Hybrid composite roofing sheets combine the strength of fiberglass with polymers, offering superior durability, enhanced resistance to weathering, and improved thermal insulation compared to traditional fiberglass sheets. These hybrid composites reduce maintenance costs and increase lifespan, making them a cost-effective roofing solution.
Table of Comparison
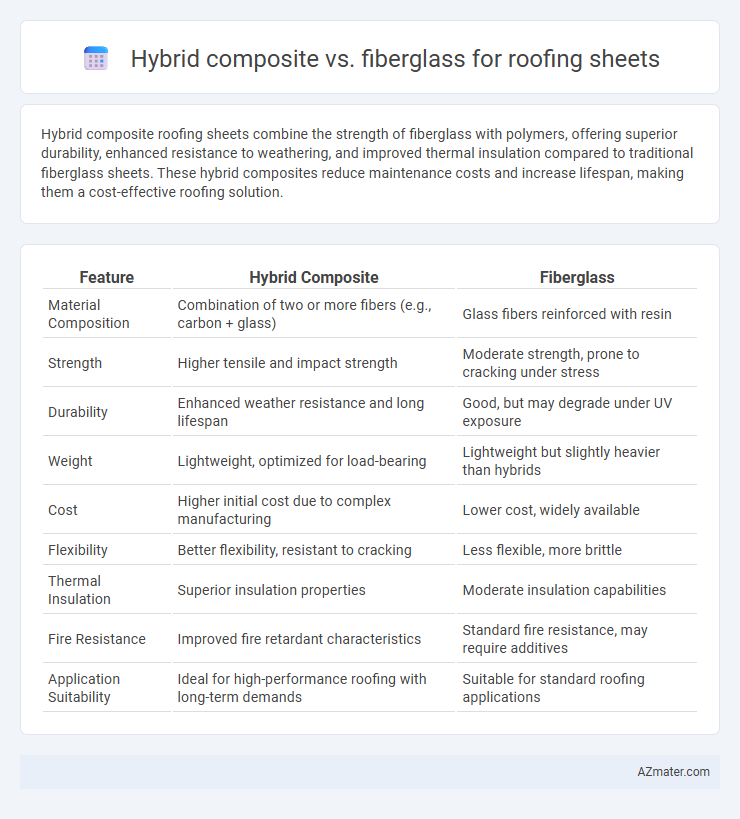
| Feature | Hybrid Composite | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Combination of two or more fibers (e.g., carbon + glass) | Glass fibers reinforced with resin |
| Strength | Higher tensile and impact strength | Moderate strength, prone to cracking under stress |
| Durability | Enhanced weather resistance and long lifespan | Good, but may degrade under UV exposure |
| Weight | Lightweight, optimized for load-bearing | Lightweight but slightly heavier than hybrids |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to complex manufacturing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Flexibility | Better flexibility, resistant to cracking | Less flexible, more brittle |
| Thermal Insulation | Superior insulation properties | Moderate insulation capabilities |
| Fire Resistance | Improved fire retardant characteristics | Standard fire resistance, may require additives |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for high-performance roofing with long-term demands | Suitable for standard roofing applications |
Introduction to Roofing Sheet Materials
Hybrid composite roofing sheets combine materials like fiberglass and polymers, offering enhanced durability, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties compared to traditional roofing options. Fiberglass roofing sheets are known for their high tensile strength, resistance to weathering, and insulating capabilities, making them suitable for various climates and structures. Both materials provide effective protection against environmental elements, but hybrid composites typically deliver superior performance through the integration of multiple material benefits.
Overview of Hybrid Composite Roofing Sheets
Hybrid composite roofing sheets combine fiberglass-reinforced polymers with other materials such as carbon fiber or aramid to enhance strength, durability, and weather resistance compared to traditional fiberglass sheets. These sheets offer superior impact resistance, improved thermal insulation, and reduced weight, making them ideal for harsh environmental conditions. The integration of hybrid composites results in roofing sheets that provide longer service life and better performance against UV radiation and corrosion.
Understanding Fiberglass Roofing Sheets
Fiberglass roofing sheets consist of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offering high tensile strength and resistance to corrosion and weathering. These sheets provide excellent durability, UV resistance, and thermal insulation, making them suitable for various roofing applications. Compared to hybrid composite materials, fiberglass roofing sheets are lightweight, cost-effective, and easier to install, while maintaining good impact resistance and longevity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Hybrid composite roofing sheets offer superior strength and durability compared to traditional fiberglass, combining materials like fiberglass, resin, and polymers to enhance impact resistance and longevity. The hybrid composition improves resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, reducing the risk of cracking and warping over time. Fiberglass roofing sheets, while strong and lightweight, generally exhibit lower tensile strength and are more prone to degradation from prolonged exposure to harsh weather conditions.
Weight and Installation Differences
Hybrid composite roofing sheets are significantly lighter than traditional fiberglass sheets, reducing the overall structural load on buildings. The lightweight nature of hybrid composites facilitates quicker and easier installation, minimizing labor costs and time. Fiberglass sheets, being heavier and more brittle, often require specialized handling and longer installation periods to prevent damage and ensure proper fitting.
Weather and Corrosion Resistance
Hybrid composite roofing sheets offer superior weather and corrosion resistance compared to traditional fiberglass, benefiting from enhanced composite materials that provide better durability against UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. Fiberglass, while resistant to corrosion, tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to harsh weather conditions, leading to brittleness and reduced lifespan. The advanced formulation of hybrid composites ensures longer-lasting protection, making them ideal for roofing applications in coastal or industrial environments with high corrosion risks.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Hybrid composite roofing sheets offer superior aesthetic appeal and design flexibility compared to traditional fiberglass, enabling customized color blends and textured finishes that mimic natural materials. Their lightweight yet durable composition allows for innovative shapes and seamless integration into modern architectural styles, enhancing visual impact. Fiberglass, while cost-effective, typically provides limited design options and less vivid color retention over time, restricting creative applications in roofing projects.
Cost Effectiveness and Longevity
Hybrid composite roofing sheets offer superior cost effectiveness compared to traditional fiberglass due to their enhanced durability and reduced maintenance needs, resulting in lower long-term expenses. The longevity of hybrid composites typically exceeds that of fiberglass, with resistance to corrosion, UV radiation, and weathering contributing to an extended lifespan of 25 to 30 years versus fiberglass's average 15 to 20 years. Investment in hybrid composites ensures a better return over time, balancing upfront costs with diminished replacement frequency and improved structural performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hybrid composite roofing sheets offer improved environmental benefits by combining natural fibers with polymers, reducing reliance on non-renewable resources compared to traditional fiberglass sheets made from glass fibers and resins. These composites exhibit enhanced recyclability and lower carbon footprints due to the use of sustainable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. Fiberglass roofing, while durable and moisture-resistant, often involves energy-intensive production and challenges in waste management, making hybrid composites a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious construction projects.
Choosing the Best Roofing Sheet Material
Hybrid composite roofing sheets offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional fiberglass, making them ideal for long-term durability. Fiberglass sheets provide excellent corrosion resistance and UV stability, suitable for varied weather conditions but may lack the hybrid composite's advanced mechanical properties. Choosing the best roofing sheet material depends on factors such as load requirements, environmental exposure, and maintenance preferences, with hybrid composites excelling in performance-driven applications and fiberglass favored for cost-effectiveness and chemical resistance.
Infographic: Hybrid composite vs Fiberglass for Roofing sheet
 azmater.com
azmater.com