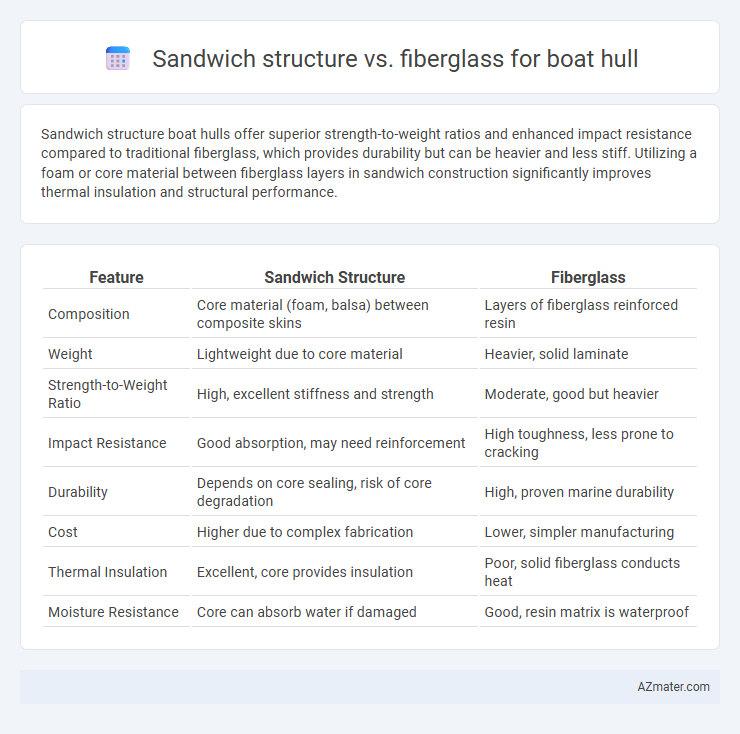
Sandwich structure boat hulls offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional fiberglass, which provides durability but can be heavier and less stiff. Utilizing a foam or core material between fiberglass layers in sandwich construction significantly improves thermal insulation and structural performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sandwich Structure | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Core material (foam, balsa) between composite skins | Layers of fiberglass reinforced resin |
| Weight | Lightweight due to core material | Heavier, solid laminate |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High, excellent stiffness and strength | Moderate, good but heavier |
| Impact Resistance | Good absorption, may need reinforcement | High toughness, less prone to cracking |
| Durability | Depends on core sealing, risk of core degradation | High, proven marine durability |
| Cost | Higher due to complex fabrication | Lower, simpler manufacturing |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, core provides insulation | Poor, solid fiberglass conducts heat |
| Moisture Resistance | Core can absorb water if damaged | Good, resin matrix is waterproof |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Sandwich structure boat hulls use a core material, often foam or balsa, laminated between fiberglass or carbon fiber skins, providing high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent stiffness. Fiberglass hulls consist of layers of glass fibers embedded in resin, offering durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of repair but typically more weight than sandwich composites. The choice between sandwich and fiberglass materials affects performance characteristics such as impact resistance, thermal insulation, and overall hull durability in marine environments.
Understanding Sandwich Structure Construction
Sandwich structure construction in boat hulls involves layering a lightweight core material, such as foam or balsa wood, between two fiberglass or composite skins, enhancing strength-to-weight ratio and impact resistance. This method provides superior insulation, stiffness, and buoyancy compared to traditional solid fiberglass hulls, which rely solely on multiple fiberglass layers for strength. The core material in sandwich construction reduces overall hull weight while maintaining rigidity, offering improved fuel efficiency and performance in marine vessels.
Overview of Fiberglass Hulls
Fiberglass hulls are composed of layers of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offering high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent resistance to corrosion. This material provides durability and flexibility, making it suitable for various boat sizes and types. Fiberglass hulls are also easier to repair and maintain compared to alternative composite structures, contributing to their widespread use in marine applications.
Material Properties: Strength and Durability
Sandwich structures in boat hulls combine lightweight cores such as foam or balsa with fiberglass skins, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional fiberglass hulls. Fiberglass alone provides good durability and corrosion resistance but tends to be heavier and less stiff, making sandwich composites advantageous for improving structural rigidity and fatigue resistance. The optimized stiffness and energy absorption of sandwich constructions contribute to longer hull lifespan and better performance in rough marine conditions.
Weight Comparison: Sandwich Structure vs Fiberglass
Sandwich structures for boat hulls typically consist of lightweight core materials like foam or balsa wood bonded between fiberglass or carbon fiber skins, significantly reducing overall weight compared to solid fiberglass hulls. The lower density core materials in sandwich construction decrease hull mass while maintaining high stiffness and strength, enhancing fuel efficiency and speed. In contrast, traditional fiberglass hulls are heavier due to their solid laminate composition, which increases weight without the added stiffness benefits of sandwich structures.
Insulation and Soundproofing Benefits
Sandwich structures for boat hulls excel in insulation and soundproofing due to their layered composition, which often includes foam or balsa cores sandwiched between fiberglass skins, providing superior thermal resistance and noise dampening. Fiberglass hulls alone offer decent durability but lack the enhanced insulation properties of sandwich constructions, leading to greater heat transfer and cabin noise. Utilizing sandwich structures significantly improves onboard comfort by minimizing temperature fluctuations and reducing engine and water noise.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Sandwich structure boat hulls, composed of a core material like foam or balsa between fiberglass layers, offer enhanced stiffness and impact resistance with reduced weight, but their maintenance demands vigilance against core water intrusion which can compromise structural integrity. Fiberglass hulls, while heavier, provide easier repair processes due to their solid laminate nature, making them favorable for long-term durability with routine gelcoat upkeep to prevent osmotic blistering. Choosing between the two hinges on balancing the sandwich structure's superior strength-to-weight ratio against the simpler maintenance and proven longevity of traditional fiberglass hull construction.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Repairs
Sandwich structures typically require a higher initial investment compared to fiberglass due to advanced materials like foam or balsa cores combined with fiberglass skins, increasing manufacturing complexity and costs. Fiberglass boat hulls present lower upfront costs, making them more accessible for budget-conscious buyers, but may incur higher long-term repair expenses due to susceptibility to impacts and water absorption. Repairing sandwich structures often involves specialized techniques and materials, leading to higher labor and material costs, whereas fiberglass repairs are generally more straightforward and less expensive.
Performance Impact on Water
Sandwich structure boat hulls, composed of a lightweight core material between layers of fiberglass or carbon fiber, offer superior stiffness and strength while reducing overall weight, resulting in enhanced speed and fuel efficiency. Fiberglass hulls alone provide good durability and impact resistance but tend to be heavier, which can decrease acceleration and increase fuel consumption. The sandwich construction also improves buoyancy and resistance to water penetration, leading to better performance and longevity in marine environments.
Choosing the Right Hull for Your Boat
Choosing the right hull for your boat involves comparing sandwich structure and fiberglass materials based on durability, weight, and performance. Sandwich structure hulls offer enhanced stiffness and impact resistance due to their layered construction with core materials like foam or balsa, reducing overall weight and improving fuel efficiency. Fiberglass hulls provide cost-effective strength and ease of repair, making them a practical choice for recreational boats, but they may lack the superior rigidity and insulation properties of sandwich composites.
Infographic: Sandwich structure vs Fiberglass for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com