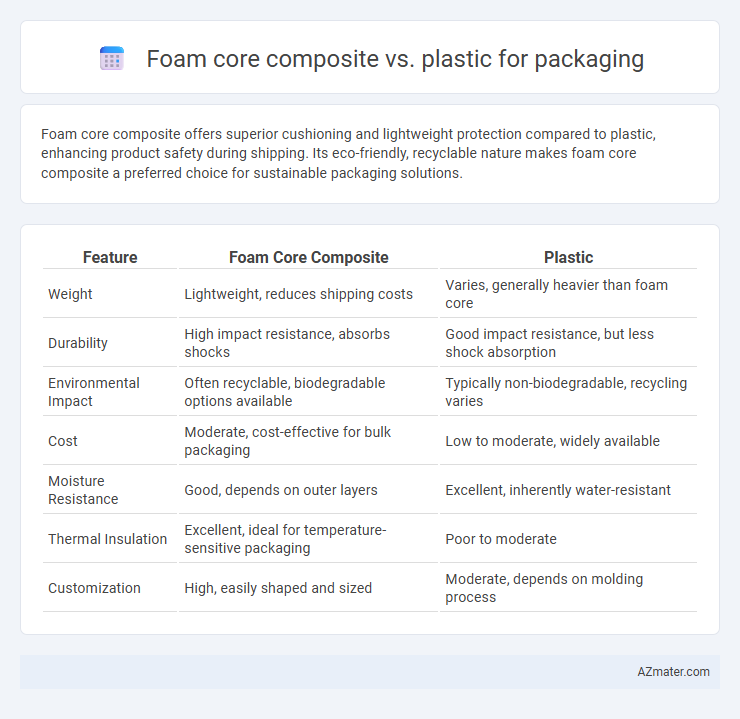
Foam core composite offers superior cushioning and lightweight protection compared to plastic, enhancing product safety during shipping. Its eco-friendly, recyclable nature makes foam core composite a preferred choice for sustainable packaging solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Foam Core Composite | Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces shipping costs | Varies, generally heavier than foam core |
| Durability | High impact resistance, absorbs shocks | Good impact resistance, but less shock absorption |
| Environmental Impact | Often recyclable, biodegradable options available | Typically non-biodegradable, recycling varies |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective for bulk packaging | Low to moderate, widely available |
| Moisture Resistance | Good, depends on outer layers | Excellent, inherently water-resistant |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, ideal for temperature-sensitive packaging | Poor to moderate |
| Customization | High, easily shaped and sized | Moderate, depends on molding process |
Introduction to Packaging Materials
Foam core composite offers lightweight, high-strength properties with excellent cushioning, making it ideal for fragile or high-value packaging applications. Plastic packaging provides versatility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, widely used in food and consumer goods industries. Both materials serve distinct packing needs, with foam core composites excelling in structural support and plastics in barrier protection.
Overview of Foam Core Composites
Foam core composites consist of a lightweight foam core sandwiched between two rigid outer layers, offering high strength-to-weight ratios ideal for protective packaging. These composites provide superior impact resistance, thermal insulation, and cushioning properties compared to traditional plastics. Commonly used in fragile item packaging, foam core composites enhance durability while reducing overall material weight and shipping costs.
Understanding Plastic Packaging
Plastic packaging offers exceptional durability, flexibility, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for protecting a wide range of products during transportation and storage. Foam core composites, while lightweight and providing excellent cushioning, often lack the structural strength and impermeability that plastic packaging delivers. Understanding plastic packaging materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and PET highlights their ability to create airtight seals, extend shelf life, and support sustainability initiatives through recyclability.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Foam core composite packaging offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to plastic, providing enhanced impact resistance and cushioning for fragile items. The cellular structure of foam core materials absorbs shocks more effectively, reducing the risk of damage during transportation. Plastic packaging, while durable and moisture-resistant, often lacks the structural rigidity found in foam core composites, making foam core a preferred choice for heavy-duty packaging applications.
Weight and Handling Efficiency
Foam core composites offer significantly lower weight compared to traditional plastic, enhancing handling efficiency in packaging by reducing transportation costs and easing manual handling. The lightweight nature of foam core composites also contributes to faster packing processes and improved worker ergonomics. Plastic packaging, while durable, often results in heavier loads that can increase shipping expenses and reduce overall handling speed.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Foam core composites offer improved insulation and lightweight properties, reducing transportation emissions compared to heavier plastic packaging materials. Unlike conventional plastics, many foam core composites can be manufactured with biodegradable or recyclable components, minimizing landfill waste and environmental pollution. However, the sustainability of foam core composites depends on the specific resin and core materials used, emphasizing the importance of selecting eco-friendly formulations to maximize environmental benefits.
Cost Analysis: Foam Core vs. Plastic
Foam core composites generally offer lower material costs compared to plastic packaging, driven by their lightweight structure and reduced raw material usage. Production expenses for foam core packaging typically involve less energy consumption, leading to overall cost savings in manufacturing. However, plastic packaging benefits from higher durability and recyclability, potentially lowering long-term costs despite higher upfront investment.
Customizability and Design Flexibility
Foam core composite packaging offers superior customizability due to its lightweight structure, allowing intricate shapes and layered designs that provide enhanced cushioning and protection. Plastic packaging, while durable, often faces limitations in mold complexity and material thickness, restricting design flexibility compared to foam core composites. The ability of foam core composites to be easily cut, shaped, and laminated enables tailored solutions that meet specific product requirements and branding needs.
Typical Applications in Packaging
Foam core composite is commonly used in packaging for protective inserts, custom display boards, and lightweight structural support, providing excellent cushioning and shock absorption for fragile items. Plastic packaging is widely utilized for flexible films, containers, and bottles, offering durability, moisture resistance, and versatility in shape and size. Both materials serve critical roles in securing, protecting, and presenting products across industries such as electronics, food, and consumer goods.
Future Trends in Packaging Materials
Foam core composites are gaining traction for packaging due to their lightweight structure and superior cushioning properties, promoting sustainability by reducing material usage and transportation emissions. Emerging trends highlight the integration of bio-based and recyclable foam core materials, enhancing eco-friendly packaging solutions in comparison to conventional plastics, which face increasing regulatory restrictions and environmental concerns. Innovations in foam core composites also emphasize improved thermal insulation and durability, aligning with the future demands for efficient, protective, and sustainable packaging options.
Infographic: Foam core composite vs Plastic for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com