends in Packaging Tray Materials
Natural fiber composites offer enhanced sustainability and biodegradability, driving growing demand for eco-friendly packaging trays amid increasing environmental regulations. Polymer matrix composites continue to advance through innovative resin formulations that improve strength, durability, and recyclability, supporting lightweight and high-performance packaging solutions. Future trends emphasize hybrid composites combining natural fibers and advanced polymers to optimize mechanical properties while minimizing environmental impact in packaging tray applications.
Infographic: Natural fiber composite vs Polymer matrix composite for Packaging tray
 azmater.com
azmater.com