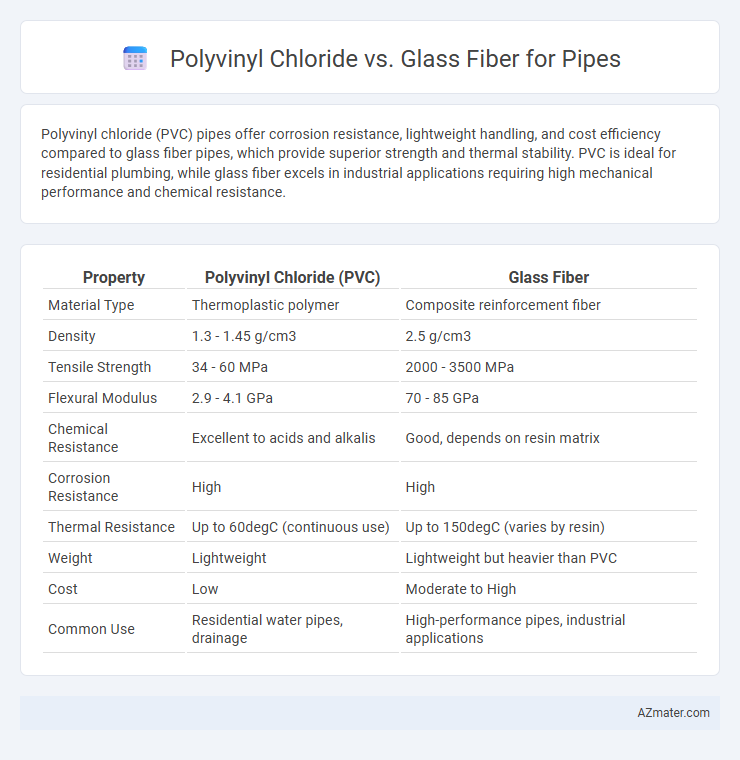
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes offer corrosion resistance, lightweight handling, and cost efficiency compared to glass fiber pipes, which provide superior strength and thermal stability. PVC is ideal for residential plumbing, while glass fiber excels in industrial applications requiring high mechanical performance and chemical resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Composite reinforcement fiber |
| Density | 1.3 - 1.45 g/cm3 | 2.5 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 34 - 60 MPa | 2000 - 3500 MPa |
| Flexural Modulus | 2.9 - 4.1 GPa | 70 - 85 GPa |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent to acids and alkalis | Good, depends on resin matrix |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | High |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 60degC (continuous use) | Up to 150degC (varies by resin) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight but heavier than PVC |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to High |
| Common Use | Residential water pipes, drainage | High-performance pipes, industrial applications |
Introduction to Pipe Materials: Polyvinyl Chloride vs Glass Fiber
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes offer lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective solutions ideal for residential and industrial plumbing systems. Glass fiber reinforced pipes provide exceptional strength, durability, and chemical resistance, making them suitable for high-pressure and demanding environmental applications. Both materials serve critical roles in piping infrastructure, with PVC favored for ease of installation and glass fiber selected for enhanced mechanical performance.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are primarily composed of synthetic polymer polyvinyl chloride combined with plasticizers, stabilizers, and fillers through an extrusion process that ensures uniformity and corrosion resistance. Glass fiber pipes incorporate a composite material made from glass fibers embedded within a resin matrix, typically manufactured via filament winding or pultrusion methods, enhancing mechanical strength and chemical resistance. The distinct material compositions and manufacturing techniques directly influence the pipes' durability, flexibility, and suitability for various industrial applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes offer good mechanical strength with high tensile and impact resistance, but glass fiber reinforced pipes (GRP) provide superior strength due to their composite structure, combining fiberglass and resin for enhanced load-bearing capacity. GRP pipes exhibit excellent durability against corrosion, chemicals, and environmental degradation, surpassing PVC which is more susceptible to UV damage and thermal expansion. In long-term applications requiring high mechanical strength and resistance to harsh conditions, glass fiber pipes outperform PVC in both structural integrity and lifespan.
Corrosion Resistance and Chemical Stability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes exhibit exceptional corrosion resistance, making them ideal for transporting aggressive chemicals and wastewater without degradation. Glass fiber-reinforced pipes offer enhanced chemical stability and mechanical strength but may require protective coatings to prevent corrosion under certain conditions. Both materials provide durable solutions, with PVC excelling in highly corrosive environments while glass fiber ensures structural integrity in chemical exposure applications.
Weight, Flexibility, and Ease of Installation
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are significantly lighter than glass fiber pipes, reducing transportation and handling costs. PVC offers superior flexibility, which minimizes risk of cracking during installation compared to the more rigid glass fiber pipes. The ease of installation is enhanced with PVC due to its lightweight nature and simple joining methods, whereas glass fiber pipes often require specialized tools and techniques.
Temperature and Pressure Handling Capabilities
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes typically handle temperatures up to 60degC (140degF) and moderate pressure levels, making them suitable for low to medium-pressure applications such as residential water supply. Glass fiber reinforced pipes (GRP) demonstrate superior temperature resistance, often withstanding up to 120degC (248degF) and higher pressure ratings due to enhanced strength and durability from the composite structure. For industrial settings requiring higher thermal and pressure performance, GRP pipes offer a distinct advantage over PVC in long-term reliability and operational safety.
Cost Analysis: Purchase and Lifecycle Expenses
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes typically offer lower initial purchase costs compared to glass fiber pipes, making them more budget-friendly for large-scale projects. Over the lifecycle, PVC pipes benefit from reduced maintenance and corrosion resistance, which lowers repair and replacement expenses relative to glass fiber pipes that may experience higher degradation costs in harsh environments. However, glass fiber pipes provide superior strength and durability, potentially extending service life and offsetting their higher upfront investment through longer-term operational savings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes generate significant environmental concerns due to their reliance on non-renewable fossil fuels and release of toxic chemicals during production and disposal. Glass fiber pipes offer a more sustainable alternative with higher recyclability and lower lifecycle carbon emissions, leveraging lightweight properties that reduce transportation energy. The durability and chemical resistance of glass fiber extend pipe lifespan, further minimizing environmental impact by reducing replacement frequency.
Typical Applications and Industry Preferences
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are widely preferred in residential plumbing, irrigation, and wastewater systems due to their corrosion resistance, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness. Glass fiber reinforced pipes excel in industrial applications such as chemical processing, oil and gas transport, and high-pressure environments because of their superior strength, durability, and resistance to high temperatures and chemical attacks. The construction and chemical industries typically favor PVC for cost-sensitive projects, while heavy industry prioritizes glass fiber pipes for enhanced performance and longevity under demanding conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Pipe Material
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes offer excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight handling, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for residential and light commercial plumbing. Glass fiber reinforced pipes provide superior strength, temperature tolerance, and long-term durability, suitable for industrial applications requiring high mechanical stress and chemical resistance. Selecting the right pipe material depends on specific project requirements such as pressure rating, environmental conditions, and budget constraints, with PVC favored for standard use and glass fiber better suited for demanding, high-performance systems.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Glass fiber for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com